一 package
1) package 相当于C++中的namespace,不同的package下可以定义相同的变量和subroutines;
2)在一个pl文件中可以定义多个package,每个package有一个单独的symboltable,每个symboltable中包含了此package中的变量和subroutines;
3) package mypack; 此语句定义一个名为mypack的包,从此以后定义的所有变量和子程序的名字都存贮在该包关联的符号表中,直到遇到另一个package语句为止。默认地存储在main package中。
4)在一个包中可以引用其它包中的变量或子程序,包名和变量名用双冒号隔开,即$mypack::var。
实例:

二 module
1)module是perl的library,相当于C++中的lib或dll,是功能相近的subroutines的集合;
2)module通常存储在同名的pm文件中;
3)通常module也同时定义在一个同名的package中;
4)EXPORT用来导出subroutines,EXPORT_OK用来导出变量;
5)use mymodule;用来引用mymoudule,no mymodule来取消mymodule的引用;
实例:
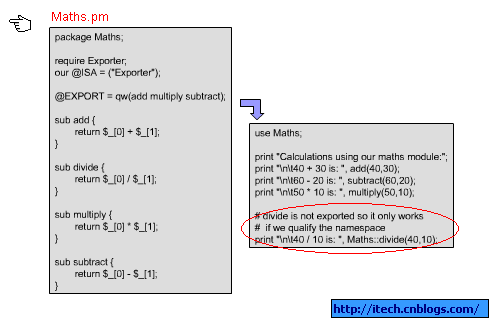
三 实例
@EXPORT contains list of symbols (subroutines and variables) of the module to be exported into the caller namespace.
@EXPORT_OK does export of symbols on demand basis.
Let us use the following sample program to understand Perl exporter.
package Arithmetic;
use Exporter;
# base class of this(Arithmetic) module
@ISA = qw(Exporter);
# Exporting the add and subtract routine
@EXPORT = qw(add subtract);
# Exporting the multiply and divide routine on demand basis.
@EXPORT_OK = qw(multiply divide);
sub add
{
my ($no1,$no2) = @_;
my $result;
$result = $no1+$no2;
return $result;
}
sub subtract
{
my ($no1,$no2) = @_;
my $result;
$result = $no1-$no2;
return $result;
}
sub multiply
{
my ($no1,$no2) = @_;
my $result;
$result = $no1*$no2;
return $result;
}
sub divide
{
my ($no1,$no2) = @_;
my $result;
$result = $no1/$no2;
return $result;
}
In the above example, we defined the arithmetic module with four functions. By default add() and subtract() functions are exported to the user’s/caller’s namespace.
“use Arithmetic” statement imports the subroutines from Arithmetic module that are exported by default.
“use Arithmetic qw(multiply divide)” indicates that these two routines gets exported only when it is specifically requested as shown in the following code snippet.
#! /usr/bin/perl use strict; use warnings; use Arithmetic; use Arithmetic qw(multiply divide); print add(1,2),"\n"; print multiply(1,2),"\n";
As we seen above, in the main program we used the Arithmetic module with default import ( add and subtract ) and on-demand import ( multiply and divide ).
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2010/06/perl-exporter-examples/
完!
