由于之前的草稿都没了,现在只有重写…. 我好痛苦
本章只是对pytorch的常规操作进行一个总结,大家看过有脑子里有印象就好,知道有这么个东西,需要的时候可以再去详细的看,另外也还是需要在实战中多运用。
 本章导视图
本章导视图
Tensor attributes:
在tensor attributes中有三个类,分别为torch.dtype, torch.device, 和 torch.layout
其中, torch.dtype 是展示 torch.Tensor 数据类型的类,pytorch 有八个不同的数据类型,下表是完整的 dtype 列表.
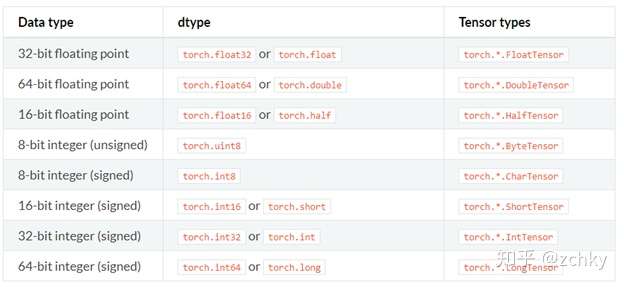
Torch.device 是表现 torch.Tensor被分配的设备类型的类,其中分为’cpu’ 和 ‘cuda’两种,如果设备序号没有显示则表示此 tensor 被分配到当前设备, 比如: 'cuda' 等同于 'cuda': X , X 为torch.cuda.current _device() 返回值
我们可以通过 tensor.device 来获取其属性,同时可以利用字符或字符+序号的方式来分配设备
通过字符串:
>>> torch.device('cuda:0')
device(type='cuda', index=0)
>>> torch.device('cpu')
device(type='cpu')
>>> torch.device('cuda') # 当前设备
device(type='cuda')
通过字符串和设备序号:
>>> torch.device('cuda', 0)
device(type='cuda', index=0)
>>> torch.device('cpu', 0)
device(type='cpu', index=0)
此外,cpu 和 cuda 设备的转换使用 'to' 来实现:
>>> device_cpu = torch.device("cuda") #声明cuda设备
>>> device_cuda = torch.device('cuda') #设备cpu设备
>>> data = torch.Tensor([1])
>>> data.to(device_cpu) #将数据转为cpu格式
>>> data.to(device_cuda) #将数据转为cuda格式
torch.layout 是表现 torch.Tensor 内存分布的类,目前只支持 torch.strided
创建tensor
- 直接创建
torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None,requires_grad=False)
data - 可以是list, tuple, numpy array, scalar或其他类型
dtype - 可以返回想要的tensor类型
device - 可以指定返回的设备
requires_grad - 可以指定是否进行记录图的操作,默认为False
需要注意的是,torch.tensor 总是会复制 data, 如果你想避免复制,可以使 torch.Tensor. detach(),如果是从 numpy 中获得数据,那么你可以用 torch.from_numpy(), 注from_numpy() 是共享内存的
>>> torch.tensor([[0.1, 1.2], [2.2, 3.1], [4.9, 5.2]])
tensor([[ 0.1000, 1.2000],
[ 2.2000, 3.1000],
[ 4.9000, 5.2000]])
>>> torch.tensor([0, 1]) # Type inference on data
tensor([ 0, 1])
>>> torch.tensor([[0.11111, 0.222222, 0.3333333]],
dtype=torch.float64,
device=torch.device('cuda:0')) # creates a torch.cuda.DoubleTensor
tensor([[ 0.1111, 0.2222, 0.3333]], dtype=torch.float64, device='cuda:0')
>>> torch.tensor(3.14159) # Create a scalar (zero-dimensional tensor)
tensor(3.1416)
>>> torch.tensor([]) # Create an empty tensor (of size (0,))
tensor([])
- 从numpy中获得数据
torch.from_numpy(ndarry)
注:生成返回的tensor会和ndarry共享数据,任何对tensor的操作都会影响到ndarry,
反之亦然
>>> a = numpy.array([1, 2, 3])
>>> t = torch.from_numpy(a)
>>> t
tensor([ 1, 2, 3])
>>> t[0] = -1
>>> a
array([-1, 2, 3])
- 创建特定的tensor
根据数值要求:
torch.zeros(*sizes, out=None, ..)# 返回大小为sizes的零矩阵
torch.zeros_like(input, ..) # 返回与input相同size的零矩阵
torch.ones(*sizes, out=None, ..) #f返回大小为sizes的单位矩阵
torch.ones_like(input, ..) #返回与input相同size的单位矩阵
torch.full(size, fill_value, …) #返回大小为sizes,单位值为fill_value的矩阵
torch.full_like(input, fill_value, …) 返回与input相同size,单位值为fill_value的矩阵
torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1, …) #返回从start到end, 单位步长为step的1-d tensor.
torch.linspace(start, end, steps=100, …) #返回从start到end, 间隔中的插值数目为steps的1-d tensor
torch.logspace(start, end, steps=100, …) #返回1-d tensor ,从10^start到10^end的steps个对数间隔根据矩阵要求:
torch.eye(n, m=None, out=None,…) #返回2-D 的单位对角矩阵
torch.empty(*sizes, out=None, …) #返回被未初始化的数值填充,大小为sizes的tensor
torch.empty_like(input, …) # 返回与input相同size,并被未初始化的数值填充的tensor
- 随机采用生成:
torch.normal(mean, std, out=None)
torch.rand(*size, out=None, dtype=None, …) #返回[0,1]之间均匀分布的随机数值
torch.rand_like(input, dtype=None, …) #返回与input相同size的tensor, 填充均匀分布的随机数值
torch.randint(low=0, high, size,…) #返回均匀分布的[low,high]之间的整数随机值
torch.randint_like(input, low=0, high, dtype=None, …) #
torch.randn(*sizes, out=None, …) #返回大小为size,由均值为0,方差为1的正态分布的随机数值
torch.randn_like(input, dtype=None, …)
torch.randperm(n, out=None, dtype=torch.int64) # 返回0到n-1的数列的随机排列
操作tensor
基本操作:
Joining ops:
torch.cat(seq,dim=0,out=None) # 沿着dim连接seq中的tensor, 所有的tensor必须有相同的size或为empty, 其相反的操作为 torch.split() 和torch.chunk()
torch.stack(seq, dim=0, out=None) #同上
#注: .cat 和 .stack的区别在于 cat会增加现有维度的值,可以理解为续接,stack会新加增加一个维度,可以
理解为叠加
>>> a=torch.Tensor([1,2,3])
>>> torch.stack((a,a)).size()
torch.size(2,3)
>>> torch.cat((a,a)).size()
torch.size(6)
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None) #返回沿着dim收集的新的tensor
>> t = torch.Tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
>> index = torch.LongTensor([[0,0],[1,0]])
>> torch.gather(t, 0, index) #由于 dim=0,所以结果为
| t[index[0, 0] 0] t[index[0, 1] 1] |
| t[index[1, 0] 0] t[index[1, 1] 1] |
对于3-D 的张量来说,可以作为
out[i][j][k] = input[index[i][j][k]][j][k] # if dim == 0
out[i][j][k] = input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # if dim == 1
out[i][j][k] = input[i][j][index[i][j][k]] # if dim == 2
clicing ops:
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0) #将tensor 拆分成相应的组块
torch.chunk(tensor, chunks, dim=0) #将tensor 拆分成相应的组块, 最后一块会小一些如果不能整除的话#
#注:split和chunk的区别在于:
split的split_size_or_sections 表示每一个组块中的数据大小,chunks表示组块的数量
>>> a = torch.Tensor([1,2,3])
>>> torch.split(a,1)
(tensor([1.]), tensor([2.]), tensor([3.]))
>>> torch.chunk(a,1)
(tensor([ 1., 2., 3.]),)
Indexing ops:
torch.index_select(input, dim, index, out=None) #返回沿着dim的指定tensor, index需为longTensor类型,不共用内存
torch.masked_select(input, mask, out=None) #根据mask来返回input的值其为1-D tensor. Mask为ByteTensor, true返回,false不返回,返回值不共用内存
>>> x = torch.randn(3, 4)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.3552, -2.3825, -0.8297, 0.3477],
[-1.2035, 1.2252, 0.5002, 0.6248],
[ 0.1307, -2.0608, 0.1244, 2.0139]])
>>> mask = x.ge(0.5)
>>> mask
tensor([[ 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 1, 1, 1],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1]], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> torch.masked_select(x, mask)
tensor([ 1.2252, 0.5002, 0.6248, 2.0139])
Mutation ops:
torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1, out=None) #返回dim0和dim1交换后的tensor
torch.t(input, out=None) #专为2D矩阵的转置,是transpose的便捷函数
torch.squeeze(input, dim, out=None) #默认移除所有size为1的维度,当dim指定时,移除指定size为1的维度. 返回的tensor会和input共享存储空间,所以任何一个的改变都会影响另一个
torch.unsqueeze(input, dim, out=None) #扩展input的size, 如 A x B 变为 1 x A x B
torch.reshape(input, shape) #返回size为shape具有相同数值的tensor, 注意 shape=(-1,)这种表述,-1表示任意的。
#注 reshape(-1,)
>>> a=torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5]) #a.size 是 torch.size(5)
>>> b=a.reshape(1,-1) #表示第一维度是1,第二维度按a的size填充满
>>> b.size()
torch.size([1,5])
torch.where(condition,x,y) #根据condition的值来相应x,y的值,true返回x的值,false返回y的值,形成新的tensor
torch.unbind(tensor, dim=0) #返回tuple 解除指定的dim的绑定,相当于按指定dim拆分
>>> a=torch.Tensor([[1,2,3],[2,3,4]])
>>> torch.unbind(a,dim=0)
(torch([1,2,3]),torch([2,3,4])) # 将一个(2,3) 分为两个(3)
torch.nonzero(input, out=None) # 返回非零值的索引, 每一行都是一个非零值的索引值
>>> torch.nonzero(torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 0, 1]))
tensor([[ 0],
[ 1],
[ 2],
[ 4]])
>>> torch.nonzero(torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.4, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.2, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0,-0.4]]))
tensor([[ 0, 0],
[ 1, 1],
[ 2, 2],
[ 3, 3]])
Tensor操作
- 点对点操作
三角函数:
torch.abs(input, out=None)
torch.acos(input, out=None)
torch.asin(input, out=None)
torch.atan(input, out=None)
torch.atan2(input, inpu2, out=None)
torch.cos(input, out=None)
torch.cosh(input, out=None)
torch.sin(input, out=None)
torch.sinh(input, out=None)
torch.tan(input, out=None)
torch.tanh(input, out=None)
基本运算,加减乘除
Torch.add(input, value, out=None)
.add(input, value=1, other, out=None)
.addcdiv(tensor, value=1, tensor1, tensor2, out=None)
.addcmul(tensor, value=1, tensor1, tensor2, out=None)
torch.div(input, value, out=None)
.div(input, other, out=None)
torch.mul(input, value, out=None)
.mul(input, other, out=None)
对数运算:
torch.log(input, out=None) # y_i=log_e(x_i)
torch.log1p(input, out=None) #y_i=log_e(x_i+1)
torch.log2(input, out=None) #y_i=log_2(x_i)
torch.log10(input,out=None) #y_i=log_10(x_i)
幂函数:
torch.pow(input, exponent, out=None) # y_i=input^(exponent)
指数运算
torch.exp(tensor, out=None) #y_i=e^(x_i)
torch.expm1(tensor, out=None) #y_i=e^(x_i) -1
截断函数
torch.ceil(input, out=None) #返回向正方向取得最小整数
torch.floor(input, out=None) #返回向负方向取得最大整数
torch.round(input, out=None) #返回相邻最近的整数,四舍五入
torch.trunc(input, out=None) #返回整数部分数值
torch.frac(tensor, out=None) #返回小数部分数值
torch.fmod(input, divisor, out=None) #返回input/divisor的余数
torch.remainder(input, divisor, out=None) #同上
其他运算
torch.erf(tensor, out=None)
torch.erfinv(tensor, out=None)
torch.sigmoid(input, out=None)
torch.clamp(input, min, max out=None) #返回 input<min,则返回min, input>max,则返回max,其余返回input
torch.neg(input, out=None) #out_i=-1*(input)
torch.reciprocal(input, out=None) # out_i= 1/input_i
torch.sqrt(input, out=None) # out_i=sqrt(input_i)
torch.rsqrt(input, out=None) #out_i=1/(sqrt(input_i))
torch.sign(input, out=None) #out_i=sin(input_i) 大于0为1,小于0为-1
torch.lerp(start, end, weight, out=None)
- 降维操作
torch.argmax(input, dim=None, keepdim=False) #返回最大值排序的索引值
torch.argmin(input, dim=None, keepdim=False) #返回最小值排序的索引值
torch.cumprod(input, dim, out=None) #y_i=x_1 * x_2 * x_3 *…* x_i
torch.cumsum(input, dim, out=None) #y_i=x_1 + x_2 + … + x_i
torch.dist(input, out, p=2) #返回input和out的p式距离
torch.mean() #返回平均值
torch.sum() #返回总和
torch.median(input) #返回中间值
torch.mode(input) #返回众数值
torch.unique(input, sorted=False) #返回1-D的唯一的tensor,每个数值返回一次.
>>> output = torch.unique(torch.tensor([1, 3, 2, 3], dtype=torch.long))
>>> output
tensor([ 2, 3, 1])
torch.std( #返回标准差)
torch.var() #返回方差
torch.norm(input, p=2) #返回p-norm的范式
torch.prod(input, dim, keepdim=False) #返回指定维度每一行的乘积
- 对比操作:
torch.eq(input, other, out=None) #按成员进行等式操作,相同返回1
torch.equal(tensor1, tensor2) #如果tensor1和tensor2有相同的size和elements,则为true
>>> torch.eq(torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]]))
tensor([[ 1, 0],
[ 0, 1]], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> torch.eq(torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]]))
tensor([[ 1, 0],
[ 0, 1]], dtype=torch.uint8)
torch.ge(input, other, out=None) # input>= other
torch.gt(input, other, out=None) # input>other
torch.le(input, other, out=None) # input=<other
torch.lt(input, other, out=None) # input<other
torch.ne(input, other, out=None) # input != other 不等于
torch.max() # 返回最大值
torch.min() # 返回最小值
torch.isnan(tensor) #判断是否为’nan’
torch.sort(input, dim=None, descending=False, out=None) #对目标input进行排序
torch.topk(input, k, dim=None, largest=True, sorted=True, out=None) #沿着指定维度返回最大k个数值及其索引值
torch.kthvalue(input, k, dim=None, deepdim=False, out=None) #沿着指定维度返回最小k个数值及其索引值
- 频谱操作
torch.fft(input, signal_ndim, normalized=False)
torch.ifft(input, signal_ndim, normalized=False)
torch.rfft(input, signal_ndim, normalized=False, onesided=True)
torch.irfft(input, signal_ndim, normalized=False, onesided=True)
torch.stft(signa, frame_length, hop, …)
- 其他操作:
torch.cross(input, other, dim=-1, out=None) #叉乘(外积)
torch.dot(tensor1, tensor2) #返回tensor1和tensor2的点乘
torch.mm(mat1, mat2, out=None) #返回矩阵mat1和mat2的乘积
torch.eig(a, eigenvectors=False, out=None) #返回矩阵a的特征值/特征向量
torch.det(A) #返回矩阵A的行列式
torch.trace(input) #返回2-d 矩阵的迹(对对角元素求和)
torch.diag(input, diagonal=0, out=None) #
torch.histc(input, bins=100, min=0, max=0, out=None) #计算input的直方图
torch.tril(input, diagonal=0, out=None) #返回矩阵的下三角矩阵,其他为0
torch.triu(input, diagonal=0, out=None) #返回矩阵的上三角矩阵,其他为0
Tips:
- 获取python number:
由于pytorch 0.4后,python number的获取统一通过 .item()方式实现:
>>> a = torch.Tensor([1,2,3])
>>> a[0] #直接取索引返回的是tensor数据
tensor(1.)
>>> a[0].item() #获取python number
1
- tensor设置
判断:
torch.is_tensor() #如果是pytorch的tensor类型返回true
torch.is_storage() # 如果是pytorch的storage类型返回ture
这里还有一个小技巧,如果需要判断tensor是否为空,可以如下
>>> a=torch.Tensor()
>>> len(a)
0
>>> len(a) is 0
True
设置: 通过一些内置函数,可以实现对tensor的精度, 类型,print打印参数等进行设置
torch.set_default_dtype(d) #对torch.tensor() 设置默认的浮点类型
torch.set_default_tensor_type() # 同上,对torch.tensor()设置默认的tensor类型
>>> torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).dtype # initial default for floating point is torch.float32
torch.float32
>>> torch.set_default_dtype(torch.float64)
>>> torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).dtype # a new floating point tensor
torch.float64
>>> torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.DoubleTensor)
>>> torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).dtype # a new floating point tensor
torch.float64
torch.get_default_dtype() #获得当前默认的浮点类型torch.dtype
torch.set_printoptions(precision=None, threshold=None, edgeitems=None, linewidth=None, profile=None)#)
## 设置printing的打印参数