1.什么是线程
进程:
- 一个正在运行的程序就叫一个进程。
- 每个进程都有独立的内存空间。
(进程是资源分派的基本单位)
线程:
- 一个进程中可以有很多线程。----> 常说的多线程
- 线程没有独立的内存空间。
(线程是调度运行的基本单位)
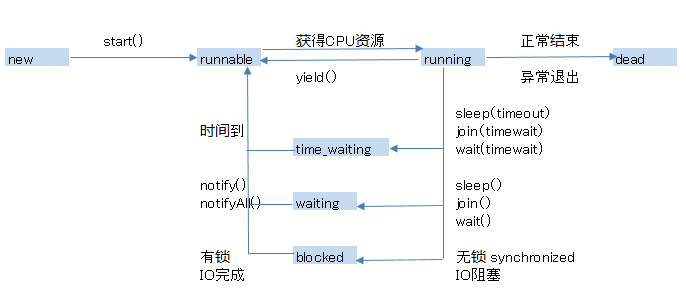
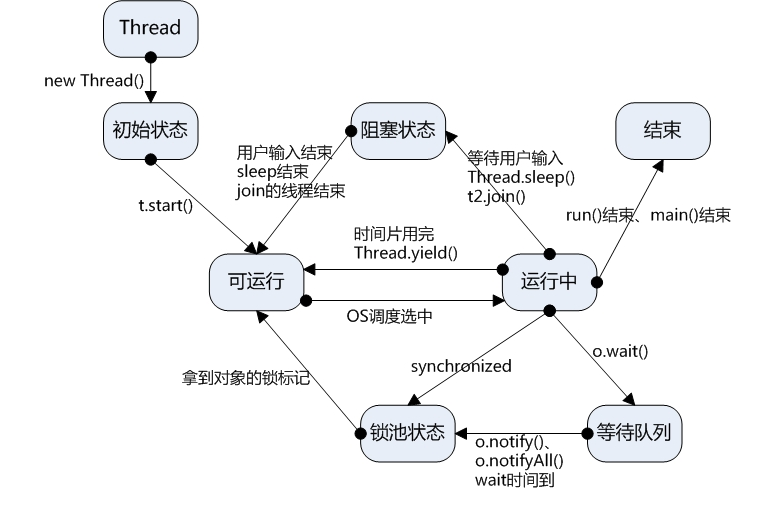
2.线程的状态
线程分为五个阶段:
- 创建new
- 就绪runnable
线程对象调用了start()方法就进入了“可执行状态”。
- 运行running
可执行状态的线程,获得了CPU权限,开始执行。(可执行状态是进入执行状态的唯一入口)
- 阻塞blocked
线程因某种原因失去CPU使用权,暂停运行。
-
- 等待阻塞:运行的线程执行了wait()方法。注意:wait()方法会释放持有的锁。
- 同步阻塞:运行的线程在获取同步锁时,锁被别的线程占用。
- 其他阻塞:运行的线程执行了sleep() / join()方法,或者发出了I/O请求。
- 终止dead:执行完run()方法,或者因异常原因退出。
3.线程调度优先级
- 优先级高的线程获得较多运行机会。
- 优先级是int型,范围1~10。Thread类有下面三个静态常量:
/** * The minimum priority that a thread can have. */ public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1; /** * The default priority that is assigned to a thread. */ public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5; /** * The maximum priority that a thread can have. */ public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
Thread类中获得优先级,设置优先级---->getPriority(),setPriority()
4.创建线程
- 实现Runnable接口
- 继承Thread方法
实现Runnable接口(java.lang.Runnable)
class ThreadRunnable implements Runnable{ private Thread t; public void run() { 。。。 } }
继承Thread方法(java.lang.Thread)
public class ThreadLearn { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread m = new MyThread(); m.start(); } } class MyThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println("进入睡眠状态"); Thread.currentThread().sleep(10000); System.out.println("睡眠完毕"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("得到中断异常"); } System.out.println("run方法执行完毕"); } }
区别:
Java单继承,多实现。因此,实现Runnable接口更利于资源共享。
5.常见函数说明
1 star() 调用该方法,可以使线程进入就绪状态,等待CPU分配资源
2 run() 就绪状态的线程,获得了CPU权限后,就开始执行run方法中的具体操作
3 Thread.currentThread() 获得当前线程
Thread.currentThread().getName() 获得当前线程名称
Thread.currentThread().getId() 获得线程的唯一标识
4 sleep() 让线程休眠一段时间,交出CPU权限,供其他线程使用。
sleep不会释放锁。
调用了sleep方法,必须捕获InterruptedException异常或者向上抛出异常。
5 yield() 与sleep()方法类似,交出CPU权限,让CPU执行其他线程;不会释放锁。
不同:
- 不能控制交出CPU的时间。
- 只能让拥有相同优先级的线程获得CPU执行机会。
注意:
- 实际中无法保证yield()达到让步目的,因为让步的线程还有可能被线程调度程序再次选中。
- yield()将导致线程从运行状态转到可运行状态。
6 isAlive()
public class MyThread01 { private int i = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread01 mt = new MyThread01(); ThreadDemo1 thread01 = mt.new ThreadDemo1(); ThreadDemo1 thread02 = mt.new ThreadDemo1(); thread01.start(); thread02.start(); } class ThreadDemo1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ synchronized(this){ i++; System.out.println("i:" + i); try { System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入睡眠状态"); Thread.currentThread().sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"睡眠结束,isAlive = "+Thread.currentThread().isAlive()); i++; System.out.println("i:"+i); } } } }
运行结果:
i:11 线程Thread-0进入睡眠状态 i:12 线程Thread-1进入睡眠状态 线程Thread-0睡眠结束,isAlive = true i:13 线程Thread-1睡眠结束,isAlive = true i:14
必须等Thread-0结束之后,Thread-1才开始执行具体任务。
6 join() 一般,主线程创建并启动了子线程,如果子线程耗时较多,主线程往往早于子线程结束。如果主线程需要等待某个子线程的结果,等子线程结束之后再结束,则需要用到join()方法。
- t.join()方法会使主线程进入等待池。
- 等待t线程执行完毕之后,主线程才会被唤醒。
- 不影响同一时刻处于运行状态的其他线程。
public class MyThread01 { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadDemo2 t1 = new ThreadDemo2("线程A"); t1.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if (i == 5) { ThreadDemo2 th = new ThreadDemo2("joined thread"); th.start(); try { th.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i); } } } class ThreadDemo2 extends Thread{ private String name; public ThreadDemo2(String name){ this.name = name; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ System.out.println(name + " run test " + i); } } }
运行结果:
main 0 main 1 main 2 main 3 main 4 线程A run test 0 线程A run test 1 线程A run test 2 线程A run test 3 线程A run test 4 joined thread run test 0 joined thread run test 1 joined thread run test 2 joined thread run test 3 joined thread run test 4 main 5 main 6 main 7 main 8 main 9
7 getName()和setName() 获得/设置线程名
8 getPriority()和setPriority() 获取/设置线程优先级