常用api第一部分
String 类
双引号字符串,都是 String 类的对象
字符串的特点:
- 字符串的内容永不可变(正是因为字符串不可改变,所以字符串是可以共享使用的)
- 字符串效果上相当于是 char[] 字符数组,但是底层原理是 byte[] 字节数组
字符串的常见的 3 + 1 种创建方式
public class DemoString { public static void main(String[] args) { // 最简单的方式创建一个字符串 String str = "johny"; // 使用空参构建 String str1 = new String(); System.out.println(str1); // "" // 根据字符数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串 char[] charArray = {'A', 'B', 'C'}; String str2 = new String(charArray); System.out.println(str2); // "ABC" // 根据字节数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串 byte[] byteArray = {97, 98, 99}; String str3 = new String(byteArray); System.out.println(str3); // "abc" } }
字符串常量池
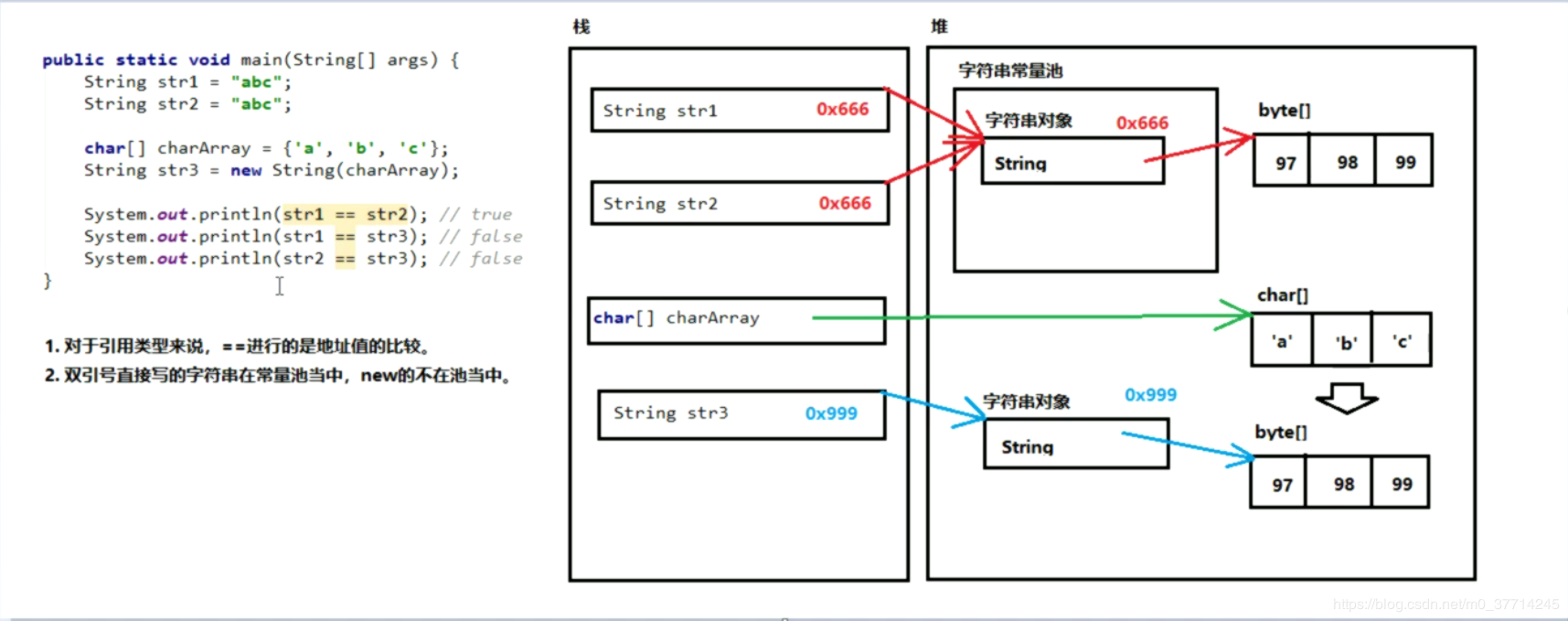
字符串的比较
- == 运算符是进行地址值的比较,比较字符串内容,可使用 equals() 方法;(python 中 == 是比较内容,is 是比较地址值)
- equals() 具有对称性,也就是 a.equals(b) 和 b.equals(a) 是一样的
- 如果是一个常量与一个变量比较,推荐把常量写在前面:"abc".equals(a),因为前面的字符串不能是null,否则会出现
NullPointerException异常 - equalsIgnoreCase() 方法在比较时忽略大小写
public class StringEquals { public static void main(String[] args) { String strA = "abc"; String strB = "abc"; char[] arrayChar = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; String strC = new String(arrayChar); System.out.println(strA.equals(strB)); // true System.out.println(strA.equals(strC)); // true // 推荐写法 System.out.println("abc".equals(strA)); // true // 空指针异常 String strD = null; // System.out.println(strD.equals(strA)); // NullPointerException // equalsIgnoreCase() System.out.println("ABC".equalsIgnoreCase(strA)); // true } }
字符串常用方法
- int length():获取字符串长度
- String concat(String str):将当前字符串和参数字符串进行拼接
- char charAt(int index):获取指定索引值位置的字符
- int indexOf(String/char args):查找参数字符串/字符在当前字符串中的第一次索引位置,如果没有找到就返回 -1
public class StringGet { public static void main(String[] args) { String strA = "abc"; char[] arrayChar = {'A', 'B', 'C'}; String strB = "ABC"; // 返回字符串长度 System.out.println(strA.length()); // 3 // 字符串拼接 System.out.println(strA.concat(strB)); // abcABC // 返回指定索引值位置上的字符 System.out.println(strA.charAt(1)); // b // 查找参数字符串在当前字符串中的第一次索引位置,没有找到就返回-1 System.out.println(strA.indexOf("bc")); // 1 System.out.println(strA.indexOf("d")); // -1 } }
字符串的截取(切片)
- String substring(int index):截取从参数位置一直到字符串末尾,返回新字符串
- String substring(int begin, int end):截取从 begin 开始,到 end 结束,顾前不顾尾(不能添加步长参数,python可以)
public class StringSubstring{ public static void main(String[] args){ String strA = "hello, world!"; // 截取 System.out.println(strA.substring(0, 5)); // hello } }
字符串转换
- char[] toCharArray():将字符串拆分成字符数组,返回该字符数组
- byte[] getBytes():获取字符串底层字节数组,返回该字节数组的地址值(引用对象)
- String replace(CharSequence oldString, CharSequence newString):将出现的所有老字符串替换成新字符串,返回替换后的结果字符串
public class StringConvert{ public static void main(String[] args){ String strA = "中国"; // 返回字符数组 System.out.println(strA.toCharArray()); // 中国 // 返回字节数组(返回的是对象的引用) byte[] byteArray1 = strA.getBytes(); System.out.println(byteArray1); // [B@1e643faf for (int i = 0; i < strA.length(); i++){ System.out.print(byteArray1[i]); // -28-72 if (i == strA.length() - 1){ System.out.println(); } } byte[] byteArray2 = "abc".getBytes(); System.out.println(byteArray2); // [B@6e8dacdf for (int i = 0; i < "abc".length(); i++){ System.out.print(byteArray2[i]); // 979899 if (i == "abc".length() - 1){ System.out.println(); } } // 字符串替换 System.out.println(strA.replace("中", "爱")); // 爱国 } }
字符串的切割
- String[] split(String regex):按照参数规则,将当前字符串分割成多个部分,返回字符串数组的地址值(引用对象)
- split() 方法的参数其实是一个正则表达式,如果按照英文句点 . 进行切分,必须写 \.(双斜线 + 点)
public class StringSplit { public static void main(String[] args) { String strA = "my name is johny"; String[] Array1 = strA.split(" "); System.out.println(Array1); // [Ljava.lang.String;@1b6d3586 for (int i=0; i < Array1.length; i++){ System.out.println(Array1[i]); // my name is johny } // 特殊写法 String strB = "a.b.c"; String[] Array2 = strB.split("\."); System.out.println(Array2); // [Ljava.lang.String;@4554617c for (int i = 0; i < Array2.length; i++){ System.out.println(Array2[i]); // a b c } } }
Scanner 类
Scanner 类可以实现键盘输入,类似于 python 中的 input,不过通过 input 接收到的都是 str,但 Scanner 对象可以生成指定类型
Scanner 是引用数据类型,需要导入 Scanner 类,(为什么 String 类不需要导入?因为只有 java.lang 包下的内容不需要导包)
import java.util.Scanner; public class DemoScanner { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // 让用户输入一个整数,用户输入的不是整数会抛出异常(InputMismatchException) int num = scanner.nextInt(); // 输入一个字符串 String str = scanner.next(); System.out.println(num + str); } }
匿名对象
匿名对象就是只有 右边的对象,没有左边的命名和赋值运算符;匿名对象只能使用唯一的一次,下次再用,不得不再 new 一个
new 类名称();
import java.util.Scanner; public class Anonymous { public static void main(String[] args) { // Scanner 匿名对象 int num = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.println(num); // 匿名对象当做参数传递 showNum(new Scanner(System.in)); } public static void showNum(Scanner scanner){ System.out.println(scanner.next()); } }
Random 类
Random 类可用来生成一个随机数;Random random = new Random()
获取一个随机 int 数字(默认是 int 所有范围,有正负两种):int num = random.nextInt();
获取一个随机 int 数字(指定范围 [0, 99),规则是顾前不顾尾):int num = random.nextInt(100);
import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; public class RandomGames { public static void main(String[] args) { int num = new Random().nextInt(100); guess(num); } public static void guess(int num){ while (true){ int input_num = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); if (input_num > num){ System.out.println("greater than"); } else if(input_num < num){ System.out.println("less than"); } else{ System.out.println("bingo~"); break; } } } }
ArrayList 类
ArrayList 类是 Array 的子类,它的长度可变,元素类型是统一的
有一个尖括号代表泛型(就是装在 ArrayList 中的元素的类型),泛型只能是 引用类型
直接打印 ArrayList,看到的不是地址值(Array是地址值),而是存储内容,如果内容为空,那么打印 []
import java.util.ArrayList; public class DemoArrayList { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个ArrayList ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add("甲"); // arrayList.add(10); // 泛型已经指明是String类型,况且只能是引用类型 System.out.println(arrayList); // [甲] } }
ArrayList 的常用方法
public boolean add(E e):添加元素,元素 e 应和 泛型 E 一致,返回值是 boolean 类型
public E get(int index):根据索引值取出元素,返回元素类型与泛型一致
public E remove(int index):根据索引值删除元素,返回元素类型与泛型一致
public int size():获取长度,返回 int 类型
demo_01:
import java.util.ArrayList; public class ArrayListMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList(); // 添加 boolean bool = arrayList.add("甲"); System.out.println(bool); // true // 获取 String str = arrayList.get(0); System.out.println(str); // 甲 // 获取大小 int count = arrayList.size(); System.out.println(count); // 1 // 删除 String delete = arrayList.remove(0); System.out.println(delete); // 甲 } }
demo_02:
// 定义以指定格式打印集合的方法,格式参照:{元素@元素@元素@元素} import java.util.ArrayList; public class ArrayListPrint { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add("2019"); arrayList.add("-02"); arrayList.add("-14"); System.out.println(arrayList); // [2019, -02, -14] arrayListPrint(arrayList); } public static void arrayListPrint(ArrayList<String> arrayList){ System.out.print("{"); for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++){ String str = arrayList.get(i); System.out.print(str); if (i != arrayList.size() - 1){ System.out.print("@"); } } System.out.print("}"); // {2019@-02@-14} } }
如果说需要往 ArrayList 中存储基本数据类型,那么可以使用基本数据类型对应的包装类
包装类与 String 类一样,都在 java.long 包下,所以可以直接使用
Byte --> byte
Short --> short
Integer --> int
Long --> long
Float --> float
Double --> double
Character --> char
Boolean --> boolean
从 JDK 1.5 开始, 支持自动装箱, 自动拆箱: 基本类型 --> 包装类
import java.util.ArrayList; public class WrapperClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // 指定集合中的泛型是Integer ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add(100); int num = arrayList.get(0); System.out.println(num); // 100 } }
包装类成员方法:
- intValue() 拆箱
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 装箱 // Integer ig = new Integer("123456"); Integer ig = Integer.valueOf("123456"); // 拆箱 int i = ig.intValue(); System.out.println(i); // 123456 // 自动装箱, 拆箱 Integer ig2 = 123456; int i2 = ig2; } }
数组工具类 Arrays
java.util.Arrays 类是一个与数组相关的工具类,里面提供了大量静态方法,用来实现常见的数组操作
public static String toString(参数数组):将参数数组转换为字符串返回(按照默认格式:[element1, element2, element3 …])
public static void sort(参数数组):将当前数组进行排序,默认升序
import java.util.Arrays; public class DemoArrays { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrayNum = {5, 1, 6, 3, 9}; String[] arrayString = {"bbb", "ccc", "aaa"}; // toString() System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayNum)); // [5, 1, 6, 3, 9] // sort() Arrays.sort(arrayNum); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayNum)); // [1, 3, 5, 6, 9] Arrays.sort(arrayString); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayString)); // [aaa, bbb, ccc] } }
数学工具类 Math
java.util.Math 类是数学相关的工具类,里面提供了大量的静态方法,完成数学运算相关的操作
- public static double abs(double num):获取绝对值
- public static double ceil(double num):向上取整
- public static double floor(double num):向下取整
- public static long round(double num):四舍五入
public class DemoMath { public static void main(String[] args) { double num = -12.24; // 绝对值 System.out.println(Math.abs(num)); // 12.24 double // 向上取整 System.out.println(Math.ceil(num)); // 12.0 double // 向下取整 System.out.println(Math.floor(num)); // 13.0 double // 四舍五入 System.out.println(Math.round(num)); // 12 long } }
静态 static 关键字
static 关键字概述
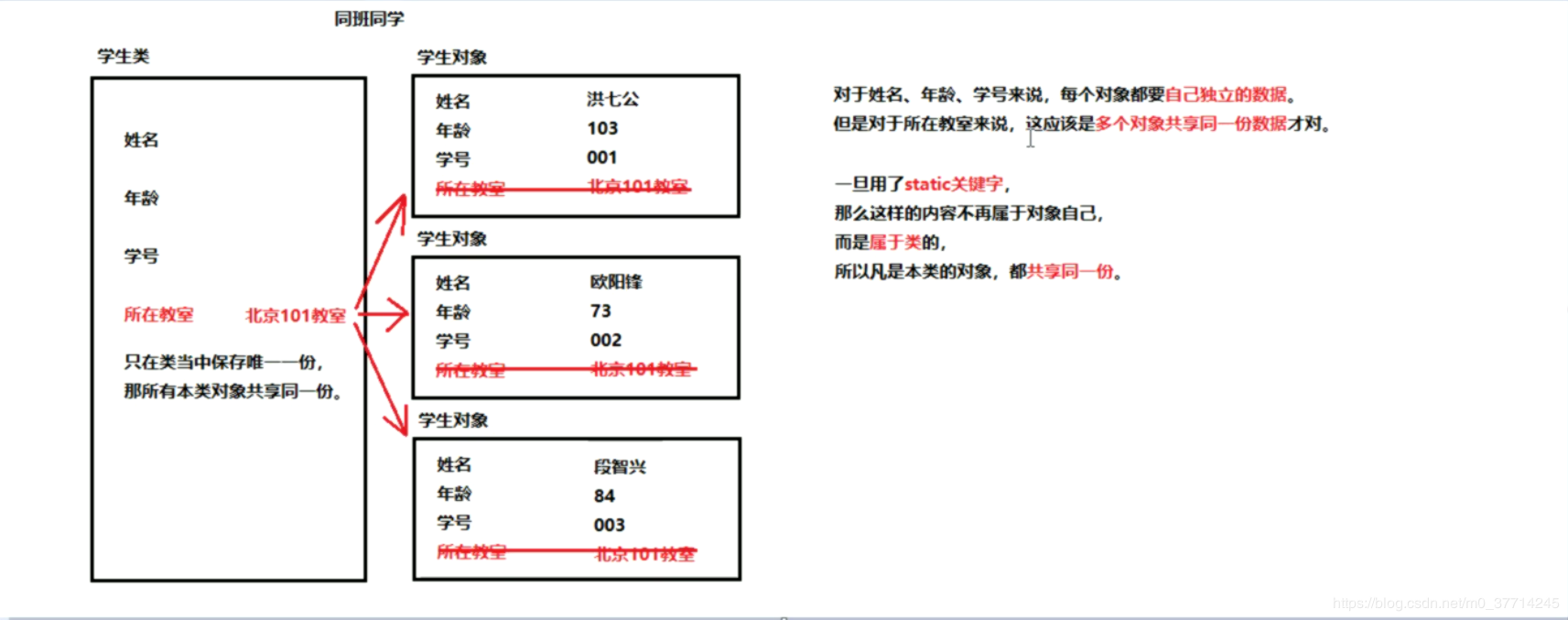
static 修饰成员变量(修饰后类似于类属性)
如果一个成员变量使用了 static 关键字,那么这个成员变量不再属于自己,而是属于所在的类,多个对象共享这个变量
推荐写法:类名.变量名
// 这里少了一个例子
static 修饰成员方法(修饰后类似于类方法)
如果没有 static 关键字,那么必须创建对象,然后通过对象来调用方法
对于静态方法来说,可以通过对象名进行调用,也可以直接通过类名称进行调用(推荐);使用对象名调用时,会被javac翻译成:类名.方法名
注意事项:
- 静态不能直接访问非静态(因为在内存中是先有的静态内容,后有的非静态内容)
- 静态方法中不能使用 this
public class StaticMethod{ private int num; static int staticNum; // 实例方法 public void method(){ System.out.println("this is obj method"); // 非静态可以访问静态 System.out.println(staticNum); // 0 } // 类方法 public static void classMethod(){ System.out.println("this is class method"); // 静态不能访问非静态 // System.out.println(num); } public static void main(String[] args){ // 使用类名调用类方法 StaticMethod.classMethod(); // 使用对象调用实例方法 StaticMethod sm = new StaticMethod(); sm.method(); } }
静态代码块(用来一次性的对类变量进行赋值)
注意事项:
- 当第一次用到当前类时,静态代码块执行唯一的一次
- 静态内容总是优先于非静态,所以静态代码块比构造方法先执行
public class StaticCodeBlock{ static{ // 静态代码块 System.out.println("static code block execution"); } // 构造方法 public StaticCodeBlock(){ System.out.println("constructor execution"); } public static void main(String[] args) { StaticCodeBlock codeOne = new StaticCodeBlock(); StaticCodeBlock codeTwo = new StaticCodeBlock(); } } // 执行结果 // static code block execution // 执行唯一一次 // constructor execution // constructor execution
ending ~