链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ggWP0OF
第 1 章 : 热更新技术学习介绍
课时1:101-热更新技术学习介绍 11:55
什么是热更新?
举例来说
游戏上线后,玩家下载第一个版本(70M左右或者更大),在运营的过程中,如果需要更换UI显示,或者修改游戏的逻辑,这个时候,如果不使用热更新,就需要重新打包,然后让玩家重新下载(浪费流量和时间,体验不好)。
热更新可以在不重新下载客户端的情况下,更新游戏的内容。
热更新一般应用在手机网游上。
为什么C#脚本不可以直接更新?
C#是一门编程语言,它运行之前需要进行编译,而这个编译的过程在移动平台无法完成,所以当我们游戏的逻辑更改,C#代码发生改变的时候,我们就需要重新在开发环境下编译,然后重新打包,然后让玩家去下载更新最新的版本。
这个体验差:包下载需要的时间长,而且很多资源没有更新,也需要重新下载,浪费流量。
热更新有哪些实现方式?
1,使用Lua脚本编写游戏的UI或者其他的逻辑
Lua是一个精悍小巧的脚本语言,可以跨平台运行解析,而且不需要编译的过程
2,使用C#Light
3,使用C#反射技术
什么是AssetBundle?
Unity提供了一个资源更新技术,就是通过AssetBundle,我们可以通过AssetBundle更新游戏UI,也可以把脚本或者其他代码当成资源打包成AssetBundle然后更新到客户端。
在所有的热更新技术中都需要AssetBundle
如何利用Lua进行热更新?
在移动端可以编写Lua的解析器,通过这个解析器,可以运行最新的Lua脚本,然后我们把控制游戏逻辑的代码都写成Lua脚本。
Lua的解析技术有哪些?
1,uLua
骏擎【CP】 ulua.org
2,Nlua
unity支持Riley G nlua.org
3,UniLua
阿楠同学
4,sLua
如何学习热更新技术?
1,学习Lua编程
2,学习通过LuaInterface和luanet进行Lua和C#的交互通信
3,学习使用AssetBundle进行资源更新
4,学习uLua SimpleFramework
利用us创建自己的热更新游戏
第 2 章 : Lua
课时2:201-Lua介绍和luaforwindows的安装 07:36
Lua 是一个小巧的脚本语言。是巴西里约热内卢天主教大学(Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro)里的一个研究小组,由Roberto Ierusalimschy、Waldemar Celes 和 Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo所组成并于1993年开发。 其设计目的是为了嵌入应用程序中,从而为应用程序提供灵活的扩展和定制功能。Lua由标准C编写而成,几乎在所有操作系统和平台上都可以编译,运行。Lua并没有提供强大的库,这是由它的定位决定的。所以Lua不适合作为开发独立应用程序的语言。Lua 有一个同时进行的JIT项目,提供在特定平台上的即时编译功能。
1,Lua的官网 lua.org
2,Luaforwindows
http://luaforge.net/projects/luaforwindows/
http://luaforwindows.luaforge.net/ (可安装的exe文件,一整套的Lua开发环境,有Lua的解释器,参考手册,范例和库,文档,和编辑器)
3,安装Luaforwindows,关于Luaforwindows的目录介绍
1,找到luaforwindows的安装目录,找到SciTE
2,打开SciTE,写入第一行Lua代码
print("Hello World")
3,保存代码,保存为HelloWorld.lua
4,按下F5运行
课时3:202-编写第一个Lua程序HelloWorld 03:58
程序分析:
1,print()是Lua内置的方法
2,在Lua中字符串用 "" 或者 '' 都可以表示
3,Lua中每一条语句后面是没有;号的
如何定义变量?
num = 100
这里定义了一个全局变量叫做num,赋值为100
在Lua中定义变量是没有类型的,根据存储什么数据,来决定是什么类型
变量的命名不能以数字开头
尽量避免下划线加大写字母开头,这种格式Lua自身保留
推荐使用C#中的命名规范和驼峰命名
如何添加注释?
1,单行注释 --注释内容
2,多行注释 --[[ 这里是注释内容 ]]--
课时4:203-变量的定义 10:03
Lua变量类型如下:
1,nil表示空数据,等同于null
2,boolean 布尔类型,存储true和false
3,string 字符串类型,字符串可以用双引号也可以使用单引号表示
4,number小数类型(Lua中没有整数类型)
5,table表类型
myTable = {34,,34,2,342,4}
myTable[3] --从1开始
我们可以使用type()来取得一个变量的类型
注:汉字为两个字节,所以删除要按两下
注意事项:
默认定义的变量都是全局的,定义局部变量需要在前面加一个local;
在代码块中声明的局部变量,当代码块运行结束的时候,这个变量就会被释放;
temp = 34
local var = 345
课时5:204-运算符和流程控制语句if语句 07:31
Lua运算符有哪些?
1,算数运算符 + - * / % (Lua中没++ -- 这样是运算符)
2,关系运算符 <= < > >= ==
3,逻辑运算符 and or not 分别表示 与 或 非(类似于C#中的 && || !)
if语句的三种用法
1, if [condition] then
end
2, if [condition] then
else
end
3, if [condition] then
elseif [condition]
else
end
num1=10
num2=20
num3=30
res1=num1 and num2
res2=true or num2
res3=not num3
print(res1,res2,res3)
local hp=40
if hp<=0 then
print("die")
elseif hp>=50 then
print("good")
else
print("bad")
end
课时6:205- 循环结构之while循环和repeat循环 07:27 Lua中没有+=这个运算符
循环结构while循环
1,while语法结构
while [condition] do
end
2,输出1到100
index=1
while index<=100 do
print(index)
index=index+1
end
3,实现1加到100
sum=0
index=1
while index<=100 do
sum=sum+index
index=index+1
end
print(sum)
4,遍历1-100中所有的奇数的和
sum=0
index=1
while index<=100 do
if index%2==1 then
sum=sum+index
end
index=index+1
end
print(sum)
循环结构repeat循环(相当于do - while)
1,语法结构
repeat
[code to execute]
until [condition]
2,输出1到100
index=1
repeat
print(index)
index=index+1
until index>100
3,实现1加到100
sum=0
index=1
repeat
sum=sum+index
index=index+1
until index>100
print(sum)
4,遍历1-100中所有的奇数的和
sum=0
index=1
repeat
if index%2==1 then
sum=sum+index
end
index=index+1
until index>100
print(sum)
课时7:206- 循环结构之for循环 02:51
for循环结构
1,语法结构
for index = [start],[end] do
[code to execute]
end
2,输出1到100
for index=1,100 do
print(index)
end
3,实现1加到100
sum=0
for index=1,100 do
sum=sum+index
end
print(sum)
4,遍历1-100中所有的奇数的和
sum=0
for index=1,100 do
if index%2==1 then
sum=sum+index
end
end
print(sum)
break可以终止循环 没有continue语法
课时8:207- 函数的定义和math数学函数 05:16
函数(方法)
1,如何定义函数
function [function name](param1,param2)
[function code]
end
2,定义一个函数用来求得两个数字的和
function Plus(num1,num2)
return num1+num2
end
标准库(标准函数)
Lua内置提供了一些常用的函数帮助我们开发
1,数学处理的math相关函数
2,字符串处理的string相关函数
3,表处理的table相关函数
4,文件操作的io相关函数
数学运算函数
math.abs
math.cos
math.max
math.maxinteger
math.min
math.random
math.sin
math.sqrt
math.tan
print(math.abs(-90))
print(math.max(12,34,56,76,43,2))
print(math.random())
课时9:208- 字符串处理 03:14
字符串处理相关函数
string.byte
string.char
string.find
sting.format
string.lower
string.sub
string.upper
.. 字符串相加
tostring() 把一个数字转化成字符串
tonumber() 把一个字符串转化成数字
name="kerHHHHHven"
print(string.lower(name))
print(string.sub(name,1,4))
print("http://"..name)
课时10:209- Lua中的table表 10:02
在Lua中的table类似C#中的字典,其实就是一个 key-value键值对的数据结构。
1,table的创建
myTable = {}
表名后面使用{}赋值,表示一个空的表
2,table的赋值
myTable[3]=34 当键是一个数字的时候的赋值方式
myTable["name"]="taikr" 当键是一个字符串的赋值方式
myTable.name = "siki"当键是一个字符串的赋值方式
3,table的访问
myTable[3] 当键是数字的时候,只有这一种访问方式
myTable.name 当键是字符串的时候有两种访问方式
myTable["name"]
4,table的第二种创建方式
myTable = {name="taikr",age=18,isMan = false}
(表创建之后依然可以添加数据)
数据访问
myTable.name
myTable["name"]
5,table的第三种方式(类似数组的使用)
myTable = {34,34,34,3,4,"sdfdsf"}
当没有键的时候,编译器会默认给每一个值,添加一个数字的键,该键从1开始
课时11:210- 表相关函数,使用表实现面向对象编程 08:07
表的遍历
表的遍历分为两种
1,如果是只有数字键,并且是连续的可以使用下面的遍历
for index = 1,table.getn(myTable) do
[code to execute]
end
2,所有的表都可以通过下面的方式遍历
for index,value in pairs(myNames) do
print(index,value)
end
表相关的函数
1.table.concat
把表中所有数据连成一个字符串
2,table.insert
向指定位置插入一个数据
3,table.move
移动数据
4,table.pack
包装成一个表
5,table.remove
移除指定位置的数据
6,table.sort
排序
7,table.unpack
返回一个数组,指定范围的数组
通过表来实现面向对象
myTable={} 申明对象
local this = myTable声明this关键字代表当前对象
--定义并声明对象中的属性
myTable.name="siki"
myTable.age = 110
--定义并声明对象中的方法
myTable.function = function ()
[code to execute]
end
function myTable.function ()
[code to execute]
end
第 3 章 :
课时12:301- LuaInterface学习,在CLR(C#)中执行lua代码 05:07(只需要引入LuaInterface.dll)
什么是LuaInterface
LuaInterface包括两个核心库一个是LuaInterface.dll,一个是Luanet.dll,我们可以通过LuaInterface完成Lua和C#(CLR)之间的互相调用
在CLR(C#)中执行lua代码
Lua lua = new Lua(); //创建Lua解析器
lua["num"]=2; //定义一个num
lua["str"]="a string"; //定义一个字符串
lua.newTable("tab"); //创建一个表 tab={}
取得Lua环境
double num = (double)lua["num"];
string str = (string)lua["str"];
课时13:302-在C#中执行Lua脚本文件,或者脚本字符串 13:02
lua.DoFile("script.lua");//执行script.lua脚本
lua.DoString("num=2");
lua.DoString("str='a string'");
object[] retVals = lua.DoString("return num,str");
在热更新中,只需要写好解析lua脚本的代码,然后c#代码不需要变动,只需要修改lua脚本就好,通过lua脚本控制游戏逻辑。lua脚本和使用的C#脚本需要在同一个目录下,既是在Debug目录下
using System;
namespace LuaInterface
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Lua lua = new Lua();//创建Lua的解释器
lua["num"] = 34;
Console.WriteLine(lua["num"]);
lua.DoString("num=2");
lua.DoString("str='a string'");
object[] retVals = lua.DoString("return num,str");
foreach (object obj in retVals)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
lua.DoFile("hello.lua");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
课时14:303-把一个C#方法注册进Lua的一个全局方法 07:26
Lua和C#中对应的类型
nil null
string System.String
number System.Double
boolean System.Boolean
table LuaInterface.LuaTable
function LuaInterface.LuaFunction
把一个C#方法注册进Lua的一个全局方法
//把一个类中的普通方法注册进去
lua.RegisterFunction("NormalMethod",obj,obj.GetType().GetMethod("NormalMethod"))
lua.DoString(" NormalMethod()");
using System;
namespace LuaInterface
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Lua lua = new Lua();//创建Lua的解释器
#region把一个类中的普通方法注册进去
Program p = new Program();
lua.RegisterFunction("CLRMethod", p, p.GetType().GetMethod("CLRMethod"));
lua.DoString("CLRMethod()");
#endregion
Console.ReadKey();
}
public void CLRMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("普通c#方法");
}
}
}
// 把一个类的静态方法注册进去
lua.RegisterFunction("StaticMethod",null,typeof(ClassName).GetMethod("StaticMethod"))
lua.DoString(" StaticMethod()")
using System;
namespace LuaInterface
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Lua lua = new Lua();//创建Lua的解释器
#region 把一个类的静态方法注册进去
lua.RegisterFunction("MyStaticMethod", null, typeof(Program).GetMethod("MyStaticMethod"));
lua.DoString("MyStaticMethod()");
#endregion
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void MyStaticMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("静态方法");
}
}
}
课时15:304-在Lua中使用c#中的类 08:43
require "luanet"
--加载CLR的类型、实例化CLR对象
luanet.load_assembly("System.Windows.Forms")
luanet.load_assembly("System.Drawing")
Form = luanet.import_type("System.Windows.Forms.Form")
StartPosition = luanet.import_type("System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition")
print(Form)
print(StartPosition)
在Lua中使用C#中的类创建对象的时候,会自动匹配最合适的构造方法
require "luanet"
luanet.load_assembly("System")
Int32=luanet.import_type("System.Int32")
num=Int32.Parse("3435")
print(Int32)
print(num)
课时16:305-在Lua中访问C#中的属性和方法 03:25
Lua代码中,访问C#对象的属性的方式和访问table的键索引一样,比如obj.name 或者 obj["name"]
Lua代码中,访问C#对象的普通函数的方式和调用table的函数一样,比如obj:method1()
require "luanet"
luanet.load_assembly("System")
luanet.load_assembly("testLuaInterface")
Program =luanet.import_type("testLuaInterface.Program")
program1= Program()
print(program1.name)
program1:Method()
课时17:306-在Lua中访问C#中的属性和方法-特殊情况-带有out和ref关键字 07:01
当函数中有out或ref参数时,out参数和ref参数和函数的返回值一起返回,并且调用的时候,out参数不需要传入
C#函数定义
class Obj{
int OutMethod1(int parameter1,out parameter2,out parameter3){
parameter2=34;parameter3=213;
return parameter1;
}
int OutMethod2(int parameter1,ref parameter2){
parameter2=parameter2+2;
return parameter1+parameter2;
Lua中的调用和返回值
obj:OutMethod1(34)
--out参数不需要参数,这个返回一个table,里面的值为parameter1,parameter2,parameter3
(34,34,213)
obj:OutMethod2(10,10)
--ref参数需要传入,返回一个table有两个值(value1,value2)
require "luanet"
luanet.load_assembly("System")
luanet.load_assembly("testLuaInterface")
Program =luanet.import_type("testLuaInterface.Program")
program1= Program()
void,strLength=program1:TestOut("www.kerven.com.cn")
print(void,strLength)
void,count=program1:TestRef("www.kerven.com",20)
print(void,count)
当有重载函数的时候,调用函数会自动匹配第一个能匹配的函数
可以使用get_method_bysig函数得到C#中指定类的指定参数的函数用法
luaMethod = get_method_bysig(Obj,"CSharpMethod","System.String")
luaMethod("siki")
在Lua中注册C#中的事件委托(event delegate)
在Lua中通过Add方法或者Remove方法把一个Lua的函数注册或者注销从C#中的事件委托中
function method()
end
obj.SomeEvent:Add(methodname(不用带引号))
第 4 章 : AssetBundle
课时18:401-什么是AssetBundle以及如何打包AssetBundle 11:04
利用AssetBundle进行简单的打包
using System.IO;
using UnityEditor;
public class CreateAssetBundles{
[MenuItem("Assets/Build AssetBundles")]
static void BuildAllAssetBundles()
{
string dir = "AssetBundles";
if (Directory.Exists(dir) == false)
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(dir);
}
BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles(dir, BuildAssetBundleOptions.None,
BuildTarget.StandaloneWindows64);
}
}
课时19:402-Manifest文件介绍 04:52
AssetBundles.manifest记录里面的资源
课时20:403-如何下载并记载AssetBundle 10:07
using System.Collections;
using UnityEngine;
public class LoadAssetBundle : MonoBehaviour {
/// <summary>
/// 第三种加载方式:www
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
IEnumerator Start()
{
string path = @"file:///F:经典学习案例,忘记了可以回头看的案例siki的热更新专题HotUpdateProjectAssetBundlesplayer.unity3d";
while (Caching.ready == false)
{
yield return null;
}
WWW www = WWW.LoadFromCacheOrDownload(path, 1);
yield return www;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(www.error) == false)
{
Debug.Log(www.error);
yield break;
}
AssetBundle ab = www.assetBundle;
//使用里面的资源
var wallPrefab = ab.LoadAsset<GameObject>("player");
Instantiate(wallPrefab);
}
}
第 5 章 : ulua
课时21:501-ulua介绍和uLua SimpleFramework下载 06:29
看官网的撕逼文章 http://ulua.org/index.html
课时22:502-ulua simpleframework目录介绍 05:09
导入工程到unity,介绍目录结构
课时23:503-案例解释LuaState和LuaScriptMgr 13:10
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
public class HelloWorld : MonoBehaviour {
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
LuaState l = new LuaState();
string str = "print('hello world 世界')";
l.DoString(str);
}
}
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
public class CreateGameObject01 : MonoBehaviour {
private string script = @"
luanet.load_assembly('UnityEngine')
GameObject = luanet.import_type('UnityEngine.GameObject')
ParticleSystem = luanet.import_type('UnityEngine.ParticleSystem')
local newGameObj = GameObject('NewObj')
newGameObj:AddComponent(luanet.ctype(ParticleSystem))
";
//反射调用
void Start () {
LuaState lua = new LuaState();
lua.DoString(script);
}
}
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
public class CreateGameObject02 : MonoBehaviour {
private string script = @"
luanet.load_assembly('UnityEngine')
GameObject = UnityEngine.GameObject
ParticleSystem = UnityEngine.ParticleSystem
local newGameObj = GameObject('NewObj')
newGameObj:AddComponent(ParticleSystem.GetClassType())
";
//非反射调用
void Start () {
LuaScriptMgr lua = new LuaScriptMgr();
lua.Start();
lua.DoString(script);
}
}
课时24:504-在Unity中访问Lua中的变量 07:01
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
public class AccessingLuaVariables01 : MonoBehaviour {
private string script = @"
luanet.load_assembly('UnityEngine')
GameObject = luanet.import_type('UnityEngine.GameObject')
ParticleSystem = luanet.import_type('UnityEngine.ParticleSystem')
particles = {}
for i = 1, Objs2Spawn, 1 do
local newGameObj = GameObject('NewObj' .. tostring(i))
local ps = newGameObj:AddComponent(luanet.ctype(ParticleSystem))
ps:Stop()
table.insert(particles, ps)
end
var2read = 42
";
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
LuaState l = new LuaState();
// Assign to global scope variables as if they're keys in a dictionary (they are really)
l["Objs2Spawn"] = 5;
l.DoString(script);
// Read from the global scope the same way
print("Read from lua: " + l["var2read"].ToString());
// Get the lua table as LuaTable object
LuaTable particles = (LuaTable)l["particles"];
// Typical foreach over values in table
foreach( ParticleSystem ps in particles.Values )
{
ps.Play();
}
}
}
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
public class AccessingLuaVariables02 : MonoBehaviour
{
//cstolua要求必须要先定义变量才能使用
private string var = @"Objs2Spawn = 0";
private string script = @"
particles = {}
ParticleSystem = luanet.import_type('UnityEngine.ParticleSystem')
for i = 1, Objs2Spawn, 1 do
local newGameObj = GameObject('NewObj' .. tostring(i))
local ps = newGameObj:AddComponent(luanet.ctype(ParticleSystem))
ps:Stop()
table.insert(particles, ps)
end
var2read = 42
";
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
LuaScriptMgr mgr = new LuaScriptMgr();
mgr.Start();
// Assign to global scope variables as if they're keys in a dictionary (they are really)
LuaState l = mgr.lua;
l.DoString(var);
l["Objs2Spawn"] = 5;
l.DoString(script);
// Read from the global scope the same way
print("Read from lua: " + l["var2read"].ToString());
// Get the lua table as LuaTable object
LuaTable particles = (LuaTable)l["particles"];
// Typical foreach over values in table
foreach( ParticleSystem ps in particles.Values )
{
ps.Play();
}
}
}
课时25:505-执行Lua脚本文件,调用Lua方法,在Lua中使用协程 07:24
讲述了第四、五、六个例子。
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
public class LuaCoroutines : MonoBehaviour
{
private string script = @"
function fib(n)
local a, b = 0, 1
while n > 0 do
a, b = b, a + b
n = n - 1
end
return a
end
function CoFunc()
print('Coroutine started')
local i = 0
for i = 0, 10, 1 do
print(fib(i))
coroutine.wait(1)
end
print('Coroutine ended')
end
function myFunc()
coroutine.start(CoFunc)
end
";
private LuaScriptMgr lua = null;
void Awake ()
{
lua = new LuaScriptMgr();
lua.Start();
lua.DoString(script);
LuaFunction f = lua.GetLuaFunction("myFunc");
f.Call();
f.Release();
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update ()
{
lua.Update();
}
void LateUpdate()
{
lua.LateUpate();
}
void FixedUpdate()
{
lua.FixedUpdate();
}
}
课时26:506-框架启动第一步GlobalGenerator,生成appview和gamemanager 12:43
GlobalGenerator--全局管理器
课时27:507-GameManager中对资源的更新处理 10:16
GameManager的工作流程
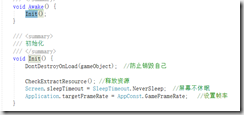
课时28:508-GameManager处理Lua的View的加载和初始化 11:51
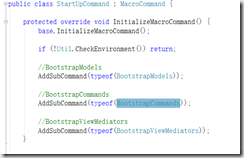
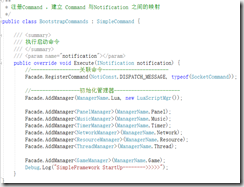
课时29:509-Lua代码中的结构和调用顺序和对资源的处理和对游戏逻辑的控制 14:19
课时30:510-创建开发UI界面 08:18
课时31:511-打包资源,创建GameManager的lua脚本 10:33
课时32:512-开发View视图层下的Lua代码,来获取UI中的组件 14:31
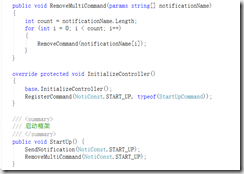
课时33:513-开发Controller控制层下的Lua代码,控制UI控件的产生和事件监听 23:32
课时34:514-发布到手机上,启动Server,进行Lua代码的更新 15:24
课时35:515-热更新完结篇-游戏资源更新和游戏逻辑的更新