1、Spring管理Bean,实例化Bean对象 三种方式
第一种:使用类构造器实例化(默认无参数)
1 package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; 2 3 /** 4 * 使用构造方法 实例化 5 * 6 * @author seawind 7 * 8 */ 9 public class Bean1 { 10 11 } 12 13 <!-- Bean 实例化第一种 方式 构造器 --> 14 <bean id="bean1" class="cn.itcast.spring.initbean.Bean1"></bean>
第二种:使用静态工厂方法实例化(简单工厂模式)
1 package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; 2 /** 3 * 使用静态工厂方法进行Bean 实例化 4 * 5 * @author seawind 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Bean2 { 9 10 } 11 12 package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; 13 // 工厂类 14 public class Bean2Factory { 15 public static Bean2 getBean2() { 16 return new Bean2(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 <!-- Bean 实例化第二种 方式 静态工厂方法 --> 21 <bean id="bean2" class="cn.itcast.spring.initbean.Bean2Factory" factory-method="getBean2" />
第三种:使用实力工厂方法实例化(工厂方法模式)
1 package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; 2 /** 3 * 通过实例 工厂方法进行构造 4 * 5 * @author seawind 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Bean3 { 9 10 } 11 12 package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; 13 public class Bean3Factory { 14 public Bean3 getBean3() { 15 return new Bean3(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 <!-- Bean 实例化 第三种 方式 实例工厂方法 --> 20 <bean id="bean3factory" class="cn.itcast.spring.initbean.Bean3Factory"></bean> 21 <bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3factory" factory-method="getBean3"></bean>
测试三种方式
1 package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 /** 8 * 实例化 Bean 三种方式 9 * 10 * @author seawind 11 * 12 */ 13 public class SpringTest { 14 @Test 15 // 实例工厂方法 实例化 Bean 16 public void demo3() { 17 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 18 "applicationContext.xml"); 19 Bean3 bean3 = (Bean3) applicationContext.getBean("bean3"); 20 System.out.println(bean3); 21 } 22 23 @Test 24 // 使用 静态工厂方法实例化Bean 25 public void demo2() { 26 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 27 "applicationContext.xml"); 28 Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2) applicationContext.getBean("bean2"); 29 System.out.println(bean2); 30 } 31 32 @Test 33 // 使用Bean 的构造方法 实例化Bean 34 public void demo1() { 35 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 36 "applicationContext.xml"); 37 // Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) applicationContext.getBean("bean1"); 38 // Spring3 集合 JDK5 泛型特性 39 Bean1 bean1 = applicationContext.getBean("bean1", Bean1.class); 40 41 System.out.println(bean1); 42 } 43 }
2、Bean的id属性和name属性

在使用Spring 配置Bean
<bean id="helloService" class=".....HelloService" />
<bean name="helloService" class="....HelloSerivce" />
* 在配置Bean过程中 id 属性 和 name 属性 都行 ,都可以通过 applicationContext.getBean(id/name) 来获得一个Bean实例
配置id 必须唯一,通常不含有特殊字符, 比如以/开始,以数字开始
配置name 属性,不必须唯一, 可以含有特殊字符
* 为什么要有name属性 ?
比如 struts1 整合 spring 需要将 请求路径 配置到spring 中
<bean id="/login" class="..... UserAction" /> ------ 在早期Spring版本 是报错的
<bean name="/login" class="..... UserAction" /> ------ 以前整合都是这样写的
3、 Bean的作用域
在配置 <bean> 元素时, 通过 scope 属性 指定 Bean的作用域
singleton : 代表Bean 在整个Spring 容器环境中 是单例的
prototype : 多例 (原型模式) , 在一个Spring 容器中,每次使用Bean 都会返回一个新的实例
request : 相当于 构造对象,保存request数据范围 (request.setAttribute())
session : 相当于 构造对象,保存session数据范围 (session.setAttribute()) 以后再次使用,同一个Session无需构造
* 在实际开发中 只需要掌握 singleton 和 prototype 就可以了 ----- 默认值是 singleton
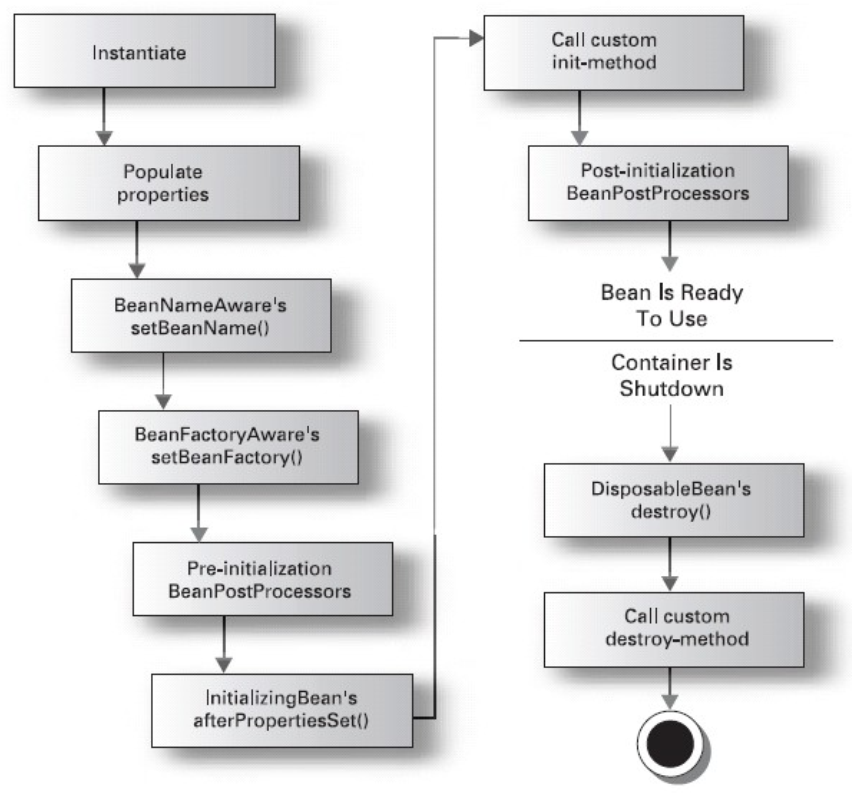
4、Bean 生命周期
在配置 <bean> 通过 init-method destroy-method 定义Bean的初始化 和 销毁的方法
1 applicationContext.xml: <bean id="product" class="cn.itcast.spring.lifecycle.Product" init-method="myinit" destroy-method="mydestroy"></bean> 2 3 public class Product { 4 public Product() { 5 System.out.println("执行 Product的 构造 ..."); 6 } 7 8 public void myinit() { 9 System.out.println("Product对象初始化...."); 10 } 11 12 public void mydestroy() { 13 System.out.println("Product对象销毁...."); 14 } 15 } 16 17 @Test 18 // 配置 init-method 和 destroy-method 执行 bean 的初始化和销毁 方法 19 public void demo1() { 20 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 21 "applicationContext.xml"); 22 Product product = (Product) applicationContext.getBean("product"); 23 System.out.println(product); 24 25 // 如果销毁 Spring 手动 调用 close方法 26 applicationContext.close(); 27 }
有构造方法,为什么要有init ?
java语言不建议在构造器 编写复杂处理逻辑,通常在构造器 只会成员变量赋值。初始化
完整Bean的生命周期
1) instantiate bean对象实例化
2) populate properties 封装属性(setXxxx方法执行)
3) 如果Bean实现BeanNameAware 执行 setBeanName(String beanName)
4) 如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAware 或者 ApplicationContextAware 设置工厂 setBeanFactory 或者上下文对象 setApplicationContext
* void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)
5) 如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization
6) 如果Bean实现InitializingBean 执行 afterPropertiesSet
7) 调用<bean init-method="init"> 指定初始化方法 init
8) 如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean) ,执行postProcessAfterInitialization
9) 执行业务处理
10)如果Bean实现 DisposableBean 执行 destroy
11)调用<bean destroy-method="customerDestroy"> 指定销毁方法 customerDestroy
3) 4) 知识点: 让Bean 了解Spring 容器
5) Bean的后处理器 BeanPostProcessor ,该类成为Bean的后处理器
* 后处理Bean 可以对 已经创建 Bean对象 进行代理增强
1 package cn.itcast.spring.lifecycle; 2 3 // 定义业务接口 4 5 public interface CustomerService { 6 public void addCustomer(); 7 } 8 9 10 package cn.itcast.spring.lifecycle; 11 12 import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; 13 import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; 14 import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; 15 import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; 16 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 17 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; 18 19 // CustomerService 一个实现类 20 public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService, BeanNameAware, 21 ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { 22 private String name; 23 24 // 第一步 25 public CustomerServiceImpl() { 26 System.out.println("第一步 Bean的构造器执行...."); 27 } 28 29 @Override 30 public void addCustomer() { 31 // 第九步 执行业务操作 32 System.out.println("第九步 ,使用业务Bean 执行业务操作...."); 33 System.out.println("添加客户"); 34 } 35 36 // 第二步 37 public void setName(String name) { 38 System.out.println("第二步 属性依赖注入...."); 39 this.name = name; 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 // 第三步,如果 Bean 实现 BeanNameAware, Spring 就会将 <bean> 配置 id 属性 、name 属性 注入 44 public void setBeanName(String beanName) { 45 System.out.println("第三步 获得当前Bean在Spring 注册 Bean 名字 :" + beanName); 46 } 47 48 @Override 49 // 第四步 如果 Bean 实现 ApplicationContextAware, Spring 就会将Spring 应用上下文 注入给 Bean 50 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) 51 throws BeansException { 52 System.out.println("第四步 获得当前 Spring上下文 :" + applicationContext); 53 // 通过该对象 操作其它Bean 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 // 第六步 58 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { 59 System.out.println("第六步 属性封装完成 ...."); 60 } 61 62 // 第七步 通过配置文件,指定初始化方法 63 public void myinit() { 64 System.out.println("第七步 自定义初始化方法..."); 65 } 66 67 @Override 68 // 第十步 释放资源 69 public void destroy() throws Exception { 70 System.out.println("第十步, 不需要配置 调用释放资源方法"); 71 } 72 73 // 第十一步 74 public void mydestroy() { 75 System.out.println("第十一步 自定义 释放资源方法"); 76 } 77 78 } 79 80 package cn.itcast.spring.lifecycle; 81 82 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 83 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 84 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 85 86 import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; 87 import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; 88 89 // 自定义 一个 Bean的 后处理器 90 91 public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { 92 93 @Override 94 // 提供两个方法,用户通过实现 两个方法,对原有Bean 进行增强 95 // 第八步 96 /** 97 * beanName 就是 配置文件 <bean> id 属性 98 * bean 增强前对象 99 */ 100 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, 101 String beanName) throws BeansException { 102 System.out.println("第八步 BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean 初始化完成后增强...."); 103 // 通过beanName 判断要对哪个Bean 进行代理增强 104 if (beanName.equals("customerService")) { 105 // 增强 106 return Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(), 107 bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { 108 @Override 109 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, 110 Object[] args) throws Throwable { 111 if (method.getName().equals("addCustomer")) { // 增强 112 System.out 113 .println("增强addCustomer======================================="); 114 } 115 116 // 不增强 117 return method.invoke(bean, args); 118 } 119 }); 120 } 121 return bean; 122 } 123 124 @Override 125 // 第五步 126 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 127 throws BeansException { 128 System.out.println("第五步BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean 初始化完成前增强... "); 129 return bean; 130 } 131 132 } 133 134 @Test 135 // 通过CustomerService 来理解Bean 的生命周期 136 public void demo2() { 137 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 138 "applicationContext.xml"); 139 CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) applicationContext 140 .getBean("customerService"); 141 customerService.addCustomer(); 142 143 applicationContext.close(); 144 } 145 146 147 <!-- 可以配置Bean 初始化和销毁 调用方法 --> 149 <bean id="customerService" class="cn.itcast.spring.lifecycle.CustomerServiceImpl" init-method="myinit" destroy-method="mydestroy"> 150 <property name="name" value="张三"></property> 151 </bean> 152 153 <!-- 配置后处理Bean ,不需要为Bean 指定id ,会对所有Bean 产生作用 --> 154 <bean class="cn.itcast.spring.lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
结果: