一,企业级Elasticsearch使用详解
1.1 基本概念
| Elasticsearch | MySQL |
|---|---|
| Index | Database |
| Type | Table |
| Document | Row |
| Field | Column |
- Node:运行单个ES实例的服务器
- Cluster:一个或多个节点构成集群
- Index:索引是多个文档的集合(必须是小写字母)
- Document:Index里每条记录称为Document,若干文档构建一个Index
- Type:一个Index可以定义一种或多种类型,将Document逻辑分组
- Field:ES存储的最小单元
- Shards:ES将Index分为若干份,每一份就是一个分片。
- Replicas:Index的一份或多份副本
1.2 实验环境说明
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| ES1 | 192.168.200.191 | elasticsearch-node1 |
| ES2 | 192.168.200.192 | elasticsearch-node2 |
| ES3 | 192.168.200.193 | elasticsearch-node3 |
| Logstash-Kibana | 192.168.200.194 | 日志可视化服务器 |
#系统初始环境调整[root@ES1 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-releaseCentOS Linux release 7.5.1804 (Core)[root@ES1 ~]# uname -r3.10.0-862.3.3.el7.x86_64[root@ES1 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld[root@ES1 ~]# setenforce 0setenforce: SELinux is disabled[root@ES1 ~]# sestatusSELinux status: disabled#更换亚洲时区[root@ES1 ~]# /bin/cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime#安装时间同步[root@ES1 ~]# yum -y install ntpdate#进行时间同步[root@ES1 ~]# ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
1.3 企业级Elasticsearch集群部署
#在三台ES上都进行如下操作#yum安装jdk1.8[root@ES1 ~]# yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk#导入yum方式安装ES的公钥[root@ES1 ~]# rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch#添加ES的yum源文件[root@ES1 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo[root@ES1 ~]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo[elastic-6.x]name=Elastic repository for 6.x packagesbaseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yumgpgcheck=1gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearchenabled=1autorefresh=1type=rpm-md#安装elasticsearch[root@ES1 ~]# yum -y install elasticsearch#配置elasticsearch的配置文件#将以下内容进行修改[root@ES1 ~]# cat -n /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.bak | sed -n '17p;23p;33p;37p;55p;59p;68p;72p'17 #cluster.name: my-application23 #node.name: node-133 path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch37 path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch55 #network.host: 192.168.0.159 #http.port: 920068 #discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["host1", "host2"]72 #discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes:[root@ES1 ~]# cat -n /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml | sed -n '17p;23p;33p;37p;55p;59p;68p;72p'17 cluster.name: elk-cluster23 node.name: node-133 path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch37 path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch55 network.host: 192.168.200.19159 http.port: 920068 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.200.191", "192.168.200.192","192.168.200.193"]72 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2#将ES1配置文件拷贝到ES2和ES3[root@ES1 ~]# scp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 192.168.200.193:/etc/elasticsearch/root@192.168.200.193's password:elasticsearch.yml 100% 2903 3.8MB/s 00:00[root@ES1 ~]# scp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 192.168.200.192:/etc/elasticsearch/root@192.168.200.192's password:elasticsearch.yml 100% 2903 5.0MB/s 00:00#只需要修改ES2和ES3的节点名称和监听端口即可[root@ES2 elasticsearch]# sed -n '23p;55p' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.ymlnode.name: node-2network.host: 192.168.200.192[root@ES3 yum.repos.d]# sed -n '23p;55p' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.ymlnode.name: node-3network.host: 192.168.200.193#启动三台ES上的elasticsearch[root@ES1 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch[root@ES2 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch[root@ES3 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch#查看集群节点的健康情况[root@ES1 ~]# curl -X GET "192.168.200.191:9200/_cat/health?v"epoch timestamp cluster status node.total node.data shards pri relo init unassign pending_tasks max_task_wait_time active_shards_percent1534519567 23:26:07 elk-cluster green 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 - 100.0%
1.4 Elasticsearch数据操作
RestFul API格式
curl -X<verb> '<protocol>://<host>:<port>/<path>?<query_string>' -d '<body>'
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| verb | HTTP方法,比如GET,POST,PUT,HEAD,DELETE |
| host | ES集群中的任意节点主机名 |
| port | ES HTTP服务端口,默认9200 |
| path | 索引路径 |
| query_string | 可选的查询请求参数。例如?pretty参数将格式化输出JSON数据 |
| -d | 里面放一个GET的JSON格式请求主体 |
| body | 自己写的JSON格式的请求主体 |
#列出数据库所有的索引[root@ES1 ~]# curl -X GET "192.168.200.191:9200/_cat/indices?v"health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size#创建一个索引[root@ES1 ~]# curl -X PUT "192.168.200.191:9200/logs-test-2018.08.17"{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"logs-test-2018.08.17"}#查看数据库所有索引[root@ES1 ~]# curl -X GET "192.168.200.191:9200/_cat/indices?v"health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.sizegreen open logs-test-2018.08.17 a-M8lGYtSIqvahUeFqd8Vg 5 1 0 0 2.2kb 1.1kb
Elasticsearch的操作,同学们了解即可。详细可以查看官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/_index_and_query_a_document.html
1.5 Head插件图形管理Elasticsearch
#head插件下载[root@ES1 ~]# wget https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node/latest-v4.x/node-v4.4.7-linux-x64.tar.gz[root@ES1 ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg node-v4.4.7-linux-x64.tar.gz[root@ES1 ~]# tar xf node-v4.4.7-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/[root@ES1 ~]# mv /usr/local/node-v4.4.7-linux-x64/ /usr/local/node-v4.4[root@ES1 ~]# echo -e 'NODE_HOME=/usr/local/node-v4.4 PATH=$NODE_HOME/bin:$PATH export NODE_HOME PATH' >> /etc/profile[root@ES1 ~]# tail -3 /etc/profileNODE_HOME=/usr/local/node-v4.4PATH=$NODE_HOME/bin:$PATHexport NODE_HOME PATH[root@ES1 ~]# source /etc/profile#安装git客户端[root@ES1 ~]# yum -y install git#git拉取elasticsearch-head代码[root@ES1 ~]# git clone git://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git[root@ES1 ~]# cd elasticsearch-head/[root@ES1 elasticsearch-head]# npm install特别提示:此安装过程报错也没关系,不影响使用#修改源码包配置文件Gruntfile.js#在95行处下边增加一行代码如下[root@ES1 elasticsearch-head]# cat -n Gruntfile.js | sed -n '90,97p'90 connect: {91 server: {92 options: {93 port: 9100,94 base: '.',95 keepalive: true, #添加一个逗号96 hostname: '*' #增加本行代码97 }#启动head插件[root@ES1 elasticsearch-head]# npm run start
现在我们在浏览器上访问http://IP:9100
虽然浏览器上我们打开了,但是我们发现插件无法连接elasticsearch的API,这是因为ES5.0+版本以后,要想连接API必须先要进行授权才行。
#先ES配置文件添加两行代码[root@ES1 ~]# echo -e 'http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"' >> /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml[root@ES1 ~]# tail -2 /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.ymlhttp.cors.enabled: truehttp.cors.allow-origin: "*"#重启动elasticsearch[root@ES1 ~]# systemctl restart elasticsearch
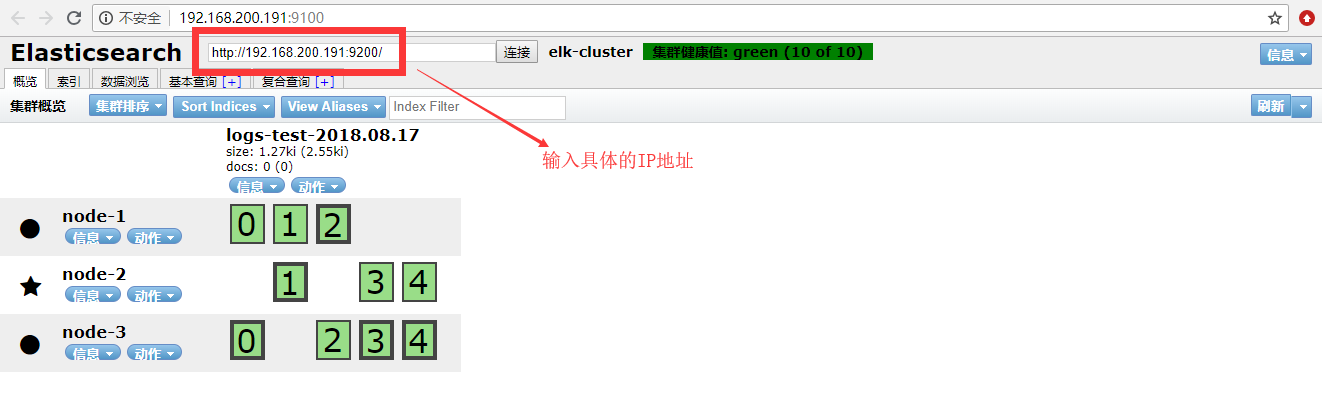
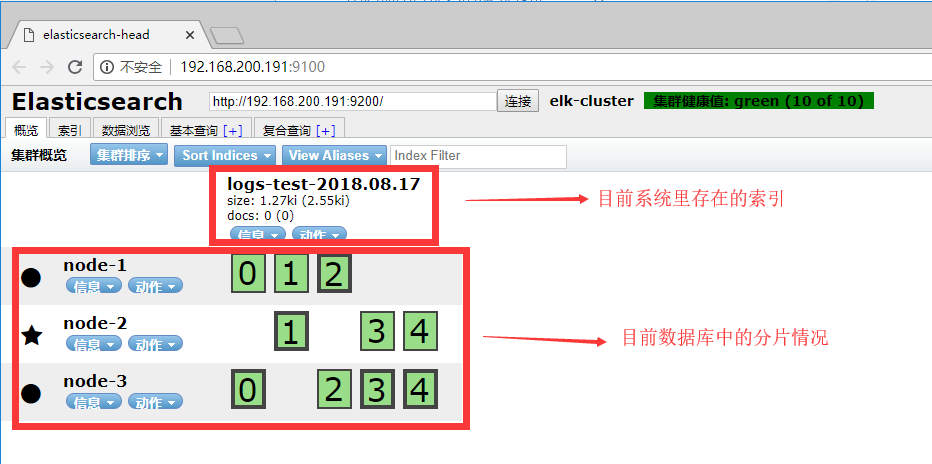
二,企业级Logstash使用详解
2.1 Logstash安装与Input常用插件
2.1.1 Logstash-安装
#yum安装jdk1.8[root@ES1 ~]# yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo[elastic-6.x]name=Elastic repository for 6.x packagesbaseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yumgpgcheck=1gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearchenabled=1autorefresh=1type=rpm-md[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# yum -y install logstash
2.1.2 Logstash-条件判断
- 比较操作符:
- 相等:==,!=,<,>,<=,>=
- 正则:=~(正则匹配),!~(不匹配正则)
- 包含:in(包含),not in(不包含)
- 布尔操作符:
- and(与)
- or(或)
- nand(非与)
- xor(非或)
- 一元运算符:
- !:取反
- ():复合表达式
- !():对复合表达式取反
2.1.3 Logstash-Input之Stdin,File,Tcp,Beats插件
#(1)stdin示例input {stdin{ #标准输入(用户交互输入数据)}}filter { #条件过滤(抓取字段信息)}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug #输出调试(调试配置文件语法用)}}#(2)File示例input {file {path => "/var/log/messages" #读取的文件路径tags => "123" #标签type => "syslog" #类型}}filter { #条件过滤(抓取字段信息)}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug #输出调试(调试配置文件语法用)}}#(3)TCP示例input {tcp {port => 12345type => "nc"}}filter { #条件过滤(抓取字段信息)}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug #输出调试(调试配置文件语法用)}}#(4)Beats示例input {beats { #后便会专门讲,此处不演示port => 5044}}filter { #条件过滤(抓取字段信息)}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug #输出调试(调试配置文件语法用)}}
(1)input ==> stdin{}标准输入插件测试
#创建logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin{}}filter {}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#测试logstash配置文件是否正确[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf -tOpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=NWARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaultsCould not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console[WARN ] 2018-08-19 23:09:16.736 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specifiedConfiguration OK #配置文件正确[INFO ] 2018-08-19 23:09:19.018 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Using config.test_and_exit mode. Config Validation Result: OK. Exiting Logstash#启动Logstash进行测试[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#此处省略若干行sadadasdasa #这就是用户输入的数据{"host" => "Logstash-Kibana","message" => "sadadasdasa", #被logstash存储在message字段中"@version" => "1","@timestamp" => 2018-08-19T15:14:48.678Z}13213121{"host" => "Logstash-Kibana","message" => "13213121","@version" => "1","@timestamp" => 2018-08-19T15:14:52.212Z}特别提示:让用户直接输入数据的方式就是标准输入stdin{};将输入的数据存储到message以后直接输出到屏幕上进行调试就是标准输出stdout{codec => rubydebug}
(2)input ==> file{}读取文件数据
#修改Logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {file {path => "/var/log/messages"tags => "123"type => "syslog"}}filter {}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动Logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#再开一个窗口向日志文件输入一句话[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# echo "1111" >> /var/log/messages#回头再去查看logstash的debug输出{"@timestamp" => 2018-08-19T15:26:10.469Z,"@version" => "1","host" => "Logstash-Kibana","tags" => [[0] "123"],"message" => "1111","path" => "/var/log/messages","type" => "syslog"}
(3)input ==> tcp{}通过监听tcp端口接收日志
#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {tcp {port => 12345type => "nc"}}filter {}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动Logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#再开一个窗口,查看12345端口监听情况[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# netstat -antup | grep 12345tcp6 0 0 :::12345 :::* LISTEN 12626/java#在ES1上安装nc向12345端口传输数据[root@ES1 ~]# yum -y install nc[root@ES1 ~]# echo "welcome to yunjisuan" | nc 192.168.200.194 12345#回头再去查看logstash的debug输出,如下{"type" => "nc","message" => "welcome to yunjisuan","port" => 41650,"@version" => "1","@timestamp" => 2018-08-19T15:43:50.543Z,"host" => "192.168.200.191"}
2.1.4 更多Input插件的用户请查看官网链接
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-inputs-file.html
2.2 Logstash-Input(Output)之Codec插件
#Json/Json_lines示例input {stdin {codec => json { #将json格式的数据转码成UTF-8格式后进行输入charset => ["UTF-8"]}}}filter {}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}
(1)codec => json {}将json格式数据进行编码转换
#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {codec => json {charset => ["UTF-8"]}}}filter {}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#再开一个窗口进入python交互界面生成json格式数据>>> import json>>> data = [{'a':1,'b':2,'c':3,'d':4,'e':5}]>>> json = json.dumps(data)>>> print json[{"a": 1, "c": 3, "b": 2, "e": 5, "d": 4}] #这就是json格式数据#将json格式数据,输入后,查看logstash数据的输出结果[{"a": 1, "c": 3, "b": 2, "e": 5, "d": 4}]{"b" => 2,"a" => 1,"host" => "Logstash-Kibana","c" => 3,"e" => 5,"d" => 4,"@version" => "1","@timestamp" => 2018-08-20T13:27:58.991Z}
2.3 Logstash-Filter之Json,Kv插件
#Json示例input {stdin {}}filter {json {source => "message" #将保存在message中的json数据进行结构化解析target => "content" #解析后的结果保存在content里}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#Kv示例filter {kv {field_split => "&?" #将输入的数据按&字符进行切割解析}}
(1)filter => json {}将json的编码进行结构化解析过滤
#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动logstash服务[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#交互式输入json格式数据{"a": 1, "c": 3, "b": 2, "e": 5, "d": 4}{"@version" => "1","message" => "{"a": 1, "c": 3, "b": 2, "e": 5, "d": 4}", #数据都保存在了message字段里"@timestamp" => 2018-08-20T14:08:54.275Z,"host" => "Logstash-Kibana"}#再次修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {json {source => "message"target => "content"}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动logstash服务[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#交互式输入以下内容进行解析{"a": 1, "c": 3, "b": 2, "e": 5, "d": 4}{"content" => { #json被结构化解析出来了"a" => 1,"e" => 5,"d" => 4,"c" => 3,"b" => 2},"@version" => "1","message" => "{"a": 1, "c": 3, "b": 2, "e": 5, "d": 4}","@timestamp" => 2018-08-20T14:05:39.915Z,"host" => "Logstash-Kibana"}
(2)filter => kv {}将输入的数据按照制定符号切割
#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {kv {field_split => "&?"}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#交互式输入以下数据,然后查看解析结果name=123&yunjisuan=benet&yun=166{"host" => "Logstash-Kibana","yunjisuan" => "benet","yun" => "166","@version" => "1","message" => "name=123&yunjisuan=benet&yun=166","@timestamp" => 2018-08-20T14:16:38.227Z,"name" => "123"}
2.4 Logstash-Filter之Grok插件
2.4.1 grok自定义正则的数据抓取模式
#日志输入示例:223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200#grok自定义正则的数据抓取示例input {stdin {}}filter {grok {match => {"message" => '(?<client>[0-9.]+)[ ]+(?<method>[A-Z]+)[ ]+(?<request>[a-zA-Z/.]+)[ ]+(?<bytes>[0-9]+)[ ]+(?<num>[0-9]+)'}}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#操作演示#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {grok {match => {"message" => '(?<client>[0-9.]+)[ ]+(?<method>[A-Z]+)[ ]+(?<request>[a-zA-Z/.]+)[ ]+(?<bytes>[0-9]+)[ ]+(?<num>[0-9]+)'}}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#输入日志进行数据抓取测试223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200{"message" => "223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200","bytes" => "15824","num" => "200","@version" => "1","method" => "GET","client" => "223.72.85.86","request" => "/index.html","host" => "Logstash-Kibana","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T13:50:27.029Z}
2.4.2 grok内置正则的数据抓取模式
为了方便用户抓取数据方便,官方自定义了一些内置正则的默认抓取方式
Grok默认的内置正则模式,官方网页示例
https://github.com/logstash-plugins/logstash-patterns-core/blob/master/patterns/grok-patterns
#logstash默认挂载的常用的内置正则库文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# rpm -ql logstash | grep grok-patterns/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/logstash-patterns-core-4.1.2/patterns/grok-patterns[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/logstash-patterns-core-4.1.2/patterns/grok-patterns...由于显示内容过多,此处省略无数行,请自行打开查看...#操作演示#日志输入示例:223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {grok {match => {"message" => "%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:num}"}}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#输入日志示例内容后,如下223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200{"client" => "223.72.85.86","method" => "GET","bytes" => "15824","host" => "Logstash-Kibana","num" => "200","message" => "223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200","@version" => "1","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T14:19:04.960Z,"request" => "/index.html"}
2.4.3 grok自定义内置正则的数据抓取模式
示例:将2.4.1的自定义正则转换成自定义的内置正则
#日志输入示例(新增一个数据):223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {grok {patterns_dir => "/opt/patterns" #自定义的内置正则抓取模板路径match => {"message" => '%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:num} "%{STRING:content}"'}}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#创建自定义内置正则的挂载模板文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /opt/patterns[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /opt/patternsSTRING .*#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#输入日志示例,查看数据抓取结果223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"{"method" => "GET","@version" => "1","bytes" => "15824","client" => "223.72.85.86","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T14:38:04.361Z,"host" => "Logstash-Kibana","request" => "/index.html","num" => "200","content" => "welcome to yunjisuan","message" => "223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan""}
2.4.4 grok多模式匹配的数据抓取
有的时候,我们可能需要抓取多种日志格式的数据
因此,我们需要配置grok的多模式匹配的数据抓取
#日志输入示例:223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 《Mr.chen-2018-8-21》#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {grok {patterns_dir => "/opt/patterns"match => [ #请注意多模式和单模式匹配的区别"message",'%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:num} "%{STRING:content}"',"message",'%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:num} 《%{NAME:name}》']}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#增加一个自定义的内置正则抓取变量[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /opt/patterns[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /opt/patternsSTRING .*NAME .*#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#输入日志示例,查看数据抓取结果223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"{"@version" => "1","client" => "223.72.85.86","request" => "/index.html","num" => "200","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T14:47:26.971Z,"content" => "welcome to yunjisuan","host" => "Logstash-Kibana","bytes" => "15824","message" => "223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"","method" => "GET"}223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 《Mr.chen-2018-8-21》{"@version" => "1","client" => "223.72.85.86","request" => "/index.html","num" => "200","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T14:47:40.430Z,"host" => "Logstash-Kibana","bytes" => "15824","name" => "Mr.chen-2018-8-21","message" => "223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 《Mr.chen-2018-8-21》","method" => "GET"}
2.5 Logstash-Filter之geoip插件
geoip插件可以对IP的来源进行分析,并通过Kibana的地图功能形象的显示出来。
#日志输入示例:223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"119.147.146.189 GET /index.html 15824 200 《Mr.chen-2018-8-21》#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {stdin {}}filter {grok {patterns_dir => "/opt/patterns"match => ["message",'%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:num} "%{STRING:content}"',"message",'%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:num} 《%{NAME:name}》']}geoip {source => "client"database => "/opt/GeoLite2-City.mmdb"}}output {stdout {codec => rubydebug}}#下载geoip插件包[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# wget http://geolite.maxmind.com/download/geoip/database/GeoLite2-City.tar.gz#解压安装geoip插件包[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# tar xf GeoLite2-City.tar.gz[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg GeoLite2-City_20180807 GeoLite2-City.tar.gz[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cp GeoLite2-City_20180807/GeoLite2-City.mmdb /opt/#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana opt]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf#输入日志示例模板,查看数据抓取结果223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"{"geoip" => {"country_code3" => "CN", #IP所在国家"city_name" => "Beijing", #IP所在城市"longitude" => 116.3889,"region_code" => "BJ","country_code2" => "CN","location" => {"lon" => 116.3889, #IP所在地图经度"lat" => 39.9288 #IP所在地图纬度},"timezone" => "Asia/Shanghai","latitude" => 39.9288,"region_name" => "Beijing","continent_code" => "AS","ip" => "223.72.85.86","country_name" => "China"},"message" => "223.72.85.86 GET /index.html 15824 200 "welcome to yunjisuan"","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T15:45:06.179Z,"content" => "welcome to yunjisuan","client" => "223.72.85.86","@version" => "1","host" => "Logstash-Kibana","method" => "GET","bytes" => "15824","num" => "200","request" => "/index.html"}119.147.146.189 GET /index.html 15824 200 《Mr.chen-2018-8-21》{"geoip" => {"country_code3" => "CN","longitude" => 113.25,"region_code" => "GD","country_code2" => "CN","location" => {"lon" => 113.25,"lat" => 23.1167},"timezone" => "Asia/Shanghai","latitude" => 23.1167,"region_name" => "Guangdong","continent_code" => "AS","ip" => "119.147.146.189","country_name" => "China"},"message" => "119.147.146.189 GET /index.html 15824 200 《Mr.chen-2018-8-21》","name" => "Mr.chen-2018-8-21","@timestamp" => 2018-08-21T15:45:55.386Z,"client" => "119.147.146.189","@version" => "1","host" => "Logstash-Kibana","method" => "GET","bytes" => "15824","num" => "200","request" => "/index.html"}
2.6 Logstash-输出(Output)插件
#ES示例output {elasticsearch {hosts => "localhost:9200" #将数据写入elasticsearchindex => "logstash-mr_chen-admin-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" #索引为xxx}}
三,企业级Kibana使用详解
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| ES1 | 192.168.200.191 | elasticsearch-node1 |
| ES2 | 192.168.200.192 | elasticsearch-node2 |
| ES3 | 192.168.200.193 | elasticsearch-node3 |
| Logstash-Kibana | 192.168.200.194 | 日志可视化服务器 |
3.1 ELK Stack配置应用案例
#利用yum源安装kibana[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# ll /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 215 8月 19 22:07 /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# yum -y install kibana#修改logstash配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.confinput {file {path => ["/var/log/messages"]type => "system" #对数据添加类型tags => ["syslog","test"] #对数据添加标识start_position => "beginning"}file {path => ["/var/log/audit/audit.log"]type => "system" #对数据添加类型tags => ["auth","test"] #对数据添加标识start_position => "beginning"}}filter {}output {if [type] == "system" {if [tags][0] == "syslog" { #通过判断可以将不同日志写到不同的索引里elasticsearch {hosts => ["http://192.168.200.191:9200","http://192.168.200.192:9200","http://192.168.200.193:9200"]index => "logstash-mr_chen-syslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"}stdout { codec => rubydebug }}else if [tags][0] == "auth" {elasticsearch {hosts => ["http://192.168.200.191:9200","http://192.168.200.192:9200","http://192.168.200.193:9200"]index => "logstash-mr_chen-auth-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"}stdout { codec => rubydebug }}}}#修改kibana的配置文件[root@Logstash-Kibana kibana]# cat -n kibana.yml.bak | sed -n '7p;28p'7 #server.host: "localhost"28 #elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"[root@Logstash-Kibana kibana]# cat -n kibana.yml | sed -n '7p;28p'7 server.host: "0.0.0.0"28 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.200.191:9200" #就写一个ES主节点即可#启动kibana进程[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# systemctl start kibana#启动logstash[root@Logstash-Kibana ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/test.conf
特别提示:
如果elasticsearch里没有任何索引,那么kibana是都取不到的
所以启动logstash先elasticsearch里写点数据就好了
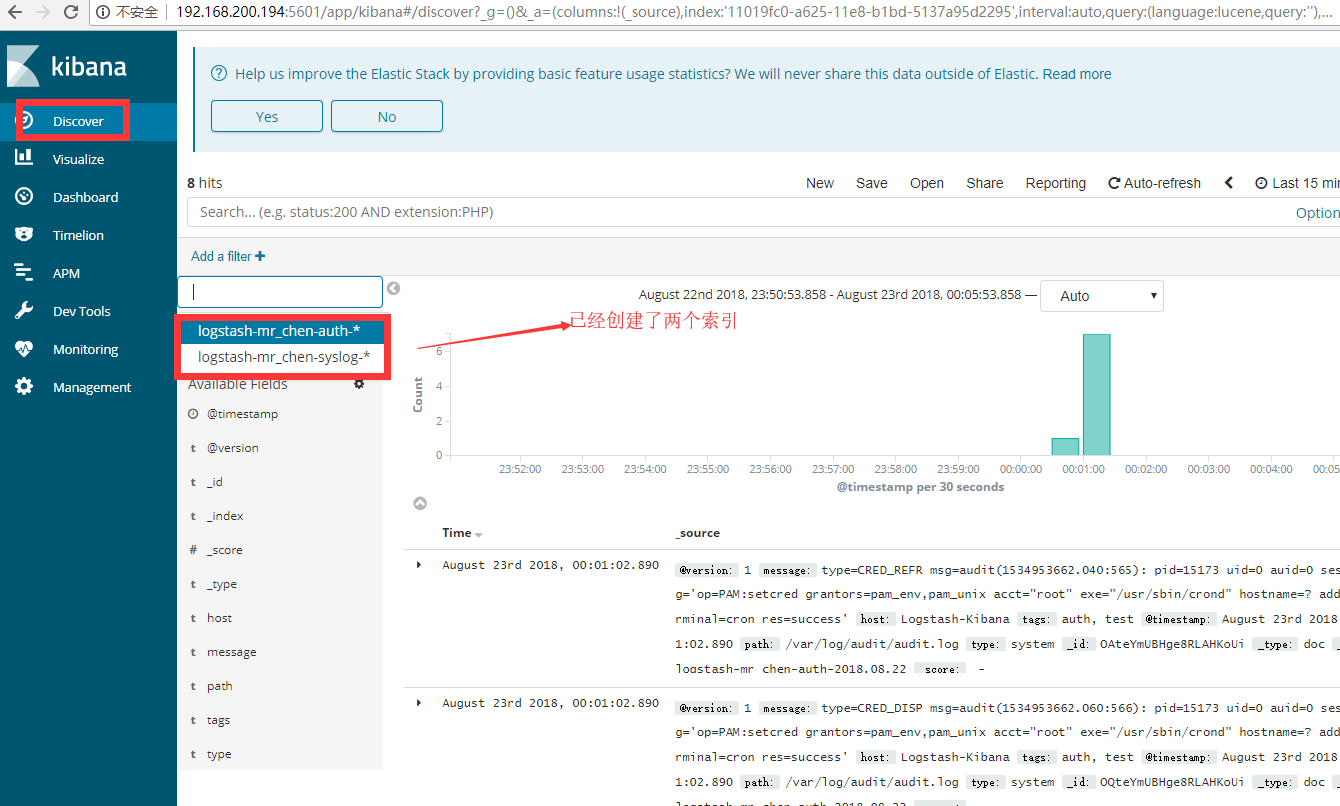
通过浏览器访问kibana

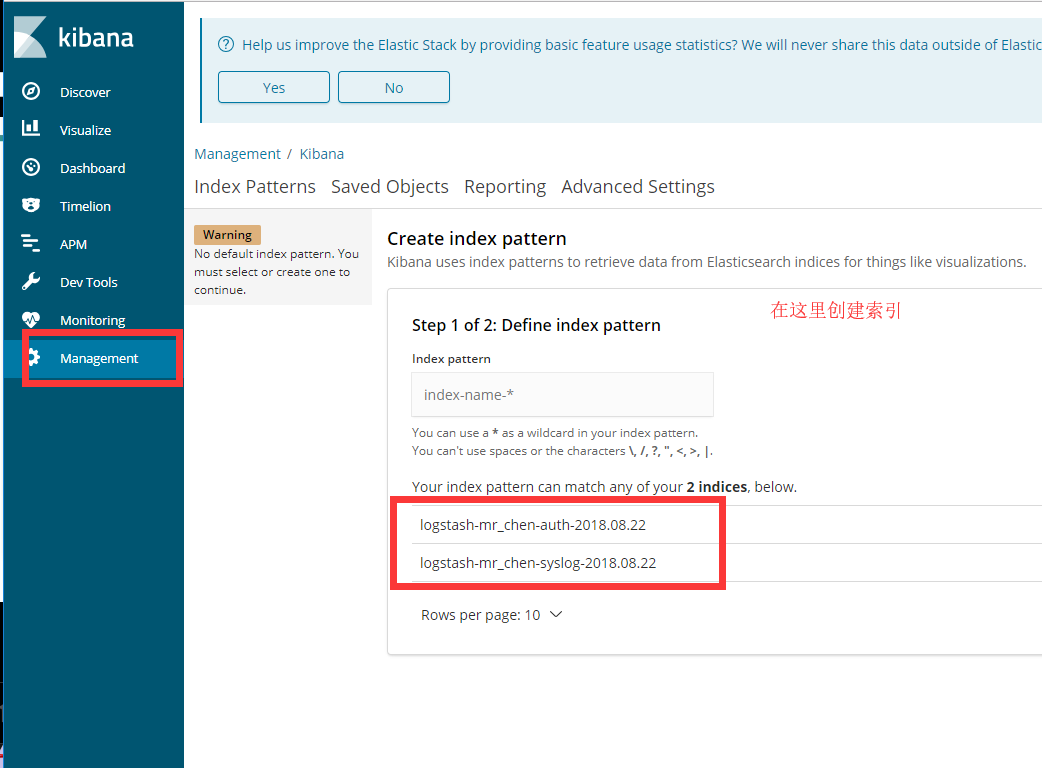
我们创建两个索引后,如下图所示
3.2 Kibana常用查询表达式
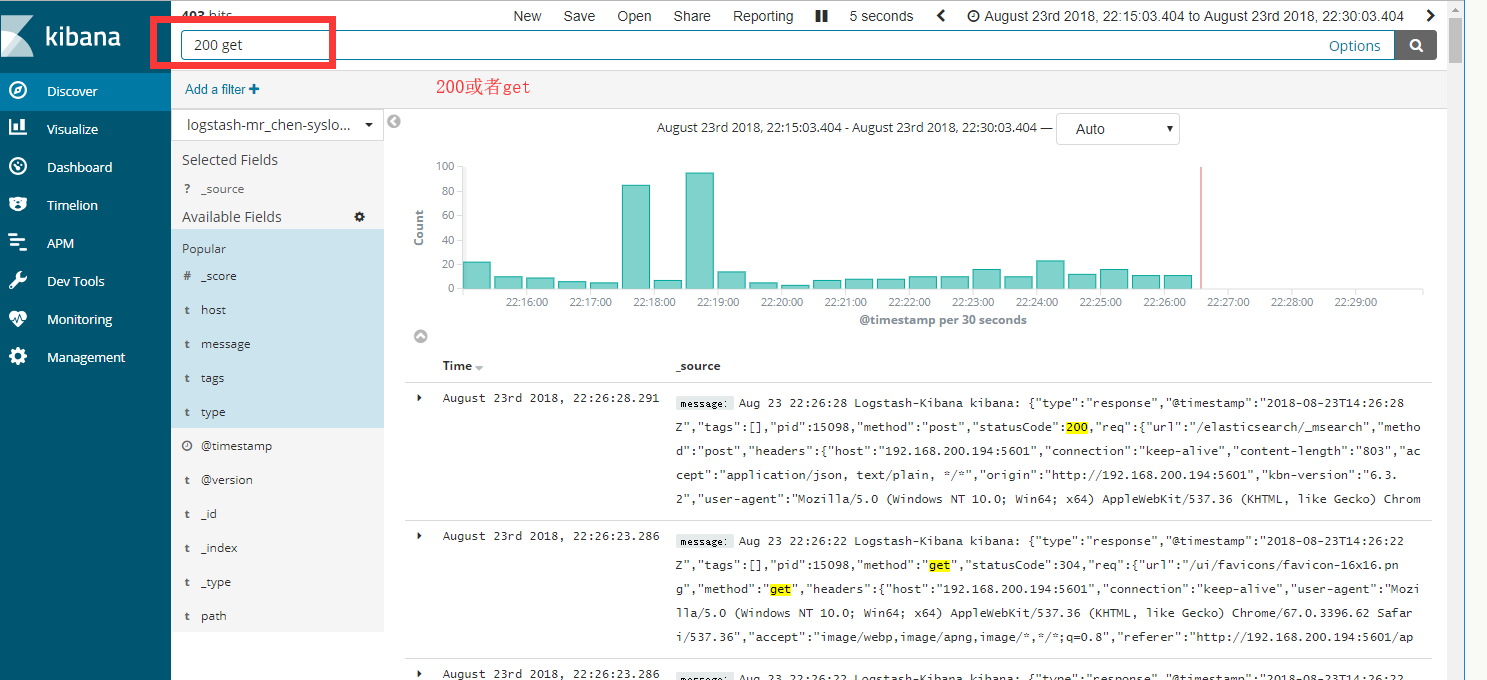
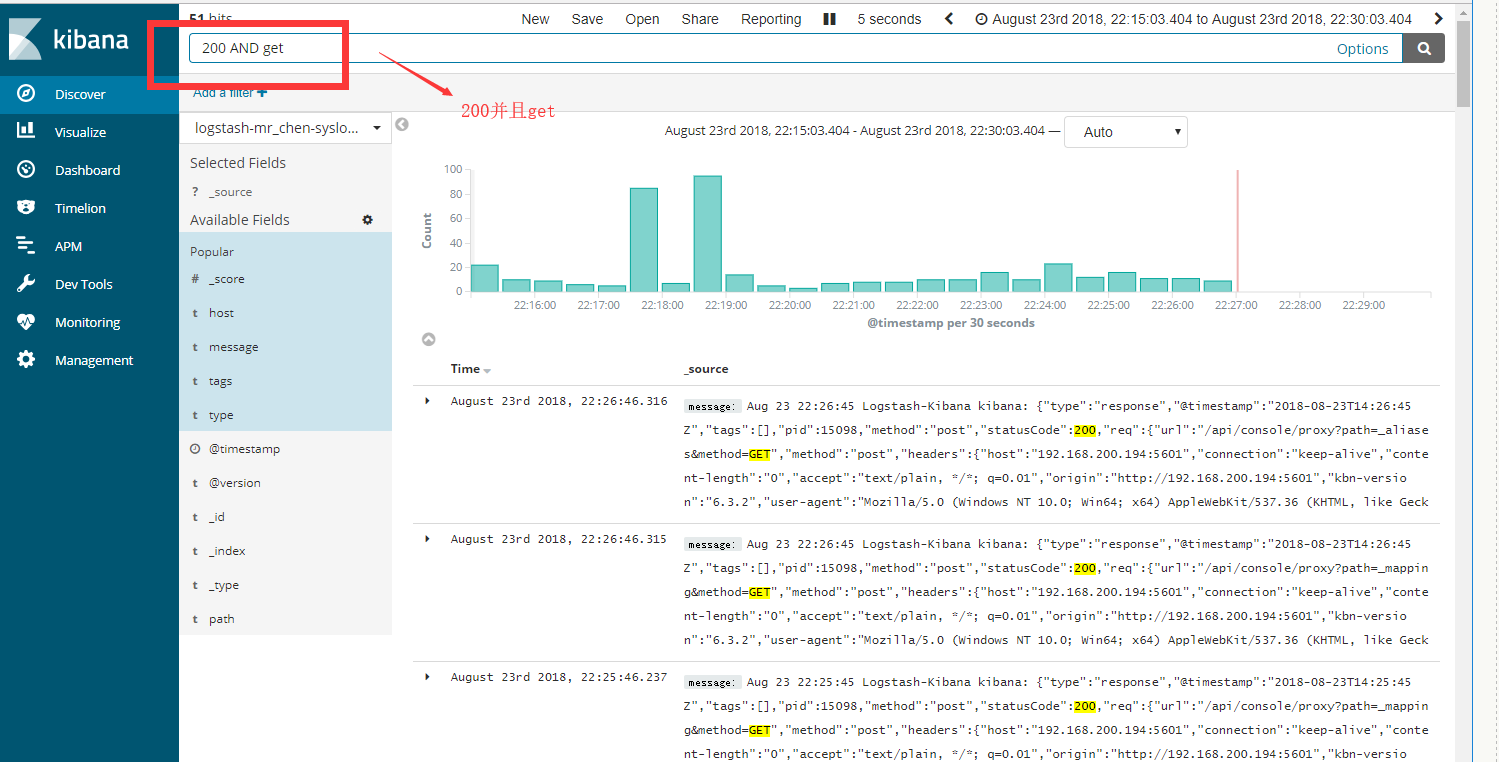
直接演示简单讲解kibana的数据检索功能
3.3 基于Nginx实现Kibana访问认证
操作方法同ELK(上),此处略过