一、异常
1.1、异常定义
异常:--不正常,程序在运行时出现不正常情况
异常由来:其实也是现实生活中一个具体的事物,马可以通过JAVA的类的形式表现描述,并封装成类。
Java对不正常情况描述后的,对象体现。
异常:两种.
一种是严重的问题:java通过Error类进行描述
对于Error一般不编写针对必的代码对其进行处理
对与非严重的:java通过Exception类进行描述
对于Exception可以使用针对必的处理方式进行处理。
示例:
package com.day10.demo1; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(div(5,0)); System.out.println("over"); } public static int div(int a,int b){ return a/b; } }
结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.day10.demo1.Demo1.div(Demo1.java:14)
at com.day10.demo1.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:7)
算术异常,因为除数为0,所以,有异常了
1.2、异常体系结构
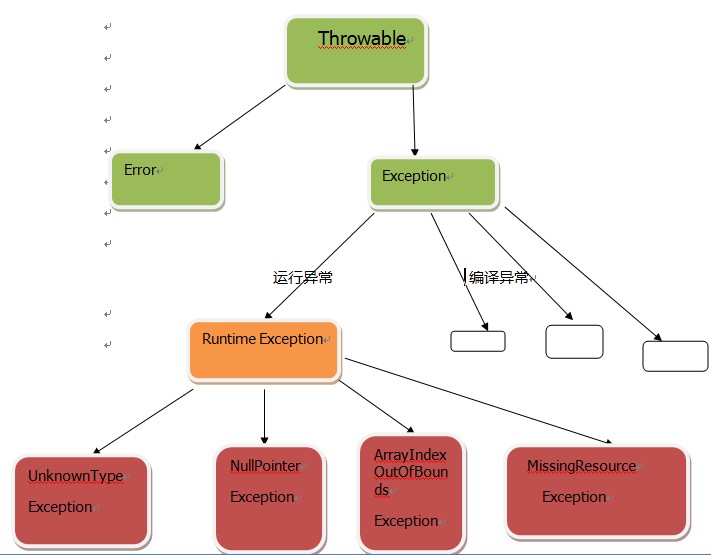
Java 提供了两类主要的异常:runtime exception 和checked exception。所有的checked exception 是从java.lang.Exception 类衍生出来的,而
runtime exception 则是从java.lang.RuntimeException 或java.lang.Error类衍生出来的。
它们的不同之处表现在两方面:机制上和逻辑上
runtime exceptions:
- 在定义方法时不需要声明会抛出runtime exception
- 在调用这个方法时不需要捕获这个runtime exception
- runtime exception 是从java.lang.RuntimeException 或
- java.lang.Error 类衍生出来的。
checked exceptions:
- 定义方法时必须声明所有可能会抛出的checked exception
- 在调用这个方法时,必须捕获它的checked exception,不然就得
- 把它的exception 传递下去
- checked exception 是从java.lang.Exception 类衍生出来的
从逻辑的角度来说,checked exceptions 和runtime exception 是有不同的使用目的的。
checked exception 用来指示一种调用方能够直接处理的异常情况。checked exception 迫使你捕获它并处理这种异常情况。
而runtime exception 则用来指示一种调用方本身无法处理或恢复的程序错误。
1.3、异常使用语句
try{ // 有可能出现异常的语句 }catch(异常类 异常对象){ // 编写异常的处理语句 }[ catch(异常类 异常对象){ // 编写异常的处理语句 } catch(异常类 异常对象){ // 编写异常的处理语句 } …. ] [finally{ 一定会运行到的程序代码 ; }
主要搭配:try-catch、try-catch-finally、try-finally三种形式

1.4、使用try--catch
没有使用异常
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int x=5; int y=0; int index=div(x,y); System.out.println("执行完成"); } public static int div(int a,int b){ return a/b; } }
结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
最后输出语句没有执行
使用try--catch
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int x=5; int y=0; try { int retsult=x/y; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("执行完成"); } }
结果:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.day10.exception.demo1.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:10)
执行完成
异常代码块后面的代码被执行了。
try-中的代码发生异常后,跳转到相就的 catch块中,捕获异常,完成后,执行异常块后面的代码
1.5、try-catch-finally
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int x=5; int y=0; try { int retsult=x/y; System.out.println("执行到我说明没有异常"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("发生异常了"); e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ System.out.println("我一定会被执行"); } System.out.println("执行完成"); } }
结果:
发生异常了
我一定会被执行
执行完成
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.day10.exception.demo1.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:10)
1.6、finally中的代码不执行
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int x=5; int y=0; try { int retsult=x/y; System.out.println("执行到我说明没有异常"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("发生异常了"); e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(0); //或者-1 }finally{ System.out.println("我一定会被执行"); } System.out.println("执行完成"); } }
发生异常了 java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at com.day10.exception.demo1.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:10)
1.7、如果有return 怎么执行
try中有return
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getException()); } public static int getException(){ try { int x=5; System.out.println("try return"); return x; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("catch return"); }finally{ System.out.println("finally return"); } return 0; } }
结果:
try return
finally return
5
try中的return并不会影响finally中的代码执行
catch中有return
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getException()); } public static int getException(){ int x=5; try { int result=x/0; System.out.println("try return"); return x; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("catch return"); return ++x; }finally{ System.out.println("finally return"); } } }
结果:
catch return
finally return
6
catch中的return也不会影响finally中的执行,但是返回结果会是catch中的return结果,会将try中的结果覆盖
finally中有return
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getException()); } public static int getException(){ int x=5; try { int result=x/0; System.out.println("try return"); return x; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("catch return"); return ++x; }finally{ System.out.println("finally return"); return ++x; } } }
结果:
catch return
finally return
7
finally中的return也不会影响finally中的执行,但是返回结果会是finally中的return结果,会将try和catch中的结果覆盖
1.8、多个catch块
exception异常 一定要放在最扣,不然下方的异常无法执行到,只会执行父类执行而子类的异常不会被捕获
package com.day10.exception.demo1; import java.util.InputMismatchException; import java.util.Scanner; /* * 求2个整数的商 当异常发生时,程序如何处理 */ public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 从键盘获得输入 try { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入被除数:"); int num1 = input.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入除数:"); int num2 = input.nextInt(); int result = num1 / num2; System.out.println(num1 + "与" + num2 + "的商: " + result); } catch (InputMismatchException e) { System.out.println("输入的不是数字"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("除数不能为0"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("其它错误!"); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("谢谢使用!"); } } }
结果1:
请输入被除数:
fsd
输入的不是数字
谢谢使用!
java.util.InputMismatchException
结果2
请输入被除数:
9
请输入除数:
0
除数不能为0
谢谢使用!
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
结果3:
请输入被除数:
7
请输入除数:
3
7与3的商: 2
谢谢使用!
1.9、自定义异常
自定义异常只需要继承Exception类就
定义异常类,只需要继承Exception类即可。
package com.day10.exception.demo1; /** * 自定义异常 * @author denny * */ public class MyException extends Exception { public MyException() { super(); } public MyException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public MyException(String message) { super(message); } public MyException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } }
上面为算定义异常,使用构造方法重载即可
1.10、throw和throws抛出异常
使用上面的算定义异常
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class Person { private String name; private int age; private String gender; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { if (age >= 0 && age <= 150) { this.age = age; } else { try { throw new MyException("年龄只能在0-150岁之间"); } catch (MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) throws MyException {// if(gender.equals("男")||gender.equals("女")){ this.gender = gender; }else{ throw new MyException("性别只能是男或者女!"); /* throw可以在方法体内抛出异常,但必须捕获或者 在方法体上用throws抛出 */ } } public void printSelf(){ System.out.println("姓名:"+this.name+" 性别:"+this.gender+" 年龄:"+this.age); } }
测试类
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p=new Person(); try { p.setName("张三"); p.setAge(200); p.setGender("人妖"); } catch (MyException e) { e.getMessage();//获取异常信息 }finally{ } } }
结果:com.day10.exception.demo1.MyException: 年龄只能在0-150岁之间
因为在执行age赋值时,已经发生异常,所以下面的性别赋没有执行
package com.day10.exception.demo1; public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p=new Person(); try { p.setName("张三"); p.setAge(20); p.setGender("人妖"); p.printSelf(); } catch (MyException e) { //System.out.println(e.getMessage());//获取异常信息 e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ } } }
结果:
com.day10.exception.demo1.MyException: 性别只能是男或者女!
二、包
2.1、包的含义
对文件进行分类管理,类似于windows中的文件夹,同一包同一层
给类提供多层命名空间,同一个文件夹文件名不相同,层次关系,
写在程序文件的第一行
类名的全称是包名.类名.
包也是一种封装形式
2.2、包的定义
package 包名,
包名必须小写,可以使用.小数点来定义多层次包
必须放在代码的第一行
javac -d . java文件名.java .代表当前文件夹目录
包的出现可以把java的class文件和源文件相分离,只需要将 class文件复制出来运行就可以
定义包名不要重复
2.3、包的导入
import 包名.类名
2.4、包与包之间的访问权限
