一:
仔细阅读示例: EnumTest.java,运行它,分析运行结果?
运行结果

你能得到什么结论?你掌握了枚举类型的基本用法了吗?
枚举不属于原始数据类型,枚举类型是引用类型它的每个具体值都引用一个特定的对象。相同的值则引用同一个对象。
二:
请运行以下代码

运行结果如下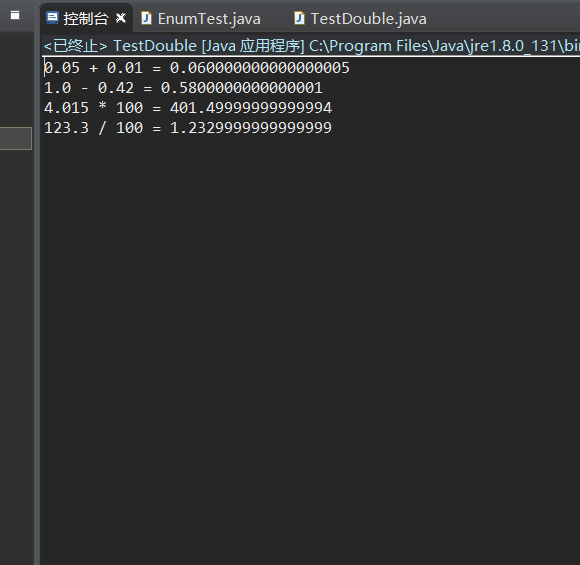
这个结果很意外,原因是java的浮点度
符号位S_指数位E_尾数位M
例如,一个float类型的数据占用4个字节共32位,其各个组成部分为:
- (1)符号位(S):最高位(31位)为符号位,表示整个浮点数的正负,0为正,1为负
- (2)指数位(E):23-30位共8位为指数位,这里指数的底数规定为2。并且指数位是以补码的形式来划分的(最高位为指数位的符号位,0为正,1为负)。另外,标准中还规定了,当指数位8位全0或全1的时候,浮点数为非正规形式,所以指数位真正范围为:-126~127。
- (3)尾数位(M):0-22位共23位为尾数位,表示小数部分的尾数,即形式为1.M或0.M,至于什么时候是 1 什么时候是 0,则由指数和尾数共同决定。小数部分最高有效位是1的数被称为正规(规格化)形式。小数部分最高有效位是0的数被称为非正规(非规格化)形式,其他情况是特殊值。
三:
以下代码的输出结果是什么?
int X=100;
int Y=200;
System.out.println("X+Y="+X+Y);
System.out.println(X+Y+"=X+Y");

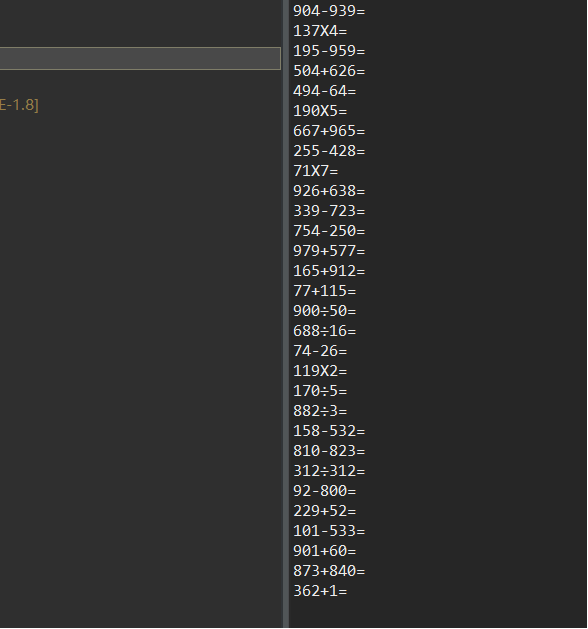
四:编写一个程序,写一个能自动生成30道小学四则运算题目的 “软件”。
代码如下
package szys;
public class Abcd {
private String[] zStrings=new String[]{"+","-","X","÷"};
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Abcd abcd=new Abcd();
for(int i=0;i<30;i++)
{
System.out.println(abcd.timu());
}
}
public String timu()
{
String dString=null;
int a=0,b=0,c=0;
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
c=(int)(Math.random()*4);
if(c==0||c==1)
{
dString=a+zStrings[c]+b+"=";
}
else if(c==2)
{
while(a*b>1000||a==1||b==1||a==0||b==0)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
}
dString=a+zStrings[c]+b+"=";
}
else if(c==3)
{
while(a==0||b==0)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
}
while(a%b!=0||b==1)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
while(a==0||b==0)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
}
}
dString=a+zStrings[c]+b+"=";
}
return dString;
}
}
private String[] zStrings=new String[]{"+","-","X","÷"};
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Abcd abcd=new Abcd();
for(int i=0;i<30;i++)
{
System.out.println(abcd.timu());
}
}
public String timu()
{
String dString=null;
int a=0,b=0,c=0;
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
c=(int)(Math.random()*4);
if(c==0||c==1)
{
dString=a+zStrings[c]+b+"=";
}
else if(c==2)
{
while(a*b>1000||a==1||b==1||a==0||b==0)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
}
dString=a+zStrings[c]+b+"=";
}
else if(c==3)
{
while(a==0||b==0)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
}
while(a%b!=0||b==1)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
while(a==0||b==0)
{
a=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
b=(int)(Math.random()*(1000+1));
}
}
dString=a+zStrings[c]+b+"=";
}
return dString;
}
}
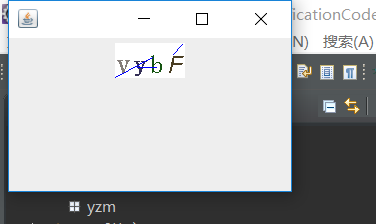
生成验证码程序
package yzm1;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
/**
* @author : Administrator
* @function : 这是用来测试随机生成验证码图片的类;
*/
public class VerificationCode {
/**
* 单元测试,试一下能不能自动生成验证码图片
*/
public static void main(String arg[])
{
JFrame mainf=new JFrame();
JPanel jp=new JPanel();
Container con=mainf.getContentPane();
VerificationCode verificationCode=new VerificationCode();
JLabel jLabel=new JLabel();
jLabel.setIcon(new ImageIcon((Image)verificationCode.getImage()));
jp.add(jLabel);
con.add(jp);
mainf.setSize(300, 200);
mainf.setVisible(true);
}
public void test_fun() {
VerificationCode vc = new VerificationCode();
BufferedImage image = vc.getImage();
try {
// 生成验证码图片,并保存到指定的路径
VerificationCode.output(image, new FileOutputStream(new File(
".\image\vcode_2.jpg")));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 将随机生成的文本内容输出到控制台,用于校验
System.out.println(vc.getText());
}
private int w = 70;// 宽
private int h = 35;// 高
private String text;// 文本内容(验证码字符串)
private Random r = new Random();
private String[] fontNames = { "宋体", "华文楷体", "黑体", "微软雅黑", "楷体_GB2312" };
// 随机字符集合中不包括0和o,O,1和l,因为这些不易区分
private String codes = "23456789abcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYXZ";
// 验证码图片的背景色:白色
private Color bgColor = new Color(255, 255, 255);
/**
* 返回一个验证码图片buffer对象:BufferedImage
*/
public BufferedImage getImage() {
BufferedImage image = createImage();
// 获取绘图环境(画笔工具)
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) image.getGraphics();
// sb : 用来保存验证码字符串文本内容
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {// 随机生成4个字符
String s = randomChar() + "";
sb.append(s);
float x = i * 1.0F * w / 4;
g2.setFont(randomFont());
g2.setColor(randomColor());
g2.drawString(s, x, h - 5);
}
this.text = sb.toString();// 记录验证码文本内容
drawLine(image);// 画干扰线
return image;
}
/**
* @return 获取验证码文本内容
*/
public String getText() {
return text;
}
/**
* @param image
* @param out
* 将文本写到指定的输出流。比如本测试中FileOutputStream指定的保存路径
*/
public static void output(BufferedImage image, OutputStream out) {
try {
ImageIO.write(image, "jpeg", out);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void drawLine(BufferedImage image) {
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) image.getGraphics();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {// 画3条干扰线
int x1 = r.nextInt(w);
int y1 = r.nextInt(h);
int x2 = r.nextInt(w);
int y2 = r.nextInt(h);
g2.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g2.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
}
private Color randomColor() {
int red = r.nextInt(150);
int green = r.nextInt(150);
int blue = r.nextInt(150);
return new Color(red, green, blue);
}
private Font randomFont() {
int index = r.nextInt(fontNames.length);
String fontName = fontNames[index];
int style = r.nextInt(4);
int size = r.nextInt(5) + 24;
return new Font(fontName, style, size);
}
private char randomChar() {
int index = r.nextInt(codes.length());
return codes.charAt(index);
}
private BufferedImage createImage() {
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(w, h,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) image.getGraphics();
g2.setColor(this.bgColor);
g2.fillRect(0, 0, w, h);
return image;
}

}