在多线程领域:所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会挂起线程(即阻塞),一旦条件满足,被挂起的线程又会自动被唤醒
为什么需要BlockingQueue
好处是我们不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为这一切BlockingQueue都给你一手操办了,在concurrent包发布以前,在多线程环境下,我们每个程序员都必须去自己控制这些细节,尤其话要兼顾效率和线程安全,而这会给我们程序带来不小的复杂度。
Collection→Queue→BlockingQueue ,这几个都是接口,BlockingQueue的实现类有以下几种:
1.ArrayBlockingQueue:由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
2.LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值为Integer.MAX_VALUE)阻塞队列。
3.PriorityBlockinigQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
4.DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列。
5.SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列。
6.LinkedTransferQueue: 由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
7.LinkedBlockingDeque:由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列。
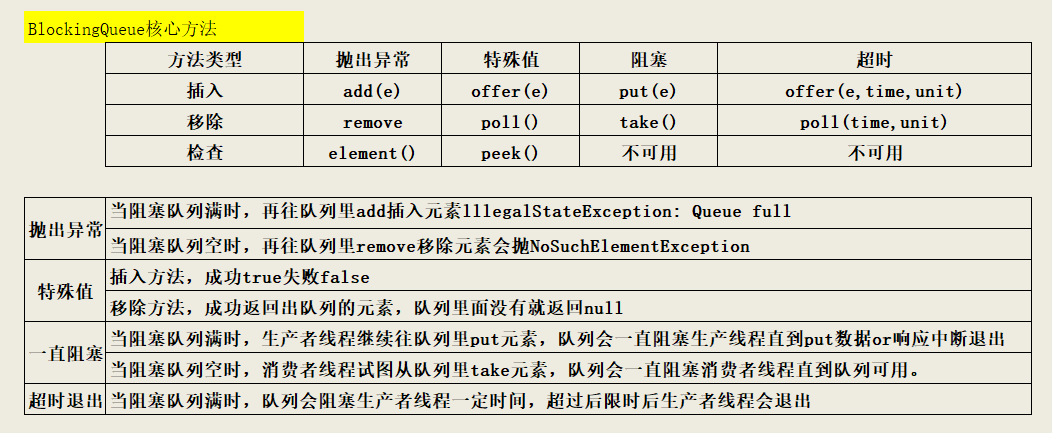
抛出异常例子:
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
//System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d")); 定义最多只能添加3个,不然会抛IllegalStateException异常
System.out.println(blockingQueue.element()); //默认返回第一个添加的元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
//System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 阻塞队列里面为空再remove抛NoSuchElementException
}
}
运行结果见下图:
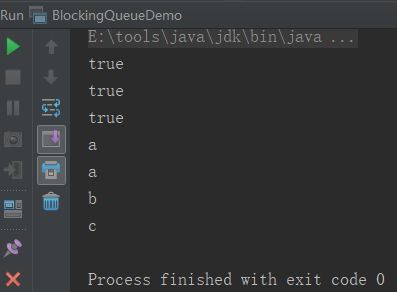
特殊值例子:
public class BlockingQueueDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
}
}
运行结果见下图:
阻塞例子:
public class BlockingQueueDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3);
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
// blockingQueue.put("d"); 会一直阻塞
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take(); //多了一个也会一直阻塞
}
}
运行结果见下图:
超时例子:
public class BlockingQueueDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
}
运行结果见下图:

SynchronousQueue没有容量,与其他BlockingQueue不同,SynchronousQueue是一个不存储元素的BlockingQueue
每一个put操作必须要等待一个take操作,否则不能继续添加元素,反之亦然。
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
//t1线程负责生产
new Thread(() ->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t1").start();
//t2线程负责消费,每隔5秒消费1次
new Thread(() ->{
try {
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+blockingQueue.take());
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+blockingQueue.take());
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t2").start();
}
}
运行结果见下图:
