

nodejs.org
https://www.npmjs.com/
https://github.com/
https://stackoverflow.com/
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/001434446689867b27157e896e74d51a89c25cc8b43bdb3000
Sublime Text 3
webstorm
http://nodejs.cn/api/
http://www.runoob.com/angularjs/angularjs-tutorial.html
1.安装 Node.js 0.10.3x为例

win:略
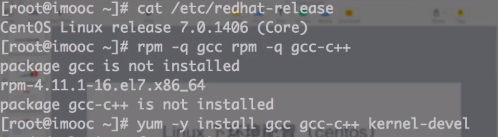
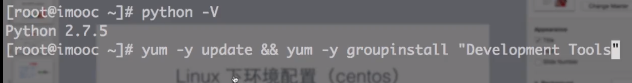
linux(源码编译安装):







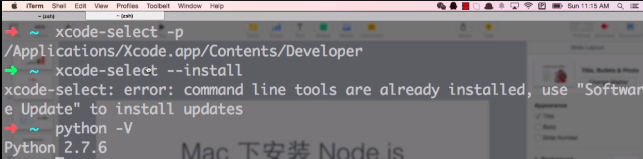
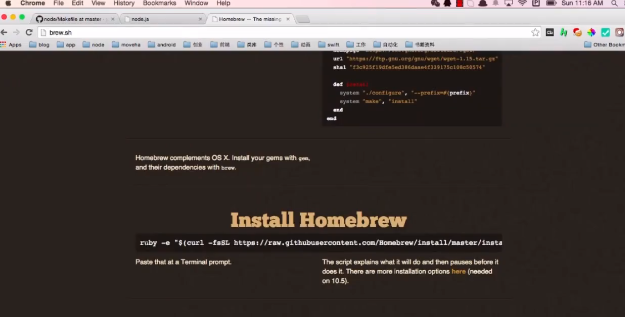
mac:



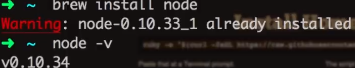
更新:
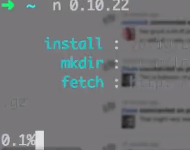

上下键切换
nodejs的模块与commonsj规范
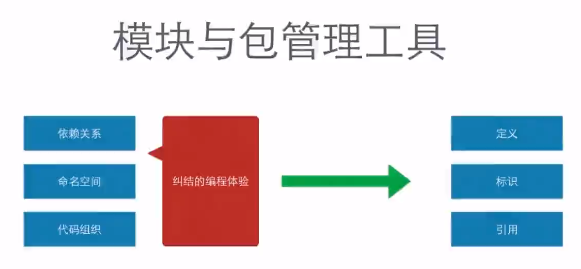

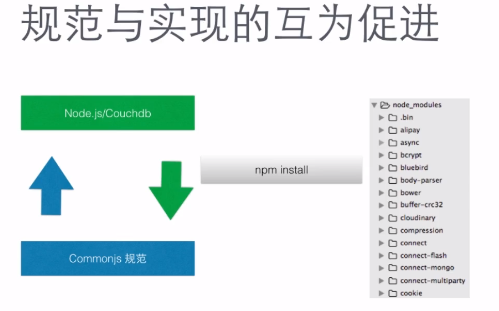






https://nodejs.org/docs/latest-v0.10.x/api/
http
http://fex.baidu.com/blog/2014/05/what-happen/
chrome://net-internals/#dns





以下转自: http://www.cnblogs.com/haoyijing/p/6478742.html
nodejs学习(imooc课程笔记, 主讲人Scott)
课程地址:
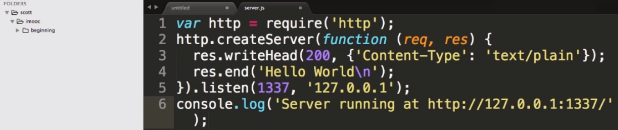
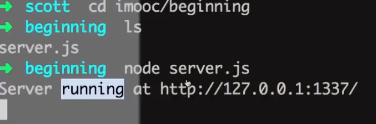
1. nodejs创建服务器
var http = require('http'); //加载http模块
//请求进来时, 告诉服务器做什么, 于是给createServer传递一个匿名回调函数.
//两个参数, 前面是请求体, 后面是响应体. 请求体用来获取请求相应信息,比如请求ip地址,请求的类型get/post,res用来返回响应
http.createServer(function(req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/palin'});
res.end('Hello World
');
}).listen(1337, '127.0.0.1'); //通过listen使服务器在1337端口监听请求
console.log('Server running at https://127.0.0.1:1337/');
2. nodejs安装:
一开始直接使用sudo apt-get install node后, 安装好的node不能启动且node -v也没有输出. node.js的版本号是v0.10.25.但是用npm安装一些包时候却说node版本不够, 没搞明白node和nodejs区别在哪里.
于是卸载掉从nodejs.org上下了新版, 是node v6.10.0. 解压后, 直接在那个目录下可以启动node, 在网上查了使用了一个链接, 分别把node 和 npm设置了全局:
sudo ln -s /media/hao/3b6b3418-c087-4836-a75d-6d7a6023e495/Programs/node-v6.10.0-linux-x64/bin/node /usr/sbin/node sudo ln -s /media/hao/3b6b3418-c087-4836-a75d-6d7a6023e495/Programs/node-v6.10.0-linux-x64/bin/npm /usr/sbin/npm
可以用了.
关于nodejs和node版本的区别,参考这个帖子吧: nodejs各版本的区别
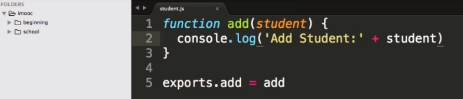
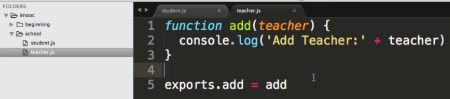
3. 模块: 从这里开始都是慕课网老师Scott进击NodeJS基础(一)(二)课程的笔记
- 创建模块
teacher.js
- 导出模块
exports.add = function(){ } - 加载模块
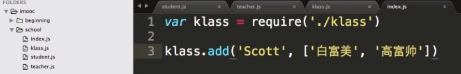
var teacher = require('./teacher.js') - 使用模块
teacher.add('Scott')
4. nodejs中一些api
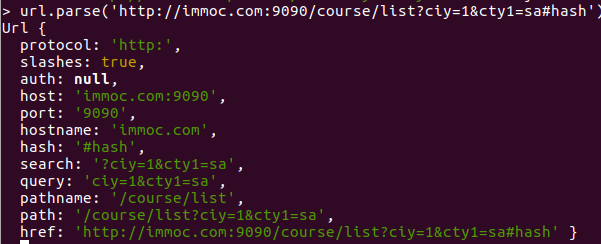
- url:
- url.parse
- url.format:
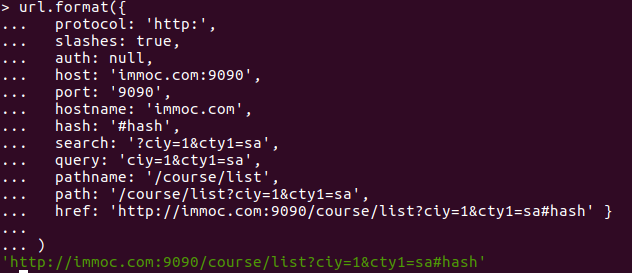
-
url.resolve

- url.parse
-
querystring

var http = require('http')
var cheerio = require('cheerio') //npm install cheerio
var url = 'http://www.imooc.com/learn/348'
function filterChapters(html){
var $ = cheerio.load(html)
var chapters = $('.chapter')
// [{
// chapterTitle: '',
// videos: [
// title:'',
// id: ''
// ]
// }]
var courseData = []
chapters.each(function(item){
var chapter = $(this)
var chapterTitle = chapter.find('strong').text().trim('
').split('
')[0]
var videos = chapter.find('.video').children('li')
var chapterData = {
chapterTitle: chapterTitle,
videos: []
}
videos.each(function(item){
var video = $(this).find(".J-media-item")
var videoTitle = video.text().split(/s+/).slice(1,-2).join(' ')
var id = video.attr('href').split('video/')[1]
chapterData.videos.push({
title: videoTitle,
id: id
})
})
courseData.push(chapterData)
})
return courseData
}
function printCourseInfo(courseData){
courseData.forEach(function(item){
var chapterTitle = item.chapterTitle
console.log(chapterTitle + '
')
item.videos.forEach(function(video){
console.log(' [' + video.id + ']' + video.title + '
')
})
})
}
http.get(url, function(res) {
var html = ''
res.on('data', function(data){
html += data
})
res.on('end', function(){
var courseData = filterChapters(html)
printCourseInfo(courseData)
})
}).on('error', function(){
console.log('获取课程数据错误')
})
6. 事件监听的一个小例子
var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter
var life = new EventEmitter()
//addEventListener
life.setMaxListeners(6) //设置事件最大监听数 默认为10. 超出这个数目会报警告
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' 倒水')
})
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' ...1')
})
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' ...2')
})
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' ...3')
})
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' ...4')
})
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' ...5')
})
life.on('求安慰', function(who){
console.log('给 ' + who + ' ...6')
})
var hasBeenListener = life.emit('求安慰', '杠子') //会返回值, 看是否被监听过
//要移除函数, 不能够使用匿名函数, 只能移除具名函数
console.log(life.listeners('求安慰').length) //查询监听事件数
console.log(EventEmitter.listenerCount(life, '求安慰'))
life.removeAllListeners('求安慰')
life.emit('求安慰','gangzi')
7. Promise.js imooc
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Promise animation</title>
<style type="text/css">
.ball{
40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 20px;
}
.ball1 { background: red;}
.ball2 { background: yellow;}
.ball3 { background: green;}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/home/hao/node_modules/bluebird/js/browser/bluebird.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ball ball1" style="margin-left: 0;"></div>
<div class="ball ball2" style="margin-left: 0;"></div>
<div class="ball ball3" style="margin-left: 0;"></div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1')
var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2')
var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3')
function animate(ball, distance, cb){
setTimeout(function(){
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10)
if(marginLeft === distance){
cb && cb()
}
else {
if(marginLeft < distance){
marginLeft++
} else {
marginLeft--
}
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px'
animate(ball,distance,cb)
}
},13);
}
// animate(ball1, 100, function(){
// animate(ball2, 200, function() {
// animate(ball3, 300, function(){
// animate(ball3, 150, function(){
// animate(ball2, 150, function(){
// animate(ball1, 150, function(){
// })
// })
// })
// })
// })
// })
var Promise = window.Promise
function promiseAnimate(ball, distance){
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
function _animate(){
setTimeout(function(){
var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10)
if(marginLeft === distance){
resolve()
}
else {
if(marginLeft < distance){
marginLeft++
} else {
marginLeft--
}
ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px'
_animate()
}
},13);
}
_animate()
})
}
promiseAnimate(ball1, 100)
.then(function() {
return promiseAnimate(ball2,200)
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball3,300)
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball3,150)
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball2,150)
}).then(function(){
return promiseAnimate(ball1,150)
})
</script>
</html>

- Promise就是对象,有三种状态: 未完成(pending), 已完成(fulfilled), 失败(rejected). 过程不可逆
- Promise A与A+不同点
- A+规范通过术语thenable来区分promise对象
- A+定义onFulfilled/onRejected必须是作为函数来调用, 而且调用过程必须是异步的
- A+严格定义了then方法链式调用时onFulfilled/onRejected的调用顺序
- 使用promise改进之前的爬虫代码:
var http = require('http') var Promise = require('bluebird') var cheerio = require('cheerio') //npm install cheerio var baseUrl = 'http://www.imooc.com/learn/' var url = 'http://www.imooc.com/learn/348' var videoIds = [728,637,197,348,259,75,134] function filterChapters(html){ var $ = cheerio.load(html) var chapters = $('.chapter') var title = $('h2.l').text() var number = $($('span.meta-value.js-learn-num')).text() // courseData = { // title: title, // number: number, // videos: [{ // chapterTitle: '', // videos: [ // title: '', // id: '' // ] // }] // } var courseData = { title: title, videos: [], number:number } chapters.each(function(item){ var chapter = $(this) var chapterTitle = chapter.find('strong').text().trim(' ').split(' ')[0] var videos = chapter.find('.video').children('li') var chapterData = { chapterTitle: chapterTitle, videos: [] } videos.each(function(item){ var video = $(this).find(".J-media-item") var videoTitle = video.text().split(/s+/).slice(1,-2).join(' ') var id = video.attr('href').split('video/')[1] chapterData.videos.push({ title: videoTitle, id: id }) }) courseData.videos.push(chapterData) }) return courseData } function printCourseInfo(coursesData){ coursesData.forEach(function(courseData){ // console.log(courseData.number + ' 人学过' + courseData.title + ' ') console.log('### ' + courseData.title + ' ') courseData.videos.forEach(function(item){ console.log(item.chapterTitle); item.videos.forEach(function(video){ console.log(' [' + video.id + ']' + video.title + ' ') }) }) }) // coursesData.forEach(function(item){ // }) } function getPageAsync(url){ return new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ console.log('正在爬取 ' + url) http.get(url, function(res) { var html = '' res.on('data', function(data){ html += data }) res.on('end', function(){ resolve(html) // var courseData = filterChapters(html) // printCourseInfo(courseData) }) }).on('error', function(e){ reject(e) console.log('获取课程数据错误') }) }) } var fetchCourseArray = [] videoIds.forEach(function(id){ fetchCourseArray.push(getPageAsync(baseUrl + id)) }) Promise .all(fetchCourseArray) .then(function(pages){ var coursesData = [] pages.forEach(function(html){ var courses = filterChapters(html) coursesData.push(courses) }) coursesData.sort(function(a,b){ return a.number < b.number }) printCourseInfo(coursesData) })
8. Buffer API
使用Buffer来读写图片的一个例子:
1 var fs = require('fs')
2
3 fs.readFile('logo.png', function(err, origin_buffer){
4 console.log(Buffer.isBuffer(origin_buffer))
5 fs.writeFile('logo_buffer.png', origin_buffer, function(err){
6 if(err) console.log(err)
7 })
8
9 // var base64Image = new Buffer(origin_buffer).toString('base64')
10 var base64Image = origin_buffer.toString('base64')
11
12 console.log(base64Image)
13
14 var decodedImage = new Buffer(base64Image, 'base64')
15
16 console.log(Buffer.compare(origin_buffer, decodedImage))
17
18 fs.writeFile('logo_decodes.png', decodedImage, function(err){
19 if(err) console.log(err)
20 })
21 })
9. Stream API
//拷贝文件
var fs = require('fs')
var source = fs.readFileSync('../buffer/logo.png')
fs.writeFileSync('stream_copy_logo.png', source)
//拷贝图片
var fs = require('fs')
var readStream = fs.createReadStream('stream_copy_logo.js')
var n = 0
readStream
.on('data', function(chunk) {
n++
console.log('data emits')
console.log(Buffer.isBuffer(chunk)) //true
// console.log(chunk.toString('utf8')) //要读的文件的内容
readStream.pause()
console.log('data pause')
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('data pause end')
readStream.resume()
}, 3000)
})
.on('readable', function(){
console.log('data readable')
})
.on('end', function() {
console.log(n)
console.log('data ends')
})
.on('close', function() {
console.log('data close')
})
.on('error', function(e){
console.log('data read error' + e)
})
//拷贝视频
var fs = require('fs')
var readStream = fs.createReadStream('1.mp4')
var writeStream = fs.createWriteStream('1-stream.mp4')
readStream.on('data', function(chunk){
//如果缓存区数据还在写, 那么暂停读数据
if( writeStream.write(chunk) === false){
console.log('still cached')
readStream.pause()
}
})
readStream.on('end', function(){
writeStream.end()
})
writeStream.on('drain', function() {
console.log('data drains')
readStream.resume()
})
10. 流与pipe
网络请求与pipe:
1 var http = require('http')
2 var fs = require('fs')
3 var request = require('request')
4
5 http
6 .createServer(function(req, res) {
7 //=====================常规做法
8 // fs.readFile('./buffer/logo.png', function(err, data){
9 // if(err){
10 // res.end('file not exist!')
11 // } else {
12 // res.writeHeader(200, {'Context-Type' : 'text/html'})
13 // res.end(data)
14 // }
15 // })
16
17 //===============使用pipe方法读取本地图片
18 // fs.createReadStream('../buffer/logo.png').pipe(res)
19
20 //从网络上获取一张图片 在不保存的前提下再返回给浏览器
21 request('http://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png?t=1.1').pipe(res)
22 //pipe会自动监听data和end事件. 可自动控制流量压力
23 })
24 .listen(8090)
使用pipe重构上面的copy视频的代码:
1 var fs = require('fs')
2 fs.createReadStream('1.mp4').pipe(fs.createWriteStream('1-pipe.mp4'))
总结:
- 可读流是为了读取外部数据, 并把数据缓存到内部的buffer数组
- 可写流是为了消费数据, 从可读流里获取数据然后对得到的chunk数据库进行处理.
1 var Readable = require('stream').Readable 2 var Writable = require('stream').Writable 3 4 var readStream = new Readable() 5 var writeStream = new Writable() 6 7 readStream.push('I ') 8 readStream.push('Love ') 9 readStream.push('Imooc ') 10 readStream.push(null) 11 12 writeStream._write = function(chunk, encode, cb) { 13 console.log(chunk.toString()) 14 cb() 15 } 16 17 readStream.pipe(writeStream)
一个自己定制的读写转换流的实现:
1 var stream = require('stream')
2 var util = require('util')
3
4 function ReadStream(){
5 stream.Readable.call(this)
6
7 }
8
9 util.inherits(ReadStream, stream.Readable)
10
11 ReadStream.prototype._read = function(){
12 this.push('I ')
13 this.push('Love ')
14 this.push('Imooc
')
15 this.push(null)
16 }
17
18 function WriteStream(){
19 stream.Writable.call(this)
20 this._cached = new Buffer('')
21 }
22
23 util.inherits(WriteStream, stream.Writable)
24
25 WriteStream.prototype._write = function(chunk, encode, cb){
26 console.log(chunk.toString())
27 cb()
28 }
29
30 function TransformStream(){
31 stream.Transform.call(this)
32 }
33
34 util.inherits(TransformStream, stream.Transform)
35
36 TransformStream.prototype._transform = function(chunk, encode, cb){
37 this.push(chunk)
38 cb()
39 }
40
41 TransformStream.prototype._flush = function(cb){
42 this.push('Oh Yeah!')
43 cb()
44 }
45
46 var rs = new ReadStream()
47 var ws = new WriteStream()
48 var ts = new TransformStream()
49
50 rs.pipe(ts).pipe(ws)
