分析volatile关键字可以从这三个方面分析,什么是程序的原子性,什么是程序的可见性,什么是程序的有序性
什么是程序的原子性
以下语句那些是原子操作?


public class ThreadCounter implements Runnable { private int count = 0; @Override public void run() { ++count; // count++; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ThreadCounter thread = new ThreadCounter(); for(int i = 0; i< 10000; i++){ new Thread(thread).start(); } Thread.sleep(1000);//确保线程执行完 System.out.println(thread.count); } }
演示结果:语句一和二是非原子操作,语句三和四是原子操作

执行指令:javap -s -c ThreadCounter
run方法的指令码(count++):


count++这行代码分成了4个指令来执行,在多线程的情况下会不一致。
解决方法:

public class ThreadCounter implements Runnable { private int count = 0; @Override public void run() { synchronized (this) { ++count; // count++; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ThreadCounter thread = new ThreadCounter(); for(int i = 0; i< 10000; i++){ new Thread(thread).start(); } Thread.sleep(1000);//确保线程执行完 System.out.println(thread.count); } }
什么是程序的可见性?


public class VolatileExample { boolean v =false; private void write(){ v =true; } private void read(){ while(!v){ } System.out.println("程序结束!"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final VolatileExample example = new VolatileExample(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{example.read();}); thread1.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{example.write();}); thread2.start(); } }
演示结果:
程序没有结束,read方法中的v没有因write方法的修改而退出循环!
解决方法:为变量v添加volatile关键字

public class VolatileExample { volatile boolean v =false; private void write(){ v =true; } private void read(){ while(!v){ } System.out.println("程序结束!"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final VolatileExample example = new VolatileExample(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{example.read();}); thread1.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{example.write();}); thread2.start(); } }




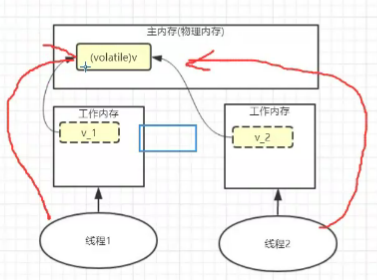
什么是程序的有序性?

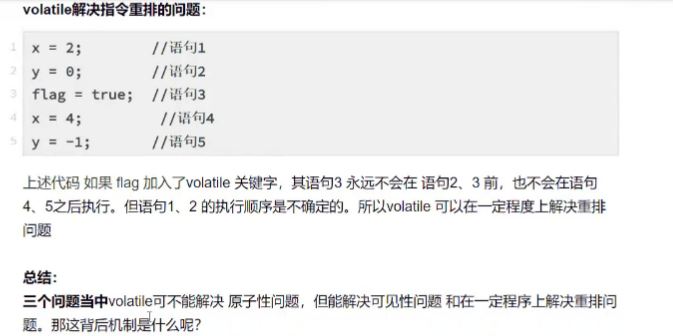

Volatile应用场景
1. 状态标记量

public class ThreadTest { private volatile boolean isContinue = false; private class HandleThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { while (isContinue) { // do something } }; } }
2. double check

总结:
volatile在可见性和有序性可以起到作用,但是不能保证原子性,是一种弱同步。
synchronized可以保证原子性,可见性,一致性,是一种强同步。
