在自己的电脑下载了npm 与 node的情况下 可使用vue-cli快速构建vue项目执行命令如下:
# 全局安装 vue-cli
$ npm install -g vue-cli
# 创建一个基于 "webpack" 模板的新项目
$ vue init webpack my-project
# 安装依赖,走你
$ cd my-project
$ npm install
$ npm run dev
// 这个vuetest是你的项目名称 自己起个名字就好了
// 之后就可以按照页面提示 一直输入enter键即可
我自己在安装的时候 报了一个关于chromedriver版本错误的问题 可以使用以下命令来解决
// 这个原因是package.json 里面引入的chromedriver 版本与自己电脑里下载的版本是不一样的所导致 npm install chromedriver --chromedriver_cdnurl=http://cdn.npm.taobao.org/dist/chromedriver // 或者是: npm install chromedriver --chromedriver_cdnurl=http://cdn.npm.taobao.org/dist/chromedriver // 运行结束之后 就可以直接使用 npm run 启动项目
下面来看一下项目结构吧
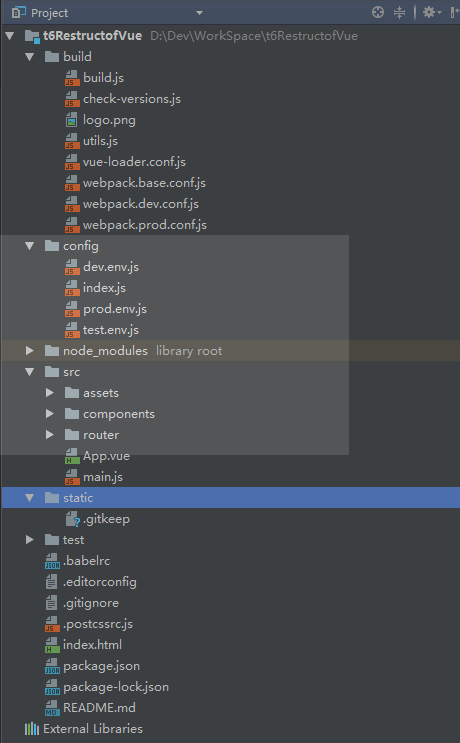
简单来介绍一下这个目录
bulid 构建服务和webpack配置 下面会有各个文件的详细介绍
config 构建项目的不同环境的配置 包括打包路径的配置 环境的声明 比如 生产环境 开发环境 测试环境。
src 项目目录
在开发环境下,我们首先考虑的是方便开发,方便代码调试,不需要考虑代码合并和css样式分离这些。
这里主要说三个 :1.css模块化;2.模块热替换功能;3.source-map(代码映射)
 webpack.dev.conf.js
webpack.dev.conf.js首先需要知道的是,webpack的配置是通过module.exports导出一个node环境下全局的对象。然后这样再去就能更方便了解webpack 的写法。
主要代码在于:
const devWebpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {}
//这个是将baseWebpackConfi与该文件里的配置进行结合。具体可以查看下merge的用法,也就是说 如果你想了解一些基本的配置,应该这时候去看下webpack.base.conf.js文件。
2:webpack.base.conf.js
先看代码注释
 webpack.base.conf.js
webpack.base.conf.js在这个文件里 配置了一些比如入口文件,打包与运行的文件路径,当然 这里都是在用变量去表示,最明显的栗子可以从
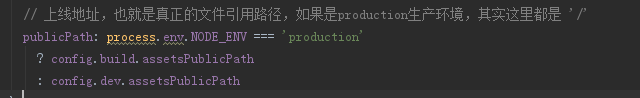
首先解释一下:process这个对象提供一系列属性,用于返回系统信息。
process.env:指向当前shell的环境变量,比如process.env.HOME 在我电脑里返回的是C:Userdell
process模块用来与当前进程互动,可以通过全局变量process访问,不必使用require命令加载。它是一个EventEmitter对象的实例。上面有很多的信息。
这里看出来,在dev.conf.js文件里 有进行判断是生产还是开发环境的判断,也许会有疑问,我们在代码里 怎么知道当前运行的是开发环境 还是生产环境呢,并没有直接去指明当前欲运行的环境。其实这个是在我们运行比如 npm run dev 或者 npm build 时 在运行命令上就已经带上了参数,指定了当前要运行的环境。这里也就不再进行细说。
3:webpack.prod.conf.js
当我们运行打包 npm run build命令时 运行的是build/build.js文件,可以看到该文件引入的是webpack.prod.conf.js另外在build.js文件里加了几个判断 还有删除打包文件的命令。
相比开发环境,生产环境打包是要最后发布到服务器部署的代码,我们需要尽量保持代码简洁,加载性能最优,不需要调试辅助工具。
我们从这几个方面优化 :1.公共模块拆分,单独打包;2. css文件分离,单独打包输出;3.代码压缩;

'use strict' const path = require('path') const utils = require('./utils') const webpack = require('webpack') const config = require('../config') const merge = require('webpack-merge') const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf') const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin') const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin') //帮做我们配置html文件中js文件的引入的 // css单独打包插件 const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin') const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin') // 压缩工具 const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin') const env = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'testing' ? require('../config/test.env') : require('../config/prod.env') const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, { module: { rules: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, extract: true, usePostCSS: true }) }, devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false, output: { path: config.build.assetsRoot, filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'), chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js') }, plugins: [ // http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html new webpack.DefinePlugin({ 'process.env': env }), new UglifyJsPlugin({ uglifyOptions: { compress: { warnings: false } }, sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, parallel: true }), // extract css into its own file new ExtractTextPlugin({ filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'), // Setting the following option to `false` will not extract CSS from codesplit chunks. // Their CSS will instead be inserted dynamically with style-loader when the codesplit chunk has been loaded by webpack. // It's currently set to `true` because we are seeing that sourcemaps are included in the codesplit bundle as well when it's `false`, // increasing file size: https://github.com/vuejs-templates/webpack/issues/1110 allChunks: true, }), // Compress extracted CSS. We are using this plugin so that possible // duplicated CSS from different components can be deduped. new OptimizeCSSPlugin({ cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap ? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } } : { safe: true } }), // generate dist index.html with correct asset hash for caching. // you can customize output by editing /index.html // see https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ filename: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'testing' ? 'index.html' : config.build.index, template: 'index.html', inject: true, minify: { removeComments: true, collapseWhitespace: true, removeAttributeQuotes: true // more options: // https://github.com/kangax/html-minifier#options-quick-reference }, // necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin chunksSortMode: 'dependency' }), // keep module.id stable when vendor modules does not change new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(), // enable scope hoisting new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(), // split vendor js into its own file new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: 'vendor', minChunks (module) { // any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor return ( module.resource && /.js$/.test(module.resource) && module.resource.indexOf( path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules') ) === 0 ) } }), // extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to // prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: 'manifest', minChunks: Infinity }), // This instance extracts shared chunks from code splitted chunks and bundles them // in a separate chunk, similar to the vendor chunk // see: https://webpack.js.org/plugins/commons-chunk-plugin/#extra-async-commons-chunk new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: 'app', async: 'vendor-async', children: true, minChunks: 3 }), // copy custom static assets new CopyWebpackPlugin([ { from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'), to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory, ignore: ['.*'] } ]) ] }) if (config.build.productionGzip) { const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin') webpackConfig.plugins.push( new CompressionWebpackPlugin({ asset: '[path].gz[query]', algorithm: 'gzip', test: new RegExp( '\.(' + config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') + ')$' ), threshold: 10240, minRatio: 0.8 }) ) } if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) { const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin()) } module.exports = webpackConfig
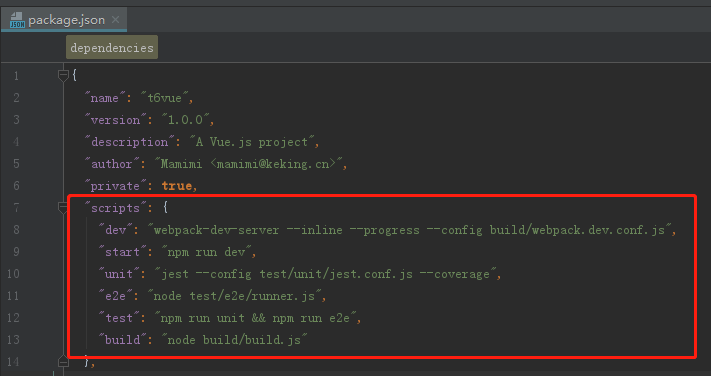
常用的一些配置更改:看注释也就能看懂了
在config文件下的index.js文件

'use strict' // Template version: 1.3.1 // see http://vuejs-templates.github.io/webpack for documentation. // path是node.js的路径模块,用来处理路径统一的问题 const path = require('path') module.exports = { dev: { // Paths assetsSubDirectory: 'static', // 编译输出的二级目录 assetsPublicPath: '/', // 编译发布的根目录,可配置为资源服务器域名或 CDN 域名 // 下面是代理表,作用是用来,建一个虚拟api服务器用来代理本机的请求,只能用于开发模式 proxyTable: { // '/api': { // target: 'http://localhost:8082', // pathRewrite: { // '^/api': '/' // } // }, // '/pop-shared-web-components': { // target: 'http://pop-shared-web-components.cn:3000', // pathRewrite: { // '^/pop-shared-web-components': '/' // } // } }, //下面是proxyTable的一般用法 //vue-cli使用这个功能是借助http-proxy-middleware插件,一般解决跨域请求api // proxyTable: { // '/list': { // target: 'http://api.xxxxxxxx.com', -> 目标url地址 // changeOrigin: true, -> 指示是否跨域 // pathRewrite: { // '^/list': '/list' -> 可以使用 /list 等价于 api.xxxxxxxx.com/list // } // } // } // Various Dev Server settings host: 'localhost', // can be overwritten by process.env.HOST port: 8080, // can be overwritten by process.env.PORT, if port is in use, a free one will be determined // 运行测试页面的端口 autoOpenBrowser: true, errorOverlay: true, notifyOnErrors: true, poll: false, // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/dev-server/#devserver-watchoptions- /** * Source Maps */ // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#development devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map', // If you have problems debugging vue-files in devtools, // set this to false - it *may* help // https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/options.html#cachebusting cacheBusting: true, cssSourceMap: true }, // 下面是build也就是生产编译环境下的一些配置 build: { // Template for index.html //path.resolve() 方法会把一个路径或路径片段的序列解析为一个绝对路径。 index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist/index.html'), // 编译输入的 index.html 文件 // Paths assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'), // 编译输出的静态资源路径 是静态资源的根目录 也就是dist目录 assetsSubDirectory: 'static', // 编译输出的二级目录 assetsPublicPath: '/', // 编译发布的根目录,可配置为资源服务器域名或 CDN 域名 /** * Source Maps */ productionSourceMap: true, // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#production devtool: '#source-map', // Gzip off by default as many popular static hosts such as // Surge or Netlify already gzip all static assets for you. // Before setting to `true`, make sure to: // npm install --save-dev compression-webpack-plugin // 下面是是否在生产环境中压缩代码,如果要压缩必须安装compression-webpack-plugin productionGzip: false, // 下面定义要压缩哪些类型的文件 productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'], // Run the build command with an extra argument to // View the bundle analyzer report after build finishes: // `npm run build --report` // Set to `true` or `false` to always turn it on or off // 下面是用来开启编译完成后的报告,可以通过设置值为true和false来开启或关闭 // 下面的process.env.npm_config_report表示定义的一个npm_config_report环境变量,可以自行设置 bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report } }
以上算是对各个文件做了简单的介绍
