两圆相交分如下集中情况:相离、相切、相交、包含。
设两圆圆心分别是O1和O2,半径分别是r1和r2,设d为两圆心距离。又因为两圆有大有小,我们设较小的圆是O1。
相离相切的面积为零,代码如下:
- double d = sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x) + (a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
- if (d >= r1+r2)
- return 0;
double d = sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x) + (a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); if (d >= r1+r2) return 0;
包含的面积就是小圆的面积了,代码如下:
- if(r2 - r1 >= d)
- return pi*r1*r1;
if(r2 - r1 >= d) return pi*r1*r1;
接下来看看相交的情况。
相交面积可以这样算:扇形O1AB - △O1AB + 扇形O2AB - △O2AB,这两个三角形组成了一个四边形,可以用两倍的△O1AO2求得,
所以答案就是两个扇形-两倍的△O1AO2
因为
所以
那么
同理
接下来是四边形面积:
代码如下:
double ang1=acos((r1*r1+d*d-r2*r2)/(2*r1*d)); double ang2=acos((r2*r2+d*d-r1*r1)/(2*r2*d)); return ang1*r1*r1 + ang2*r2*r2 - r1*d*sin(ang1);
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; #define pi acos(-1.0) typedef struct node { int x; int y; }point; double AREA(point a, double r1, point b, double r2) { double d = sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x) + (a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); if (d >= r1+r2) return 0; if (r1>r2) { double tmp = r1; r1 = r2; r2 = tmp; } if(r2 - r1 >= d) return pi*r1*r1; double ang1=acos((r1*r1+d*d-r2*r2)/(2*r1*d)); double ang2=acos((r2*r2+d*d-r1*r1)/(2*r2*d)); return ang1*r1*r1 + ang2*r2*r2 - r1*d*sin(ang1); } int main() { point a, b; a.x=2, a.y=2; b.x=7, b.y=2; double result = AREA(a, 3, b, 5); printf("%lf ", result); return 0; }
Intersection
Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3443 Accepted Submission(s): 1302
Problem Description
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.

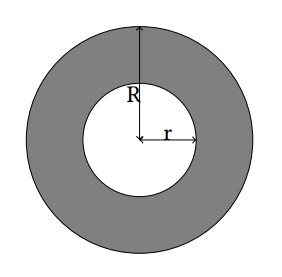
A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.

Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 105), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Output
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
Sample Input
2
2 3
0 0
0 0
2 3
0 0
5 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 15.707963
Case #2: 2.250778
#include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; double x1,ya,x2,y2,dis,s1,s2,s3,R,r; double sov(double R,double r){ if(dis>=r+R) return 0; if(dis<=R-r) return acos(-1.0)*r*r; double x=(R*R-r*r+dis*dis)/2.0/dis; double y=(r*r-R*R+dis*dis)/2.0/dis; double seta1=2*acos(x/R); double seta2=2*acos(y/r); double ans=seta1*R*R/2.0+seta2*r*r/2.0; double h=sqrt(R*R-x*x); return ans-dis*h; } int main(){ int tas=1,T; for(scanf("%d",&T);T--;){ scanf("%lf%lf",&r,&R); scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x1,&ya,&x2,&y2); dis=sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(ya-y2)*(ya-y2)); s1=sov(R,R),s2=sov(R,r),s3=sov(r,r); printf("Case #%d: %.6f ",tas++,s1-2*s2+s3); } }








