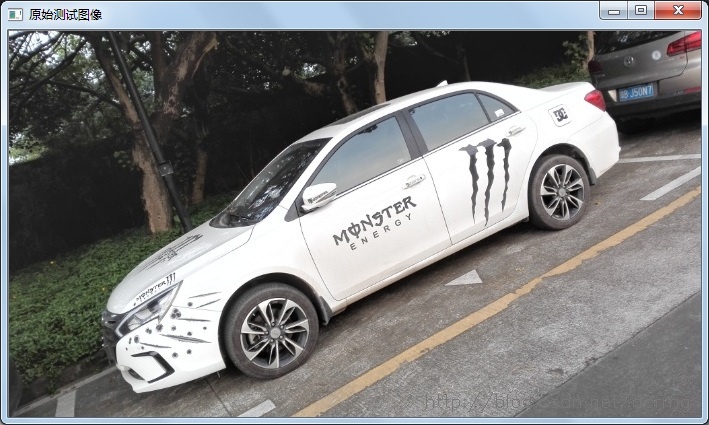
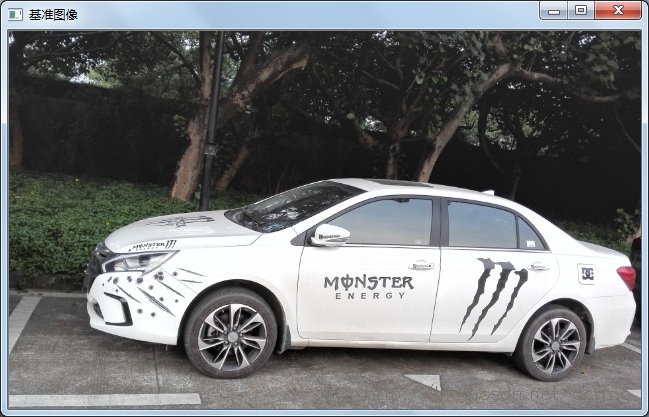
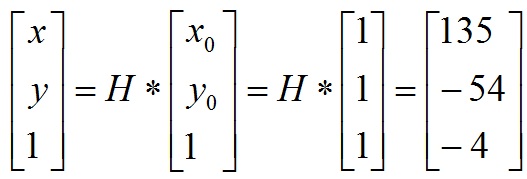图像配准需要将一张测试图片按照第二张基准图片的尺寸、角度等形态信息进行透视(仿射)变换匹配,本例通过Surf特征的定位和匹配实现图像配准。
配准流程:
- 1. 提取两幅图像的Surf特征
- 2. 对Surf特征进行匹配,找到最匹配的特征点对
- 3. 提取最优配对点的坐标,生成透视变换矩阵
- 4. 对测试图像经过透视变换,生成配准图像
以下是Opencv代码实现:
#include "highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
Mat image01=imread(argv[1]);
Mat image02=imread(argv[2]);
imshow("原始测试图像",image01);
imshow("基准图像",image02);
//灰度图转换
Mat image1,image2;
cvtColor(image01,image1,CV_RGB2GRAY);
cvtColor(image02,image2,CV_RGB2GRAY);
//提取特征点
SurfFeatureDetector surfDetector(800); // 海塞矩阵阈值
vector<KeyPoint> keyPoint1,keyPoint2;
surfDetector.detect(image1,keyPoint1);
surfDetector.detect(image2,keyPoint2);
//特征点描述,为下边的特征点匹配做准备
SurfDescriptorExtractor SurfDescriptor;
Mat imageDesc1,imageDesc2;
SurfDescriptor.compute(image1,keyPoint1,imageDesc1);
SurfDescriptor.compute(image2,keyPoint2,imageDesc2);
//获得匹配特征点,并提取最优配对
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch> matchePoints;
matcher.match(imageDesc1,imageDesc2,matchePoints,Mat());
sort(matchePoints.begin(),matchePoints.end()); //特征点排序
//获取排在前N个的最优匹配特征点
vector<Point2f> imagePoints1,imagePoints2;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
imagePoints1.push_back(keyPoint1[matchePoints[i].queryIdx].pt);
imagePoints2.push_back(keyPoint2[matchePoints[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
//获取图像1到图像2的投影映射矩阵 尺寸为3*3
Mat homo=findHomography(imagePoints1,imagePoints2,CV_RANSAC);
////也可以使用getPerspectiveTransform方法获得透视变换矩阵,不过要求只能有4个点,效果稍差
//Mat homo=getPerspectiveTransform(imagePoints1,imagePoints2);
cout<<"变换矩阵为:
"<<homo<<endl<<endl; //输出映射矩阵
//图像配准
Mat imageTransform1,imageTransform2;
warpPerspective(image01,imageTransform1,homo,Size(image02.cols,image02.rows));
imshow("经过透视矩阵变换后",imageTransform1);
waitKey();
return 0;
}测试图像:
配准基准(目标)图像:
配准效果:
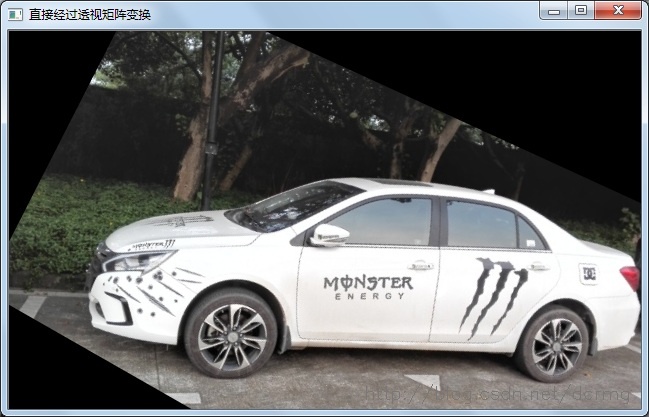
可以看到,使用Surf特征自动配准的效果还算可以,也不需要手动选取特征点,但是有点小遗憾是配准后原图的部分图像缺失了,如原始图像的左上角和左下角区域。
怎么解释这个现象呢?其实是因为原图像缺失部分经过透视矩阵变换后在新图像中位置坐标变成负的了,导致这部分直接被截取掉了。
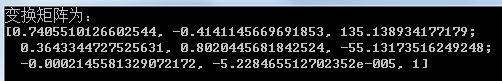
拿原始图像中的坐标为左上角的点(x0,y0)=(1,1)为例,本例中生成的透视变换矩阵H为:
经过矩阵H变换后目标图像的对应坐标为X(x,y):
所以变换后的目标点X(x,y)=(135/-4,-54/-4)= (-34,13) ,即x的坐标等于-34,小于零,所以直接被截取干掉了。
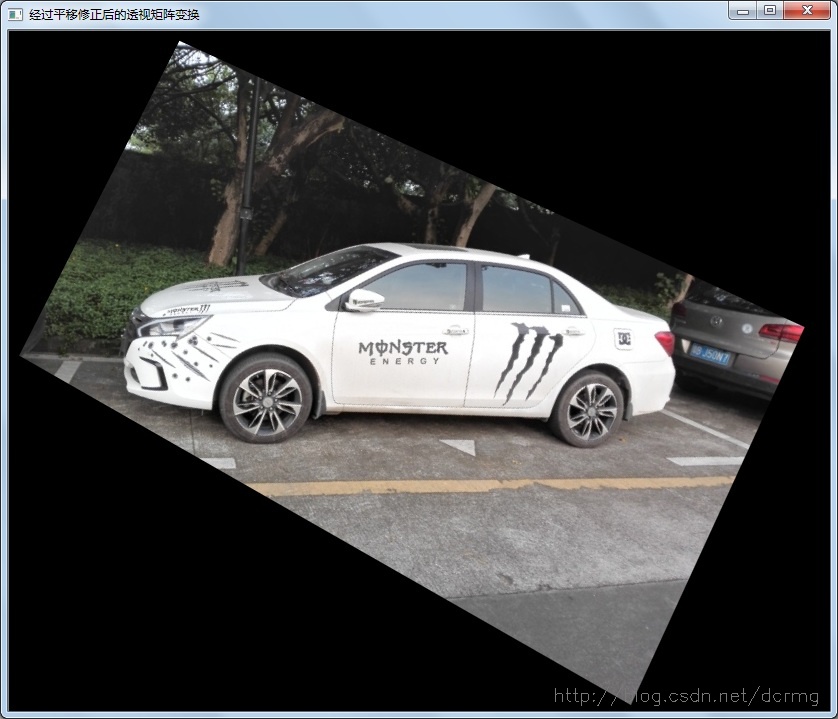
解决办法之一可以通过修正变换矩阵,对其加一个水平或垂直方向上的平移分量,保证变换后的目标坐标有一个偏移,偏移后的坐标大于0即可。其中H矩阵的第一行数据影响水平(x)方向的偏移,第二行数据影响垂直(y)方向的偏移。所以水平偏移需要修正H矩阵的第一行数据,垂直偏移需要修正H矩阵的第二行数据。
H矩阵数值的调整可以通过用一个3*3的矩阵相乘实现,水平方向的修正矩阵:
Mat adjustMat=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1.0,0,adjustValue,0,1.0,0,0,0,1.0);
垂直方向上的修正矩阵:
Mat adjustMat=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1.0,0,0,0,1.0,adjustValue,0,0,1.0);
水平和垂直两个方向上的修正矩阵:
Mat adjustMat=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1.0,0,adjustValue1,0,1.0,adjustValue2,0,0,1.0);
上边的修正(平移)系数adjustValue数值越大,在目标图像上坐标的偏移也就越大,大于零的adjustValue对应正方向上的平移,小于零的adjustValue对应负方向的平移。
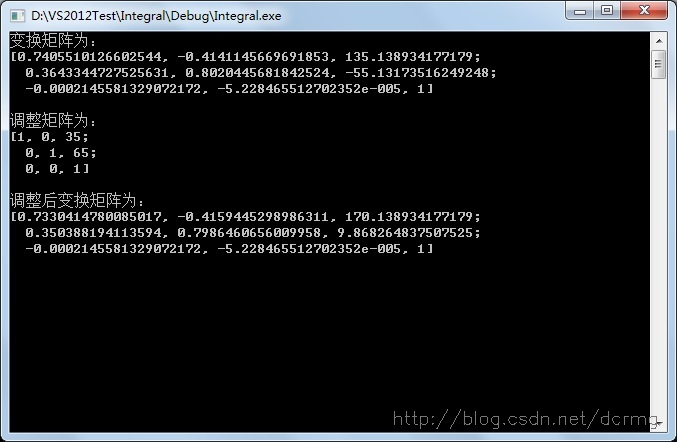
以下是经过adjustMat矩阵修正过的H矩阵数据变化对比:
经过水平和垂直方向的平移修正之后的透视效果,两个角落区域的内容都可以显示出来了:
以下是对透视变换矩阵平移修正的完整代码,有兴趣可以参考试一试。
#include "highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
Mat image01=imread(argv[1]);
Mat image02=imread(argv[2]);
imshow("原始测试图像",image01);
imshow("基准图像",image02);
//灰度图转换
Mat image1,image2;
cvtColor(image01,image1,CV_RGB2GRAY);
cvtColor(image02,image2,CV_RGB2GRAY);
//提取特征点
SurfFeatureDetector surfDetector(800); // 海塞矩阵阈值
vector<KeyPoint> keyPoint1,keyPoint2;
surfDetector.detect(image1,keyPoint1);
surfDetector.detect(image2,keyPoint2);
//特征点描述,为下边的特征点匹配做准备
SurfDescriptorExtractor SurfDescriptor;
Mat imageDesc1,imageDesc2;
SurfDescriptor.compute(image1,keyPoint1,imageDesc1);
SurfDescriptor.compute(image2,keyPoint2,imageDesc2);
//获得匹配特征点,并提取最优配对
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch> matchePoints;
matcher.match(imageDesc1,imageDesc2,matchePoints,Mat());
sort(matchePoints.begin(),matchePoints.end()); //特征点排序
//获取排在前N个的最优匹配特征点
vector<Point2f> imagePoints1,imagePoints2;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
imagePoints1.push_back(keyPoint1[matchePoints[i].queryIdx].pt);
imagePoints2.push_back(keyPoint2[matchePoints[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
//获取图像1到图像2的投影映射矩阵 尺寸为3*3
Mat homo=findHomography(imagePoints1,imagePoints2,CV_RANSAC);
////也可以使用getPerspectiveTransform方法获得透视变换矩阵,不过要求只能有4个点,效果稍差
//Mat homo=getPerspectiveTransform(imagePoints1,imagePoints2);
cout<<"变换矩阵为:
"<<homo<<endl<<endl; //输出映射矩阵
double adjustValue=image1.cols;
Mat adjustMat=(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1.0,0,35,0,1.0,65,0,0,1.0);
cout<<"调整矩阵为:
"<<adjustMat<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"调整后变换矩阵为:
"<<adjustMat*homo<<endl;
//图像配准
Mat imageTransform1,imageTransform2;
warpPerspective(image01,imageTransform1,homo,Size(image02.cols,image02.rows));
warpPerspective(image01,imageTransform2,adjustMat*homo,Size(image02.cols*1.3,image02.rows*1.8));
imshow("直接经过透视矩阵变换",imageTransform1);
imshow("经过平移修正后的透视矩阵变换",imageTransform2);
waitKey();
return 0;
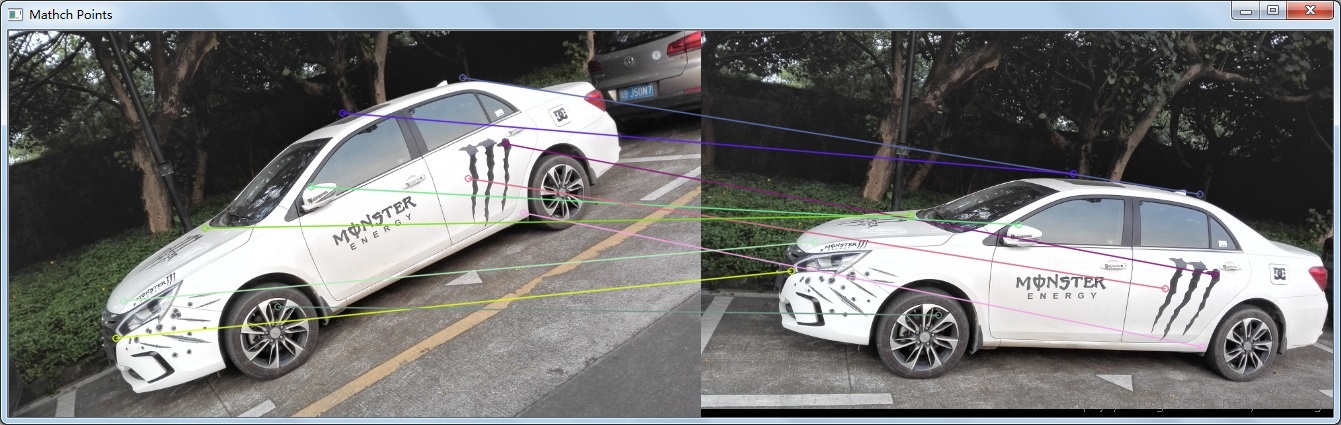
}顺便贴一下特征点的匹配效果: