Looploop
XXX gets a new toy named Looploop. The toy has N elements arranged in a loop, an arrow pointing to one of the elements, and two preset parameters k1 and k2. Every element has a number on it.
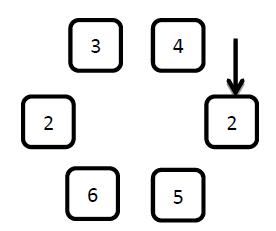
The figure above shows a Looploop of 6 elments. Let's assuming the preset parameter k1 is 3, and k2 is 4.
XXX can do six operations with the toy.
1: add x
Starting from the arrow pointed element, add x to the number on the clockwise first k2 elements.
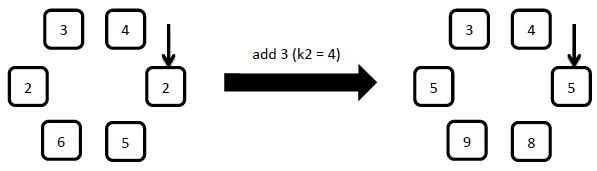
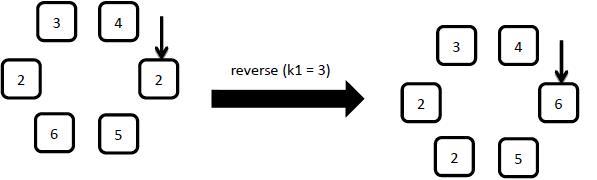
2: reverse
Starting from the arrow pointed element, reverse the first k1 clockwise elements.
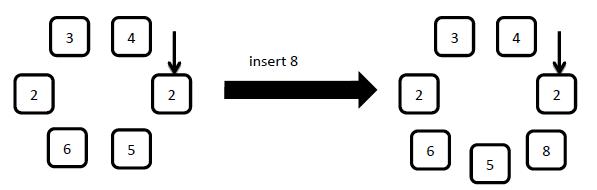
3: insert x
Insert a new element with number x to the right (along clockwise) of the arrow pointed element.
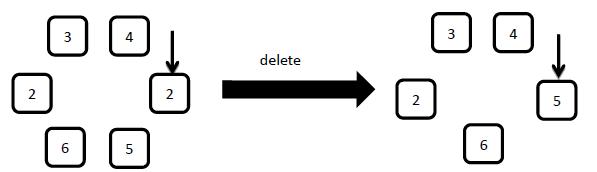
4: delete
Delete the element the arrow pointed and then move the arrow to the right element.
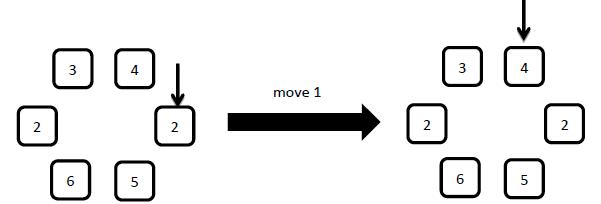
5: move x
x can only be 1 or 2. If x = 1 , move the arrow to the left(along the counterclockwise) element, if x = 2 move the arrow to the right element.
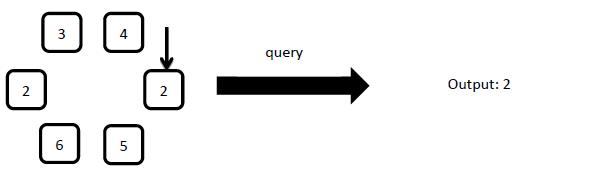
6: query
Output the number on the arrow pointed element in one line.
XXX wants to give answers to every query in a serial of operations.
For each test case the first line contains N,M,k1,k2(2≤k1<k2≤N≤105, M≤105) indicating the initial number of elements, the total number of operations XXX will do and the two preset parameters of the toy.
Second line contains N integers ai(-104≤ai≤104) representing the N numbers on the elements in Looploop along clockwise direction. The arrow points to first element in input at the beginning.
Then m lines follow, each line contains one of the six operations described above.
It is guaranteed that the "x" in the "add","insert" and "move" operations is always integer and its absolute value ≤104. The number of elements will never be less than N during the operations.
The input ends with a line of 0 0 0 0.
题意很简单,就像题目中 图片中描述的一样。Splay大法好啊。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 7 const int maxn = 100086; 8 int pre[maxn],ch[maxn][2],key[maxn],addv[maxn],rev[maxn],siz[maxn]; 9 int tot1,tot2,root,s[maxn]; //s为内存池 10 int a[maxn],n,m,k1,k2; 11 void update_add(int r,int val) 12 { 13 if (!r) 14 return; 15 key[r] += val; 16 addv[r] += val; 17 } 18 void update_rev(int r) 19 { 20 if (!r) 21 return; 22 swap(ch[r][0],ch[r][1]); 23 rev[r] ^= 1; 24 } 25 void push_down(int r) 26 { 27 if (rev[r]) 28 { 29 update_rev(ch[r][0]); 30 update_rev(ch[r][1]); 31 rev[r] = 0; 32 } 33 if (addv[r]) 34 { 35 update_add(ch[r][0],addv[r]); 36 update_add(ch[r][1],addv[r]); 37 addv[r] = 0; 38 } 39 } 40 void push_up(int r) 41 { 42 siz[r] = siz[ch[r][0]] + siz[ch[r][1]] + 1; 43 } 44 void NewNode (int &r,int father,int k) 45 { 46 if (tot2) 47 r = s[tot2--]; 48 else 49 r = ++tot1; 50 pre[r] = father; 51 siz[r] = 1; 52 rev[r] = 0; 53 addv[r] = 0; 54 ch[r][0] = ch[r][1] = 0; 55 key[r] = k; 56 } 57 void build(int &x,int l,int r,int father) 58 { 59 if (l > r) 60 return ; 61 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 62 NewNode(x,father,a[mid]); 63 build(ch[x][0],l,mid-1,x); 64 build(ch[x][1],mid+1,r,x); 65 push_up(x); 66 } 67 void init() 68 { 69 tot1 = tot2 = root = 0; 70 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 71 scanf ("%d",a+i); 72 NewNode(root,0,inf); 73 NewNode(ch[root][1],root,inf); 74 build(ch[ch[root][1]][0],1,n,ch[root][1]); 75 push_up(root); 76 push_up(ch[root][1]); 77 } 78 void Rotate(int r,int kind) 79 { 80 int y = pre[r]; 81 push_down(y); 82 push_down(r); 83 ch[y][!kind] = ch[r][kind]; 84 pre[ch[r][kind]] = y; 85 if (pre[y]) 86 ch[pre[y]][ch[pre[y]][1] == y] = r; 87 ch[r][kind] = y; 88 pre[r] = pre[y]; 89 pre[y] = r; 90 push_up(y); 91 } 92 93 void Splay(int r,int goal) 94 { 95 push_down(r); 96 while (pre[r] != goal) 97 { 98 if (pre[pre[r]] == goal) 99 { 100 push_down(pre[r]); 101 push_down(r); 102 Rotate(r,ch[pre[r]][0] == r); 103 } 104 else 105 { 106 int y = pre[r]; 107 int kind = (ch[pre[y]][1] == y); 108 push_down(pre[y]); 109 push_down(y); 110 push_down(r); 111 if (ch[y][kind] == r) 112 { 113 Rotate(y,!kind); 114 Rotate(r,!kind); 115 } 116 else 117 { 118 Rotate(r,kind); 119 Rotate(r,!kind); 120 } 121 } 122 } 123 push_up(r); 124 if (goal == 0) 125 root = r; 126 } 127 int Get_kth(int r,int k) 128 { 129 push_down(r); 130 int t = siz[ch[r][0]] + 1; 131 if (t == k) 132 return r; 133 if (t > k) 134 return Get_kth(ch[r][0],k); 135 else 136 return Get_kth(ch[r][1],k-t); 137 } 138 void ADD(int x) 139 { 140 Splay (Get_kth(root,1),0); 141 Splay(Get_kth(root,k2+2),root); 142 update_add(ch[ch[root][1]][0],x); 143 push_up(ch[root][1]); 144 push_up(root); 145 } 146 void Reverse(int u,int v) 147 { 148 Splay(Get_kth(root,u),0); 149 Splay(Get_kth(root,v+2),root); 150 update_rev(ch[ch[root][1]][0]); 151 push_up(ch[root][1]); 152 push_up(root); 153 } 154 void Insert(int x) 155 { 156 Splay(Get_kth(root,2),0); 157 Splay(Get_kth(root,3),root); 158 NewNode(ch[ch[root][1]][0],ch[root][1],x); 159 push_up(ch[root][1]); 160 push_up(root); 161 } 162 void eraser(int r) 163 { 164 if (!r) 165 return; 166 s[++tot2] = r; 167 eraser(ch[r][0]); 168 eraser(ch[r][1]); 169 } 170 void Delete() 171 { 172 Splay(Get_kth(root,1),0); 173 Splay(Get_kth(root,3),root); 174 eraser(ch[ch[root][1]][0]); 175 pre[ch[ch[root][1]][0]] = 0; 176 ch[ch[root][1]][0] = 0; 177 push_up(ch[root][1]); 178 push_up(root); 179 } 180 void Move(int x) //Move操作就是两个 区间reverse操作。 181 { 182 if (x == 1) 183 { 184 Reverse(1,n); 185 Reverse(2,n); 186 } 187 if (x == 2) 188 { 189 Reverse(1,n); 190 Reverse(1,n-1); 191 } 192 } 193 int query() 194 { 195 Splay(Get_kth(root,1),0); 196 Splay(Get_kth(root,3),root); 197 return key[ch[ch[root][1]][0]]; 198 } 199 int main(void) 200 { 201 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE 202 freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 203 #endif 204 int cas = 1; 205 while (~scanf ("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k1,&k2)) 206 { 207 if (n == 0 && m == 0 && k1 == 0 && k2 == 0) 208 break; 209 printf("Case #%d: ",cas++); 210 init(); 211 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 212 { 213 char op[8]; 214 int x; 215 scanf ("%s",op); 216 if (op[0] == 'a') 217 { 218 scanf ("%d",&x); 219 ADD(x); 220 } 221 if (op[0] == 'r') 222 Reverse(1,k1); 223 if (op[0] == 'i') 224 { 225 scanf ("%d",&x); 226 Insert(x); 227 n++; // insert一个数 n自然加1 228 } 229 if (op[0] == 'd') 230 { 231 Delete(); 232 n--; //delete一个数 n减1 233 } 234 if (op[0] == 'm') 235 { 236 scanf ("%d",&x); 237 Move(x); 238 } 239 if (op[0] == 'q') 240 printf("%d ",query()); 241 } 242 } 243 return 0; 244 }