1、简介
能够动态执行 C# 代码是一件很酷的功能,比如,我们可以在控制台中输入一行 C# 代码,然后程序自动编译并执行这一行代码,将结果显示给我们。这差不多就是一个最简单的 C# 代码解释器了。
动态执行 C# 代码又是一件很有用的功能,比如,我们可以将某些代码写在某个文件之中,由程序集在执行时进行加载,改变这些代码不用中止程序,当程序再次加载这些代码时,就自动执行的是新代码了。
下面,我将在写一个简单C# 代码解释器,然后将在 C# 代码解释器之中加入动态代码与解释器环境间的动态交互机制,来演示一个很好很强大的应用。
2、简单的 C# 代码解释器
关于如何动态执行 C# 代码在 Jailu.Net 的《如何用C#动态编译、执行代码》一文中讲述的很清晰。采用该文所述方式写一个 C# 代码解释器:
 using System;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Reflection;
using System.Reflection; using System.Globalization;
using System.Globalization; using Microsoft.CSharp;
using Microsoft.CSharp; using System.CodeDom;
using System.CodeDom; using System.CodeDom.Compiler;
using System.CodeDom.Compiler; using System.Text;
using System.Text; using System.IO;
using System.IO; using System.Xml;
using System.Xml;
 namespace Test
namespace Test

 {
{ class Program
class Program

 {
{ static void Main(string[] args)
static void Main(string[] args)

 {
{ Console.Write(">> ");
Console.Write(">> "); String cmd;
String cmd; Context cxt = new Context();
Context cxt = new Context(); while ((cmd = Console.ReadLine().Trim()) != "exit")
while ((cmd = Console.ReadLine().Trim()) != "exit")

 {
{ if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(cmd))
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(cmd))

 {
{ Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(); cxt.Invoke(cmd);
cxt.Invoke(cmd); }
} Console.Write("\n>> ");
Console.Write("\n>> "); }
} }
} }
}
 public class Context
public class Context

 {
{
 public CSharpCodeProvider CodeProvider
public CSharpCodeProvider CodeProvider  { get; set; }
{ get; set; }
 public IDictionary<String, Assembly> Assemblys
public IDictionary<String, Assembly> Assemblys  { get; set; }
{ get; set; }
 public Context()
public Context()

 {
{
 CodeProvider = new CSharpCodeProvider(new Dictionary<string, string>()
CodeProvider = new CSharpCodeProvider(new Dictionary<string, string>()  {
{  { "CompilerVersion", "v3.5" } });
{ "CompilerVersion", "v3.5" } }); Assemblys = new Dictionary<String, Assembly>();
Assemblys = new Dictionary<String, Assembly>(); Assembly[] al = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies();
Assembly[] al = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies(); foreach (Assembly a in al)
foreach (Assembly a in al)

 {
{ AddAssembly(a);
AddAssembly(a); }
} AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AssemblyLoad += new AssemblyLoadEventHandler(CurrentDomain_AssemblyLoad);
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AssemblyLoad += new AssemblyLoadEventHandler(CurrentDomain_AssemblyLoad); }
}
 private void AddAssembly(Assembly a)
private void AddAssembly(Assembly a)

 {
{ if (a != null)
if (a != null)

 {
{ Assemblys.Add(a.FullName, a);
Assemblys.Add(a.FullName, a); }
} }
}
 void CurrentDomain_AssemblyLoad(object sender, AssemblyLoadEventArgs args)
void CurrentDomain_AssemblyLoad(object sender, AssemblyLoadEventArgs args)

 {
{ Assembly a = args.LoadedAssembly;
Assembly a = args.LoadedAssembly; if (!Assemblys.ContainsKey(a.FullName))
if (!Assemblys.ContainsKey(a.FullName))

 {
{ AddAssembly(a);
AddAssembly(a); }
} }
}
 public CompilerParameters CreateCompilerParameters()
public CompilerParameters CreateCompilerParameters()

 {
{ CompilerParameters cp = new CompilerParameters();
CompilerParameters cp = new CompilerParameters(); cp.GenerateExecutable = false;
cp.GenerateExecutable = false; cp.GenerateInMemory = true;
cp.GenerateInMemory = true; if (Assemblys != null)
if (Assemblys != null)

 {
{ foreach (Assembly a in Assemblys.Values)
foreach (Assembly a in Assemblys.Values)

 {
{ cp.ReferencedAssemblies.Add(a.Location);
cp.ReferencedAssemblies.Add(a.Location); }
} }
} return cp;
return cp; }
}
 public void Invoke(String cmd)
public void Invoke(String cmd)

 {
{ String inputCmdString = cmd.Trim();
String inputCmdString = cmd.Trim(); if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(inputCmdString)) return;
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(inputCmdString)) return;
 String fullCmd = BuildFullCmd(inputCmdString);
String fullCmd = BuildFullCmd(inputCmdString);
 CompilerResults cr = CodeProvider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(CreateCompilerParameters(), fullCmd);
CompilerResults cr = CodeProvider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(CreateCompilerParameters(), fullCmd);
 if (cr.Errors.HasErrors)
if (cr.Errors.HasErrors)

 {
{ Boolean recompileSwitch = true;
Boolean recompileSwitch = true;
 foreach (CompilerError err in cr.Errors)
foreach (CompilerError err in cr.Errors)

 {
{ //CS0201 : Only assignment, call, increment, decrement, and new object expressions can be
//CS0201 : Only assignment, call, increment, decrement, and new object expressions can be //used as a statement
//used as a statement if (!err.ErrorNumber.Equals("CS0201"))
if (!err.ErrorNumber.Equals("CS0201"))

 {
{ recompileSwitch = false;
recompileSwitch = false; break;
break; }
} }
}
 // 重新编译
// 重新编译 if (recompileSwitch)
if (recompileSwitch)

 {
{ String dynaName = "TempArg_Dynamic_" + DateTime.Now.Ticks.ToString();
String dynaName = "TempArg_Dynamic_" + DateTime.Now.Ticks.ToString(); inputCmdString = String.Format(" var {0} = ", dynaName) + inputCmdString;
inputCmdString = String.Format(" var {0} = ", dynaName) + inputCmdString; inputCmdString += ";\n System.Console.WriteLine(" + dynaName + ");";
inputCmdString += ";\n System.Console.WriteLine(" + dynaName + ");";
 fullCmd = BuildFullCmd(inputCmdString);
fullCmd = BuildFullCmd(inputCmdString); cr = CodeProvider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(CreateCompilerParameters(), fullCmd);
cr = CodeProvider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(CreateCompilerParameters(), fullCmd); }
}
 if (cr.Errors.HasErrors)
if (cr.Errors.HasErrors)

 {
{ Console.WriteLine("编译错误:");
Console.WriteLine("编译错误:"); foreach (CompilerError err in cr.Errors)
foreach (CompilerError err in cr.Errors)

 {
{ Console.WriteLine(err.ErrorNumber);
Console.WriteLine(err.ErrorNumber); Console.WriteLine(err.ErrorText);
Console.WriteLine(err.ErrorText); }
}
 return;
return; }
} }
}
 Assembly assem = cr.CompiledAssembly;
Assembly assem = cr.CompiledAssembly; Object dynamicObject = assem.CreateInstance("Test.DynamicClass");
Object dynamicObject = assem.CreateInstance("Test.DynamicClass"); Type t = assem.GetType("Test.DynamicClass");
Type t = assem.GetType("Test.DynamicClass"); MethodInfo minfo = t.GetMethod("MethodInstance");
MethodInfo minfo = t.GetMethod("MethodInstance"); minfo.Invoke(dynamicObject, null);
minfo.Invoke(dynamicObject, null); }
}
 private String BuildFullCmd(String inputCmdString)
private String BuildFullCmd(String inputCmdString)

 {
{ String fullCmd = String.Empty;
String fullCmd = String.Empty;
 fullCmd += @"
fullCmd += @" namespace Test
namespace Test  {
{  public class DynamicClass
public class DynamicClass {
{ public void MethodInstance()
public void MethodInstance() {
{ " + inputCmdString + @";
" + inputCmdString + @"; }
} }
} }";
}"; return fullCmd;
return fullCmd; }
} }
} }
}
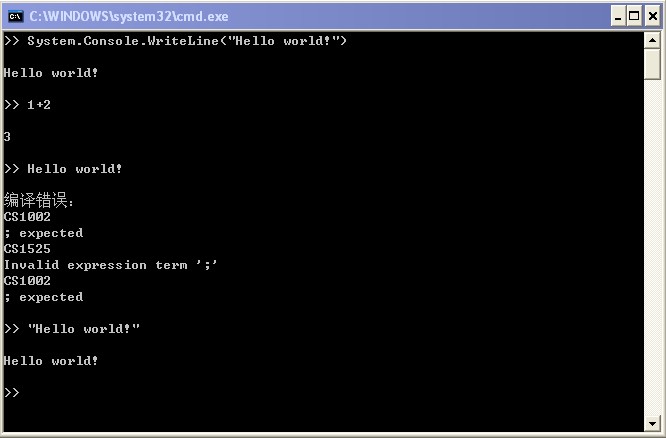
编译执行后就得到一个傻傻的 C# 代码解析器,也可以当一个简单的计算器用:
3、解释器与所解释的代码之间进行变量交互
如果将所解释的代码中的某些变量储存下来,供给以后的代码用,这一解释器的功能又会强大很多。假设这类变量名称以$打头,如:
$myblogname = “http://xiaotie.cnblogs.com”
将在解释器环境中定义(如果该变量未存在)或赋值于(如果该变量已存在)一个名为 myblogname 的字符串变量,指向字符串“http://xiaotie.cnblogs.com”。而,System.Console.WriteLine($myblogname)则取出并打印出字符串该变量所引用的。
简单说来,也就是让所解释的代码中能够初始化并引用解释器中的变量。
如何实现呢?这是本文的重点。
首先,在 Context 类中定义一个SortedDictionary储存变量,并提供索引访问:

 public SortedDictionary<String, Object> Instances
public SortedDictionary<String, Object> Instances  { get; set; }
{ get; set; } public Object this[String instanceName]
public Object this[String instanceName]

 {
{ get
get

 {
{ if (Instances.ContainsKey(instanceName))
if (Instances.ContainsKey(instanceName))

 {
{ return Instances[instanceName];
return Instances[instanceName]; }
} else
else

 {
{ return null;
return null; }
} }
} set
set

 {
{ if (Instances.ContainsKey(instanceName))
if (Instances.ContainsKey(instanceName))

 {
{ Instances.Remove(instanceName);
Instances.Remove(instanceName); }
} Instances.Add(instanceName, value);
Instances.Add(instanceName, value); }
} }
}BuildFullCmd方法改变为:
 private String BuildFullCmd(String inputCmdString)
private String BuildFullCmd(String inputCmdString)

 {
{ String fullCmd = String.Empty;
String fullCmd = String.Empty;
 fullCmd += @"
fullCmd += @" using Test;
using Test;
 public class DynamicClass
public class DynamicClass {
{ private Context m_context;
private Context m_context;
 public void MethodInstance(Context context)
public void MethodInstance(Context context) {
{ m_context = context;
m_context = context; " + inputCmdString + @";
" + inputCmdString + @"; }
} }";
}"; return fullCmd;
return fullCmd; }
}这样,在动态生成的对象中,便可以引用Context对象。
对于inputCmdString 中未定义的外部变量,在第一次遇见时将$argname替换为一个随机生成的内部变量,在代码的最后,将这个内部变量储存在 Context 中。
虽然通过 (Context[argname].GetType())(Context[argname]) 便可引用外部变量 $argname,但是这样引用赋值时,编译器会报错。解决这个问题需要一个新的类:
 public class ObjectHelper<T>
public class ObjectHelper<T>

 {
{ private String m_objName;
private String m_objName;

 public Context Context
public Context Context  { get; private set; }
{ get; private set; }
 public T Obj
public T Obj

 {
{ get
get

 {
{ Object obj = Context[m_objName];
Object obj = Context[m_objName]; return (T)obj;
return (T)obj; }
}
 set
set  { Context[m_objName] = value; }
{ Context[m_objName] = value; } }
}
 public ObjectHelper(Context cxt, String objName)
public ObjectHelper(Context cxt, String objName)

 {
{ m_objName = objName;
m_objName = objName; Context = cxt;
Context = cxt; }
} }
}将inputCmdString中的外部变量$argname统一替换为(new ObjectHelper <m_context[“argname”].GetType()> (m_context, “argname”)).Obj" 即可实现在动态代码中对已定义外部变量的引用。
上述对inputCmdString的预处理代码为:
 Regex re;
Regex re;
 // 处理未初始化的环境变量
// 处理未初始化的环境变量 re = new Regex(@"^(\$)(\w)+");
re = new Regex(@"^(\$)(\w)+"); if (inputCmdString != null)
if (inputCmdString != null)

 {
{ Match m = re.Match(inputCmdString);
Match m = re.Match(inputCmdString); if (m != null && m.Length > 1)
if (m != null && m.Length > 1)

 {
{ String outArgName = inputCmdString.Substring(m.Index, m.Length).Substring(1);
String outArgName = inputCmdString.Substring(m.Index, m.Length).Substring(1); if (this[outArgName] == null)
if (this[outArgName] == null)

 {
{ String innerArgName = "TempArg_" + outArgName;
String innerArgName = "TempArg_" + outArgName; inputCmdString = "var " + inputCmdString.Replace("$" + outArgName, innerArgName);
inputCmdString = "var " + inputCmdString.Replace("$" + outArgName, innerArgName); inputCmdString += ";m_context[\"" + outArgName + "\"]=" + innerArgName + ";";
inputCmdString += ";m_context[\"" + outArgName + "\"]=" + innerArgName + ";"; }
} }
} }
}
 // 处理其它环境变量
// 处理其它环境变量 re = new Regex(@"(\$)(\w)+");
re = new Regex(@"(\$)(\w)+"); IDictionary<String, String> ArgsList = new Dictionary<String, String>();
IDictionary<String, String> ArgsList = new Dictionary<String, String>(); if (inputCmdString != null)
if (inputCmdString != null)

 {
{ MatchCollection mc = re.Matches(inputCmdString);
MatchCollection mc = re.Matches(inputCmdString); if (mc != null)
if (mc != null)

 {
{ foreach (Match m in mc)
foreach (Match m in mc)

 {
{ if (m.Length > 1)
if (m.Length > 1)

 {
{ String outArgName = inputCmdString.Substring(m.Index, m.Length).Substring(1);
String outArgName = inputCmdString.Substring(m.Index, m.Length).Substring(1); if (!ArgsList.ContainsKey(outArgName))
if (!ArgsList.ContainsKey(outArgName))

 {
{ Object obj = this[outArgName];
Object obj = this[outArgName]; if (obj == null) throw new Exception("不存在环境变量" + outArgName);
if (obj == null) throw new Exception("不存在环境变量" + outArgName); String innerArgName = String.Format(@"(new ObjectHelper<{0}>(m_context,""{1}"")).Obj", obj.GetType(), outArgName);
String innerArgName = String.Format(@"(new ObjectHelper<{0}>(m_context,""{1}"")).Obj", obj.GetType(), outArgName); ArgsList.Add(outArgName, innerArgName);
ArgsList.Add(outArgName, innerArgName); }
} }
} }
} }
}
 foreach (String outArg in ArgsList.Keys)
foreach (String outArg in ArgsList.Keys)

 {
{ inputCmdString = inputCmdString.Replace("$" + outArg, ArgsList[outArg]);
inputCmdString = inputCmdString.Replace("$" + outArg, ArgsList[outArg]); }
} }
}这里做了个简化,即定义外部变量的格式必须为 $argname = value,其中 $argname 必须在行首。
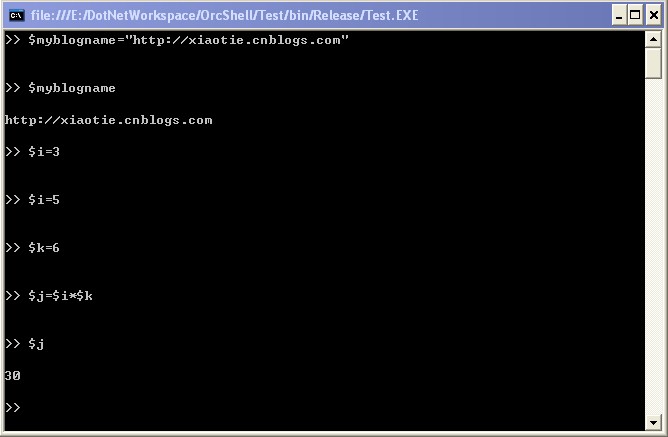
这样,对于:$myblogname = "http://xiaotie.cnblogs.com". 因为 myblogname 变量不存在,被解析为:
var TempArg_myblogname = "http://xiaotie.cnblogs.com";
m_context["myblogname"]=TempArg_myblogname;;
定义后,当再出现 $myblogname,则被解析为 (new ObjectHelper<System.String>(m_context,"myblogname")).Obj;
看看实际执行情况:
4、一个很好很强大的应用—---打入.Net 程序内部,看看其执行情况。
采用上面的方法改进了 OrcShell(OrcShell详情见我前面的随笔: 实现简单的CSharpShell -- OrcShell )。新版 OrcShell 程序于此下载(需要.Net 3.5)。基本上是一个可用的 小型 .Net Framework Shell 了,可以动态的查看、创建、执行 .Net 的类型了。不过,自动提示与完成功能还没有做,使用起来还是较不方便的。
help 指令可以查看常用指令列表:
lsc 列出当前命名空间中的类型和下属命名空间。格式: lsc [name]
dirc 同 lsc
cdc 改变当前的命名空间,格式: cdc [.|..|name]
my 查看全部变量。格式:my。可通过$ArgName来引用变量。
alias 查看全部别名。格式:alias
use 添加命名空间。格式: use [namespace]
unuse 移除命名空间。格式:unuse [namespace]
import 导入程序集,有两种导入方式: "import -f [fullpath]","import [partname]"
摘自:xiaoties