0 简介
0.1 主题

0.2 目标

1. Bootstraping与Bagging策略
1.1 Bootstraping/自助算法


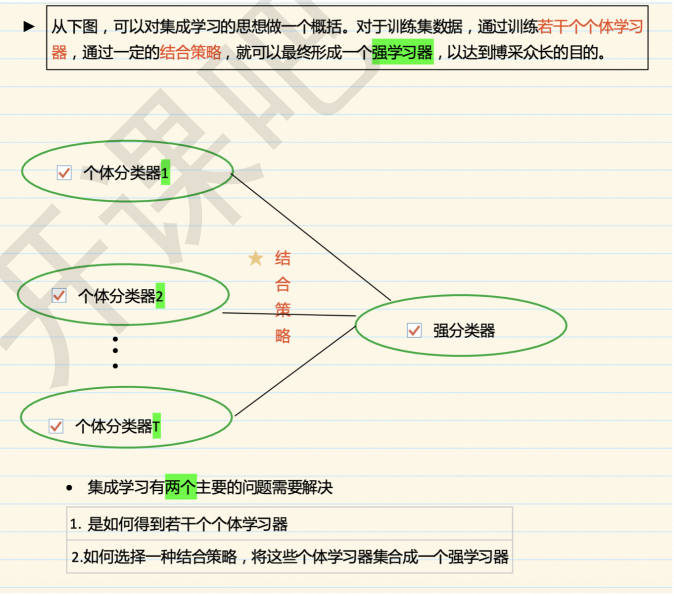


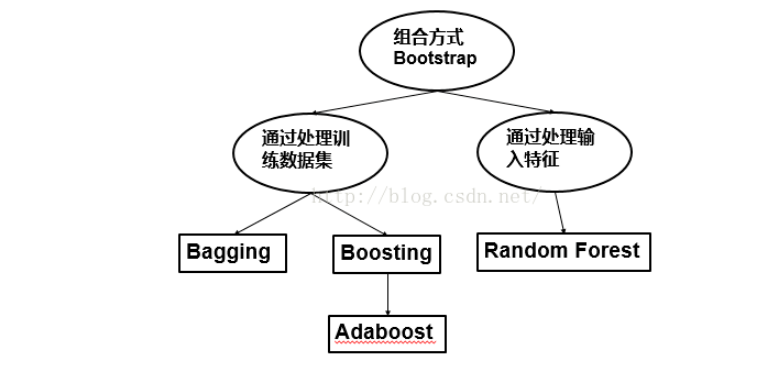
1.2 分类
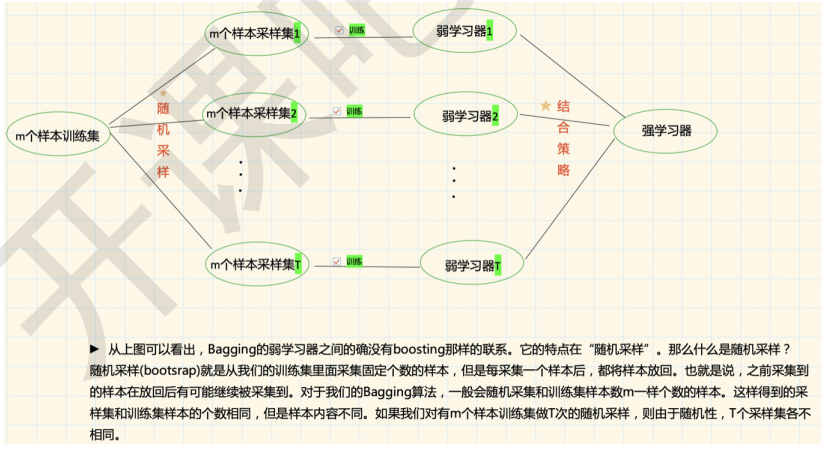
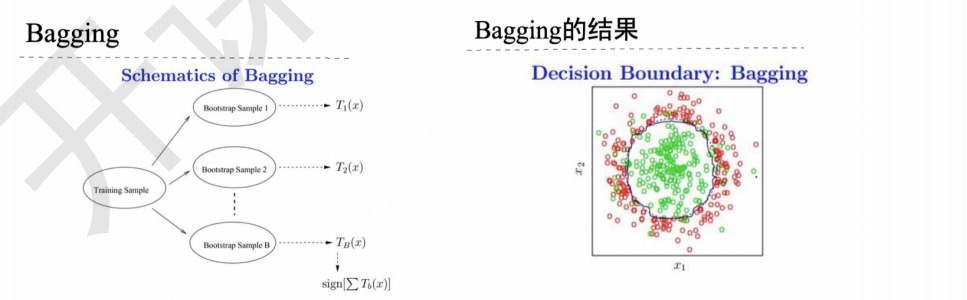
1.3 Bagging/套袋法

1.4 集成学习之结合策略





1.5 代码实验
import numpy as np import os %matplotlib inline import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['axes.labelsize'] = 14 plt.rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 12 plt.rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 12 import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') np.random.seed(42)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 分割数据集 from sklearn.datasets import make_moons # 生成数据 """ 主要参数作用如下: n_numbers:生成样本数量 noise:默认是false,数据集是否加入高斯噪声 random_state:生成随机种子,给定一个int型数据,能够保证每次生成数据相同。 """ X,y = make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.30, random_state=42) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
plt.plot(X[:,0][y==0],X[:,1][y==0],'yo',alpha = 0.6) # 黄色的圆 plt.plot(X[:,0][y==0],X[:,1][y==1],'bs',alpha = 0.6) # 蓝色的矩形
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1a1322ad50>]

from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier # 投票分类器 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.svm import SVC log_clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=42) rnd_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42) svm_clf = SVC(random_state=42) # 投票 参数估计 voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators =[('lr',log_clf),('rf',rnd_clf),('svc',svm_clf)],voting='hard') # voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators =[('lr',log_clf),('rf',rnd_clf),('svc',svm_clf)],voting='soft')
voting_clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
VotingClassifier(estimators=[('lr',
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None,
dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1,
l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100,
multi_class='warn',
n_jobs=None, penalty='l2',
random_state=42, solver='warn',
tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)),
('rf',
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None,
criterion='gini',
max_depth=None,
ma...
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
presort=False,
random_state=42,
splitter='best')),
('svc',
SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None,
coef0=0.0, decision_function_shape='ovr',
degree=3, gamma='auto_deprecated',
kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False,
random_state=42, shrinking=True, tol=0.001,
verbose=False))],
flatten_transform=True, n_jobs=None, voting='hard',
weights=None)
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score # 导入准确率 for clf in (log_clf,rnd_clf,svm_clf,voting_clf): clf.fit(X_train,y_train) y_pred = clf.predict(X_test) print (clf.__class__.__name__,accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred))
LogisticRegression 0.864 DecisionTreeClassifier 0.856 SVC 0.888 VotingClassifier 0.896

from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier """ n_estimators:int, optional (default=10),要集成的基估计器的个数 max_samples: int or float, optional (default=1.0)。 决定从x_train抽取去训练基估计器的样本数量。int 代表抽取数量,float代表抽取比例 bootstrap : boolean, optional (default=True) 决定样本子集的抽样方式(有放回和不放回) n_jobs : int, optional (default=1) random_state:如果int,random_state是随机数生成器使用的种子 """ # 用集成BaggingClassifier分类器 bag_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), n_estimators = 500, max_samples = 100, bootstrap = True, n_jobs = -1, random_state = 42 ) bag_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) y_pred = bag_clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
0.904
# 用随机森林分类器 tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 42) tree_clf.fit(X_train,y_train) y_pred_tree = tree_clf.predict(X_test) accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred_tree)
0.856
2 随机森林



3 扩展点
3.1 使用场景:数据维度相对低(几十维),同时对准确性有较高要求时
3.2 随机森林在现实分析中被大量使用,它相对于决策树,在准确性上有了很大的提升
4.总结
4.1 随机森林的生成步骤

4.2 RF与传统bagging的区别

4.3 RF的优点
