LinkedHashMap概述
JDK对LinkedHashMap的介绍:
Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from HashMap in that it maintains a doubly-linked list running through all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map (insertion-order). Note that insertion order is not affected if a key is re-inserted into the map. (A key k is reinserted into a map m if m.put(k, v) is invoked when m.containsKey(k) would return true immediately prior to the invocation.)
大意是:LinkedHashMap是通过哈希表和链表来实现Map接口,它通过维护一个链表来保证对哈希表迭代时的有序性,而这个有序是指键值对插入的顺序。另外,当向哈希表中重复插入某个键的时候,不会影响到原来的有序性。
继承结构

可以看到LinkedHashMap直接继承了HashMap,复用了HashMap的很多方法,比如put、resize等方法,LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上实现了自己的功能:有序插入。
数据结构
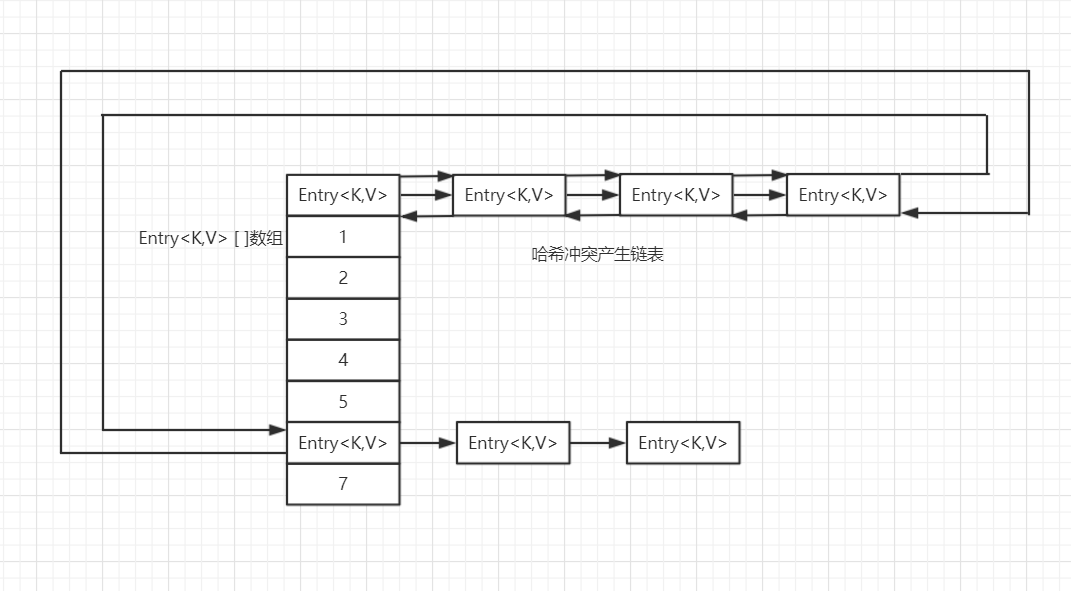
可以看到,LinkedHashMap数据结构相比较于HashMap来说,添加了双向指针,其中before指向节点的前继节点,after指向节点的后继节点,从而将所有的节点串联在一起形成一个双向链表。
内部字段及构造方法
内部字段
//双链表头节点
transient Entry<K,V> head;
//双链表尾节点
transient Entry<K,V> tail;
//accessOrder为true则表示按照基于访问的顺序来排列,意思就是最近使用的entry,
//放在链表的最末尾,为false表示按照基于插入的顺序来排列,后插入的放在链表末尾,不指定默认为false
final boolean accessOrder;
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
//双链表前继、后继节点
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
构造方法
可以看到,LinkedHashMap调用了父类的构造方法,而且默认的accessOrder是false,至于是怎么通过accessOrder控制元素顺序,我们将在方法讲到。
//指定accessOrder的值
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
//按照默认值初始化
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
//指定初始化时的容量
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
//指定初始化时的容量,和扩容的加载因子
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
存储元素
LinkedHashMap并没有重写父类的put方法,所以增加元素调用的是父类方法,具体来说是putVal方法,下面是HashMap的putVal方法:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
...
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
...
afterNodeAccess(e);
...
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
...
LinkedHashMap重写了newNode和回调方法afterNodeAccess、afterNodeInsertion:
//在构建新节点时,构建的是LinkedHashMap.Entry 不再是Node.
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
Entry<K,V> p =
new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
//将新增的节点,连接在链表的尾部
private void linkNodeLast(Entry<K,V> p) {
Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
//若集合是空的
if (last == null)
head = p;
//新节点插到链表顶部
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
//仅仅在accessOrder为true时进行,把当前访问的元素移动到链表尾部
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
Entry<K,V> last;
//当accessOrder的值为true,且e不是尾节点
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
//将e赋值临时节点p, b是e的前一个节点, a是e的后一个节点
Entry<K,V> p =
(Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
//设置p的后一个节点为null,因为执行后p在链表末尾,after肯定为null
p.after = null;
//p的前一个节点不存在,p就是头节点,那么把p放到最后,a就是头节点
if (b == null)
head = a;
//p的前一个节点存在,p放到最后,b的后一个节点指向a
else
b.after = a;
//p的后一个节点存在,p放到最后,a的前一个节点指向a
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
//p的后一个节点不存在
else
last = b;
//只有一个p节点
if (last == null)
head = p;
//last不为空,把p放到last节点后面
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
//p为尾节点
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
//回调函数,新节点插入之后回调 , 根据evict和accessOrder判断是否需要删除最老/早插入的节点。
//如果实现LruCache会用到这个方法。
//removeEldestEntry制定删除规则,JDK8中默认返回false
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
注:HashMap定义了三个回调方法,用于LinkedHashMap维持有序:
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
取出元素
LinkedHashMap的get方法,调用HashMap的getNode方法后,对accessOrder的值进行了判断,我们之前提到:accessOrder为true时进行,把当前访问的元素移动到链表尾部,调用重写的afterNodeAccess方法来调整顺序。
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
删除元素
LinkedHashMap删除元素调用的是弗雷德remove方法,在removeNode设置了回调方法afterNodeRemoval
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
...
afterNodeRemoval(node);
...
LinkedHashMap回调方法的实现:
//在删除节点e时,同步将e从双向链表上删除
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
Entry<K,V> p =
(Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
//待删除节点 p 的前置后置节点都置空,相当于从双链表上取下来
p.before = p.after = null;
//p是尾节点,它的前一个节点为空,那么它的后一个节点做头节点
if (b == null)
head = a;
//p的前一个节点不为空,把它的后一个节点指向a
else
b.after = a;
//同理,a为空,b就是尾节点
if (a == null)
tail = b;
//a不为空,
else
a.before = b;
}
迭代器
abstract class LinkedHashIterator {
//记录下一个迭代的节点
Entry<K,V> next;
//当前迭代的节点
Entry<K,V> current;
//用于fail-fast机制
int expectedModCount;
//迭代器初始化next指向head
LinkedHashIterator() {
next = head;
expectedModCount = modCount;
current = null;
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
//链表方式迭代
final Entry<K,V> nextNode() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
current = e;
//双链表的后继节点节点指向next
next = e.after;
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
利用LinkedHashMap简单实现LRU算法
在查阅相关资料时,都提到利用LinkedHashMap实现LRU算法,首先介绍一下LRU(Least Recently Used)算法:
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。也就是说,当有限的空间已存满数据时,应当把最久没有被访问到的数据淘汰。
根据上面的源码,我们知道当把accessOrder设为true时,LinkedHashMap就会根据访问顺序排序,把最近访问过的元素放在链表的尾部,而没有访问的元素就放在链表头部,只要重写removeEldestEntry设置丢弃头部节点条件就行了。这样就可以简单实现LRU算法了
public class LRUCache<K, V> {
private final int CACHE_SIZE;
private final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTORY = 0.75f;
LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
public LRUCache(int cacheSize) {
CACHE_SIZE = cacheSize;
int capacity = (int)Math.ceil(CACHE_SIZE / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTORY) + 1;
map = new LinkedHashMap<K,V>(capacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTORY, true) {
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return map.size() > cacheSize;
}
};
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
map.put(key, value);
}
public V get(K key) {
return map.get(key);
}
public void remove(K key) {
map.remove(key);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : map.entrySet()) {
stringBuilder.append(String.format("%s: %s ", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache<Integer, Integer> cache = new LRUCache<>(5);
cache.put(1,1);
cache.put(2,2);
cache.put(3,3);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.get(1);
cache.put(4,4);
cache.put(5,5);
cache.put(6,6);
System.out.println(cache);
}
}
结果:
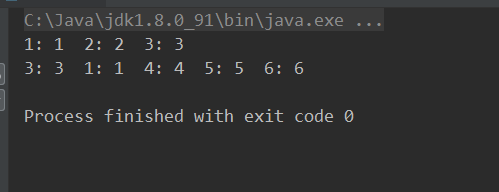
超出范围后,1:1键值对被访问过,最早没有被访问过的2:2键值对就被丢弃了。
总结
LinkedHashMap基于HashMap,所谓大树底下好乘凉,重写了部分代码就能够实现有序插入。LinkedHashMap总体上较为简单,在理解了HashMap的基础上就能很快理解LinkedHashMap的实现。