树状数组小结
背景
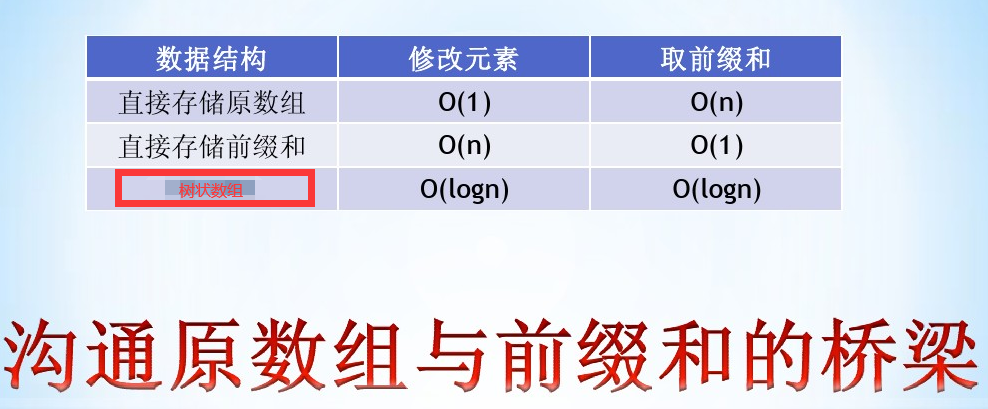
树状数组本质是区间前缀和,但是众所周知,暴力和前缀和各有优缺点……
(图片中本来是线段树的,但是其实差不多吧)
所以诞生了树状数组这个东西。
树状数组分为以下几步
声明部分
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <map> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <vector> #define IL inline #define re register #define LL long long using namespace std; IL LL read() { LL ans = 0; bool fu = 0; char ch = getchar(); while ((ch > '9' || ch < '0') && ch != '-') ch = getchar(); if (ch == '-') fu = 1, ch = getchar(); while (ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') ans = (ans << 3) + (ans << 1) + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar(); if (fu) ans *= -1; return ans; } LL n, m; LL a[1000010]; LL s[1000010]; LL b[1000010];
建树
IL void add(LL x, LL y) { for (; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) a[x] += y; } int main() { n = read(); m = read(); for (re int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ add(i,read()); }
使用了add函数,见下面的单点修改。
当然这是简单的O(nlogn)建树,还有更快的:
更快的建树
n = read(); m = read(); for (re int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ b[i]=read(); a[i]+=b[i]; a[i+(i&-i)]+=a[i]; }
时间复杂度为O(n)
单点修改
IL void add(LL x, LL y) { for (; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) a[x] += y; }
查询前缀和
IL LL ask(LL x) { re LL ans = 0; for (; x; x -= x & (-x)) ans += a[x]; return ans; }
由此可以查询区间。
Code
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <map> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <vector> #define IL inline #define re register #define LL long long using namespace std; IL LL read() { LL ans = 0; bool fu = 0; char ch = getchar(); while ((ch > '9' || ch < '0') && ch != '-') ch = getchar(); if (ch == '-') fu = 1, ch = getchar(); while (ch <= '9' && ch >= '0') ans = (ans << 3) + (ans << 1) + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar(); if (fu) ans *= -1; return ans; } LL n, m; LL a[1000010]; LL s[1000010]; LL b[1000010]; IL void add(LL x, LL y) { for (; x <= n; x += x & (-x)) a[x] += y; } IL LL ask(LL x) { re LL ans = 0; for (; x; x -= x & (-x)) ans += a[x]; return ans; } int main() { n = read(); m = read(); for (re int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ b[i]=read(); a[i]+=b[i]; a[i+(i&-i)]+=a[i]; } LL t, x, y; while (m--) { t = read(); x = read(); y = read(); if (t == 1) add(x, y); else cout << ask(y) - ask(x - 1) << endl; } return 0; }
小结
这应该是最快的RSQ算法了。如果这都过不去请参见zkw线段树……
(我还真就遇到过……)

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #define ll long long 3 #define go(i,j,n,k) for(ll i=j;i<=n;i+=k) 4 #define fo(i,j,n,k) for(ll i=j;i>=n;i-=k) 5 #define mn 1000010 6 inline ll read(){ll x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar(); } 7 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}return x*f;} 8 ll z[mn << 2], M, n, m; 9 inline void update(ll rt){z[rt] = z[rt<<1] + z[rt<<1|1];} 10 inline void build(){for(M=1;M<n+2;M<<=1);go(i,M+1,M+n,1)z[i]=read();fo(i,M,1,1) update(i);} 11 inline void modify(ll now,ll v){for(z[now+=M]+=v,now>>=1;now;now>>=1)update(now);} 12 inline ll query(ll l,ll r){ll ans=0;for(--l+=M,++r+=M;l^r^1;l>>=1,r>>=1){if(~l&1)ans+=z[l^1];if(r&1)ans+=z[r^1];}return ans;} 13 int main(){ 14 n=read(),m=read();build(); 15 go(i,1,m,1){ 16 int s=read(),x=read(),y=read(); 17 if(s==1)modify(x,y);else printf("%lld ",query(x,y)); 18 } 19 }
