临近区域赛,想要系统地过一下知识点,发现了一个好网站,推荐一波。
HDOJ 根据题目类型做的分类(杭电牛逼)
第一次做凸包题
题意就是求凸包构成的多边形周长+一个圆的周长
凸包的概念
在二维欧几里得空间中,凸包可想象为一条刚好包着所有点的橡皮圈。
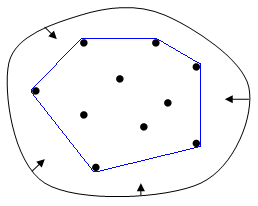
求凸包的方法
《算导》给了两种方法
- Graham扫描法
- Jarvis步近法
详见《算导》
我这边用的是《算法竞赛入门经典-训练指南》里的模板,基于水平序的Andrew算法(是 Graham扫描法的变种,更快且数值稳定性更好)。
int ConvexHull(Point *p,int n,Point *ch)
{
sort(p,p+n);//先比较x坐标,再比较y坐标
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
while(m>1 && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
int k=m;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
{
while(m>k && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
if(n>1)
m--;
return m;
}
实在是太菜了,感觉对的啊,又没能AC
My Wrong Code And Online AC Code
/*
核心:求凸包
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1005;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
//构造函数
Point(double x=0,double y=0 ):x(x),y(y){}
};
typedef Point Vector;// 别名
const double eps=1e-10;
Vector operator + (Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);
}
Vector operator - (Point A,Point B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
Vector operator * (Point A,double p)
{
return Vector(A.x*p,A.y*p);
}
Vector operator / (Point A,double p)
{
return Vector(A.x/p,A.y/p);
}
bool operator <(const Point&a,const Point &b)
{
return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y);
}
//向量判断符号
int dcmp(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps)
return 0;
else
return x<0?-1:1;
}
bool operator ==(const Point&a,const Point &b)
{
return dcmp(a.x-b.x)==0 &&dcmp(a.y-b.y)==0;
}
//点积
double Dot(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.x+A.y*B.y;
}
// 叉积
double Cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
// 判断线段相交,忽略两端点
bool SegmentProperIntersection(Point a1,Point a2,Point b1,Point b2)
{
double c1=Cross(a2-a1,b1-a1), c2=Cross(a2-a1,b2-a1),
c3=Cross(b2-b1,a1-b1), c4=Cross(b2-b1,a2-b1);
return dcmp(c1)*dcmp(c2)<0 && dcmp(c3)*dcmp(c4)<0;
}
// 点是否在线段上
bool OnSegment(Point p,Point a1,Point a2)
{
return dcmp(Cross(a1-p,a2-p))==0&&dcmp(Dot(a1-p,a2-p))<0;
}
int ConvexHull(Point *p,int n,Point *ch)
{
sort(p,p+n);//先比较x坐标,再比较y坐标
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
while(m>1 && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
int k=m;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
{
while(m>k && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
if(n>1)
m--;
return m;
}
double distance (Point a,Point b)
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
Point p[maxn],ch[maxn];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n,l;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&l);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
}
int hlength=ConvexHull(p,n,ch);
double res=0;
for(int i=1;i<hlength;i++)
{
res+=distance(ch[i],ch[i-1]);
}
res+=distance(ch[0],ch[hlength-1]);
res+=2*3.14*l;
printf("%d
",(int)res);
if (t) cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
//又是网上别人AC的代码
//我为什么这么菜
//参考 https://blog.csdn.net/yuanxu716/article/details/73433752
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1005;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double EPS = 1E-6;
int T, N, L;
struct Point{
int x;
int y;
} p[MAXN];
vector<Point> vec;
double dist(Point a, Point b) {
return sqrt((a.x - b.x)*(a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y)*(a.y - b.y));
}
double crossProduct(Point a, Point b, Point c) { // ab * ac
return (b.x - a.x)*(c.y - a.y) - (b.y - a.y)*(c.x - a.x) - 0.0;
}
bool cmp(Point a, Point b) {
double cp = crossProduct(p[0], a, b);
if (cp > EPS) return true;
else if (cp < -EPS) return false;
else return dist(p[0], a) < dist(p[0], b);
}
int findLf(Point p[]) { // find lowest leftest point/vertice.
int index = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (p[i].y < p[index].y) index = i;
else if (p[i].y == p[index].y && p[i].x < p[index].x) index = i;
}
return index;
}
void graham(Point p[]) { // graham algorithm for convex hall.
vec.clear();
vec.push_back(p[0]); vec.push_back(p[1]);
int top = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) { // another way: i <= N, and comment the line below:ans += dist(vec[vec.size() - 1], vec[0]);
while (top >= 1 && crossProduct(vec[top - 1], vec[top], p[i]) <= 0) {
vec.pop_back();
top--;
}
vec.push_back(p[i]);
top++;
}
}
int main() {
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
cin >> N >> L;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
int lf = findLf(p);
swap(p[0], p[lf]);
p[N] = p[0];
sort(p + 1, p + N, cmp);
graham(p);
double ans = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i < (int)vec.size(); i++) {
ans += dist(vec[i - 1], vec[i]);
}
ans += dist(vec[vec.size() - 1], vec[0]);
ans += 2 * PI * L;
cout << (int)round(ans) << endl;
if (T) cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
*/