项目结构
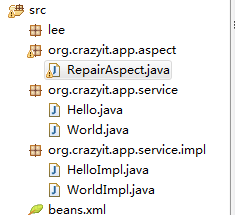
业务代码
@Component("hello")
public class HelloImpl implements Hello
{
// 定义一个简单方法,模拟应用中的业务逻辑方法
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("执行Hello组件的foo()方法");
}
// 定义一个addUser()方法,模拟应用中的添加用户的方法
public int addUser(String name , String pass)
{
System.out.println("执行Hello组件的addUser添加用户:" + name);
if(name.length() < 3 || name.length() > 10)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name参数的长度必须大于3,小于10!");
}
return 20;
}
} @Component("world")
public class WorldImpl implements World
{
// 定义一个简单方法,模拟应用中的业务逻辑方法
public void bar()
{
System.out.println("执行World组件的bar()方法");
}
}定义切面Bean
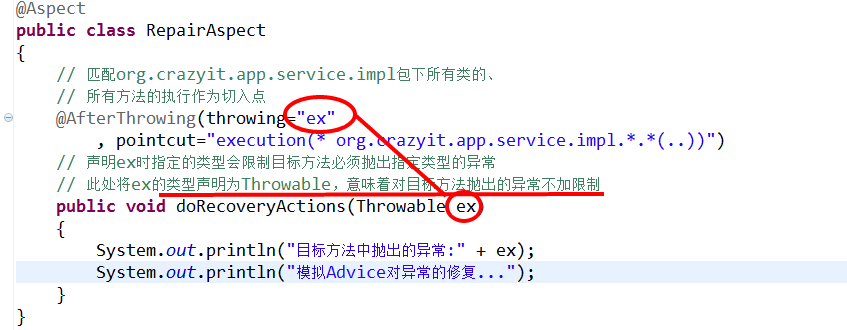
说明:
如果ex的类型是NullPointer-Exception,则只匹配该类型的异常;
@Aspectpublic class RepairAspect{// 匹配org.crazyit.app.service.impl包下所有类的、// 所有方法的执行作为切入点@AfterThrowing(throwing="ex", pointcut="execution(* org.crazyit.app.service.impl.*.*(..))")// 声明ex时指定的类型会限制目标方法必须抛出指定类型的异常// 此处将ex的类型声明为Throwable,意味着对目标方法抛出的异常不加限制public void doRecoveryActions(Throwable ex){System.out.println("目标方法中抛出的异常:" + ex);System.out.println("模拟Advice对异常的修复...");}}
配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 指定自动搜索Bean组件、自动搜索切面类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="org.crazyit.app.service
,org.crazyit.app.aspect">
<context:include-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect"/>
</context:component-scan>
<!-- 启动@AspectJ支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans> 测试
public class BeanTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Hello hello = ctx.getBean("hello" , Hello.class);
hello.foo();
hello.addUser("悟空" , "7788"); //抛出异常--名字长度不够
World world = ctx.getBean("world" , World.class);
world.bar();
}
} 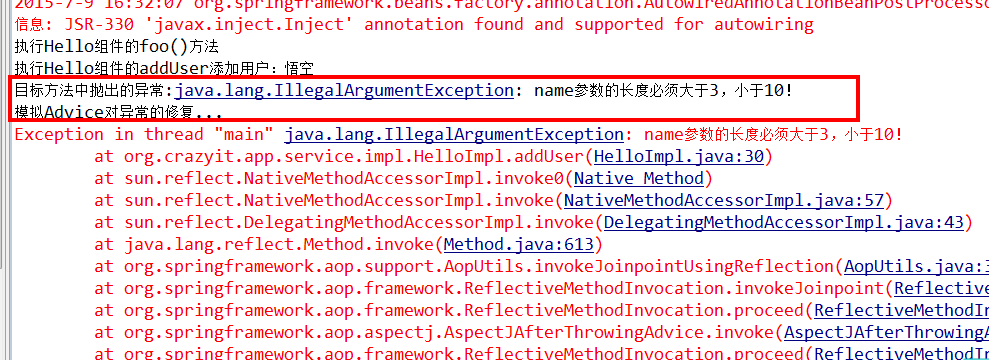
说明:
从上面可以看出,虽然AfterThrowing可以对目标方法的异常进行处理,但这种处理方法和直接使用catch捕捉不同,如下:
- catch:意味着完全处理该异常,如果catch语句中没有重新抛出新异常,则该方法可以正常结束;
- AfterThrowing:虽然处理了该异常,但它不能完全处理异常,该异常依然会传播到上一级调用者。
链接:
《@AfterReturning增强处理简单示例》http://www.cnblogs.com/ssslinppp/p/4633496.html
《@After后向增强处理简单示例》http://www.cnblogs.com/ssslinppp/p/4633427.html
《@Before前向增强处理简单示例》 http://www.cnblogs.com/ssslinppp/default.html?page=7