题目描述
One cow from each of N farms (1 ≤ N ≤ 1000) conveniently numbered 1..N is going to attend the big cow party to be held at farm #X (1 ≤ X ≤ N). A total of M (1 ≤ M ≤ 100,000) unidirectional (one-way roads connects pairs of farms; road i requires Ti (1 ≤ Ti ≤ 100) units of time to traverse.
Each cow must walk to the party and, when the party is over, return to her farm. Each cow is lazy and thus picks an optimal route with the shortest time. A cow's return route might be different from her original route to the party since roads are one-way.
Of all the cows, what is the longest amount of time a cow must spend walking to the party and back?
寒假到了,N头牛都要去参加一场在编号为X(1≤X≤N)的牛的农场举行的派对(1≤N≤1000),农场之间有M(1≤M≤100000)条有向路,每条路长Ti(1≤Ti≤100)。
每头牛参加完派对后都必须回家,无论是去参加派对还是回家,每头牛都会选择最短路径,求这N头牛的最短路径(一个来回)中最长的一条路径长度。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行三个整数N,M, X;
第二行到第M+1行:每行有三个整数Ai,Bi, Ti ,表示有一条从Ai农场到Bi农场的道路,长度为Ti。
输出格式:
一个整数,表示最长的最短路得长度。
输入输出样例
4 8 2 1 2 4 1 3 2 1 4 7 2 1 1 2 3 5 3 1 2 3 4 4 4 2 3
10
说明
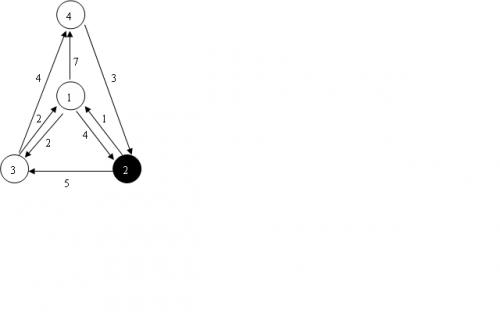
最短路裸题,来回两边spfa
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define inf 2000000000 using namespace std; struct edge{ int v,next,w; }edge1[100001],edge2[100001]; int n,m,s; int head1[1001],head2[1001]; int in[1001]; int d1[1001]; int d2[1001]; int num; void add_edge(int x,int y,int w) { edge1[++num].v=y;edge1[num].w=w;edge1[num].next=head1[x];head1[x]=num; edge2[++num].v=x;edge2[num].w=w;edge2[num].next=head2[y];head2[y]=num; } void spfa(){ queue<int> q; q.push(s); in[s]=1; d1[s]=0; while(!q.empty()){ int t=q.front(); q.pop(); in[t]=0; for(int i=head1[t];i;i=edge1[i].next){ if(d1[t]+edge1[i].w<d1[edge1[i].v]){ d1[edge1[i].v]=d1[t]+edge1[i].w; if(!in[edge1[i].v]){ in[edge1[i].v]=1; q.push(edge1[i].v); } } } } } void spfa2(){ queue<int> q; q.push(s); in[s]=1; d2[s]=0; while(!q.empty()){ int t=q.front(); q.pop(); in[t]=0; for(int i=head2[t];i!=0;i=edge2[i].next){ if(d2[t]+edge2[i].w<d2[edge2[i].v]){ d2[edge2[i].v]=d2[t]+edge2[i].w; if(!in[edge2[i].v]){ in[edge2[i].v]=1; q.push(edge2[i].v); } } } } } int main(){ cin>>n>>m>>s; memset(d1,0x3f,sizeof d1); memset(d2,0x3f,sizeof d2); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int a,b,w; scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&w); add_edge(a,b,w); } spfa(); memset(in,0,sizeof(in)); spfa2(); int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ ans=max(ans,d1[i]+d2[i]); } cout<<ans; return 0; }