题目描述:
城市的天际线是从远处观看该城市中所有建筑物形成的轮廓的外部轮廓。给你所有建筑物的位置和高度,请返回由这些建筑物形成的 天际线 。
每个建筑物的几何信息由数组 buildings 表示,其中三元组 buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti] 表示:
lefti是第i座建筑物左边缘的x坐标。righti是第i座建筑物右边缘的x坐标。heighti是第i座建筑物的高度。
天际线 应该表示为由 “关键点” 组成的列表,格式 [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],...] ,并按 x 坐标 进行 排序 。关键点是水平线段的左端点。列表中最后一个点是最右侧建筑物的终点,y 坐标始终为 0 ,仅用于标记天际线的终点。此外,任何两个相邻建筑物之间的地面都应被视为天际线轮廓的一部分。
注意:输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如 [...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...] 是不正确的答案;三条高度为 5 的线应该在最终输出中合并为一个:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
实例:
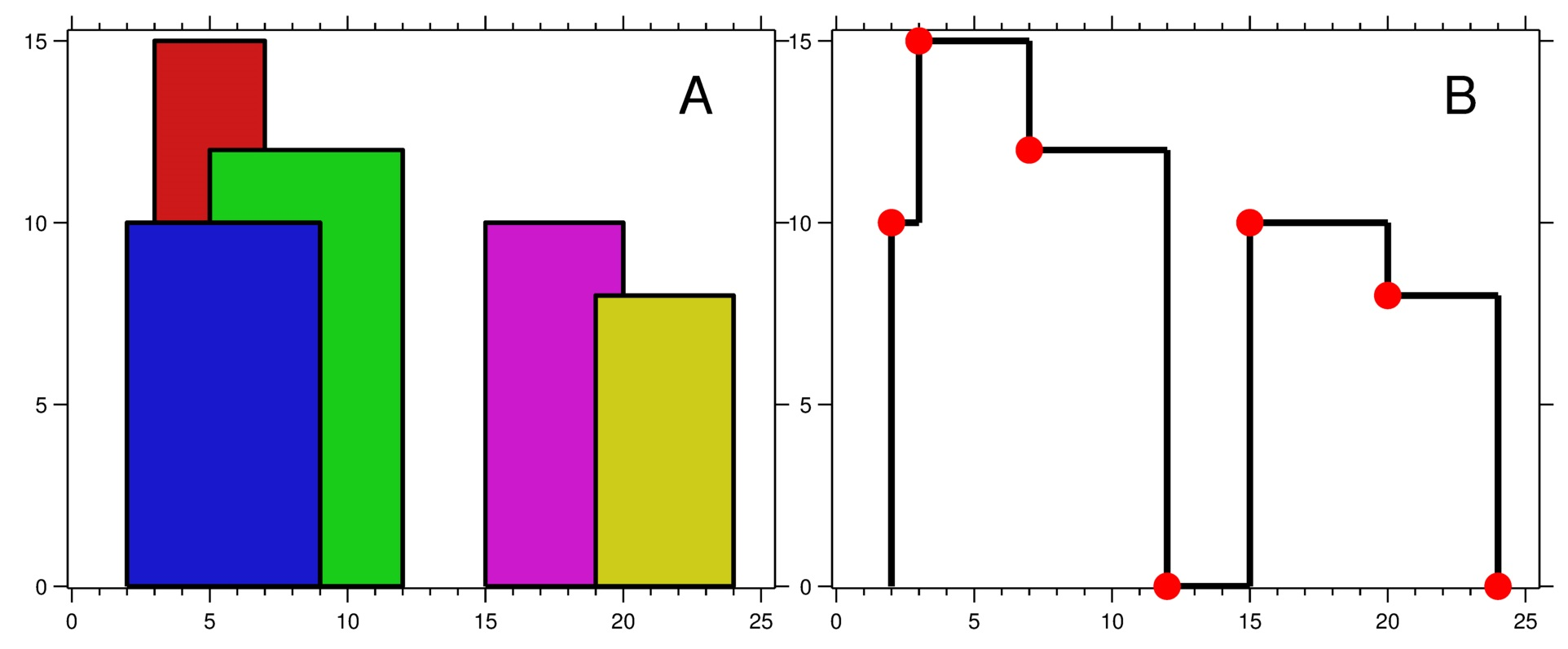
输入:buildings = [[2,9,10],[3,7,15],[5,12,12],[15,20,10],[19,24,8]]
输出:[[2,10],[3,15],[7,12],[12,0],[15,10],[20,8],[24,0]]
解释:
图 A 显示输入的所有建筑物的位置和高度,
图 B 显示由这些建筑物形成的天际线。图 B 中的红点表示输出列表中的关键点。
题源:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/the-skyline-problem/
代码:
class Solution { public: /* struct node { int x,y,h; }; static bool cmp(node a,node b) { if(a.h!=b.h) return a.h>b.h; else if(a.x!=b.x) return a.x<b.x; else return a.y<b.y; } vector<vector<int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) { map<int,int> mp; for(auto i:buildings) { mp[i[0]]=0; mp[i[1]]=0; } node a[10005]; for(int i=0;i<buildings.size();i++) { a[i].x=buildings[i][0]; a[i].y=buildings[i][1]; a[i].h=buildings[i][2]; } sort(a,a+buildings.size(),cmp); for(int i=0;i<buildings.size();i++) { auto l=mp.lower_bound(a[i].x); auto r=mp.upper_bound(a[i].y); //用法不确定 r--; for(auto j=l;j!=r;j++) if(mp[j->first]==0) mp[j->first]=a[i].h; } vector<vector<int>> res; int preh=-1; for(auto i : mp) { if (i.second!=preh) { res.push_back({i.first,i.second}); preh=i.second; } } return res; } */ //tle vector<vector<int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) { multiset<pair<int,int>> boundry; // 这个排序不太能理解 vector<vector<int>> res; multiset<int> height; for(auto i : buildings) { boundry.insert(make_pair(i[0],-i[2])); // 负数 左起点 boundry.insert(make_pair(i[1],i[2])); // 正数,右结束点 } int preh=-1; height.insert(0); // 因为地平线一定存在0 for(auto i:boundry) { if(i.second<0) height.insert(-i.second); //高度起点开始了 else height.erase(height.find(i.second)); int nowhighet=*height.rbegin(); if(nowhighet!=preh)// if(-i[1]!=preh) 应该比现在最高的 如果和前面端点高度不一样,就记录 { res.push_back({i.first,nowhighet}); preh=nowhighet; } } return res; } };
另一种写法:
class Solution { public: vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) { vector<pair<int, int>> high, ans; multiset<int> m; for(auto& a : buildings){ high.push_back({a[0], -a[2]}); high.push_back({a[1], a[2]}); } int pre = 0, cur = 0; sort(high.begin(), high.end()); m.insert(0); for(auto& a : high){ if(a.second < 0) m.insert(-a.second); else m.erase(m.find(a.second)); cur = *m.rbegin(); if(cur != pre){ ans.push_back({a.first, cur}); pre = cur; } } return ans; } };