guavacache源码阅读笔记
官方文档:
https://github.com/google/guava/wiki/CachesExplained
中文版:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/88ec858cc021?from=singlemessage
参考文档:
美团技术团队:《缓存那些事儿》
https://tech.meituan.com/2017/03/17/cache-about.html
缓存在很多数情况下都非常有用,例如,如果计算一个值或者获取一个值时,代价十分昂贵的话,你就可以考虑使用缓存,并且针对某个特定的输入,你可能不止一次需要它的值。
缓存Cache和ConcurrentMap很相像,但又不完全一样。最根本的区别是,ConcurrentMap会保存所有添加到其中的元素直到它们被明确的移除。在另一方面,Cache通常可以配置一个自动化的回收策略去限制它的内存空间。在某些情况下,LoadingCache还是非常有用的,即使它不清除条目。
Guava Cache是Google开源的Java重用工具集库Guava里的一款缓存工具,其主要实现的缓存功能有:
- 自动将entry节点加载进缓存结构中;
- 当缓存的数据超过设置的最大值时,使用LRU算法移除;
- 具备根据entry节点上次被访问或者写入时间计算它的过期机制;
- 缓存的key被封装在WeakReference引用内;
- 缓存的Value被封装在WeakReference或SoftReference引用内;
- 统计缓存使用过程中命中率、异常率、未命中率等统计数据。
Guava Cache的架构设计灵感来源于ConcurrentHashMap,我们前面也提到过,简单场景下可以自行编码通过hashmap来做少量数据的缓存,但是,如果结果可能随时间改变或者是希望存储的数据空间可控的话,自己实现这种数据结构还是有必要的。
核心类图
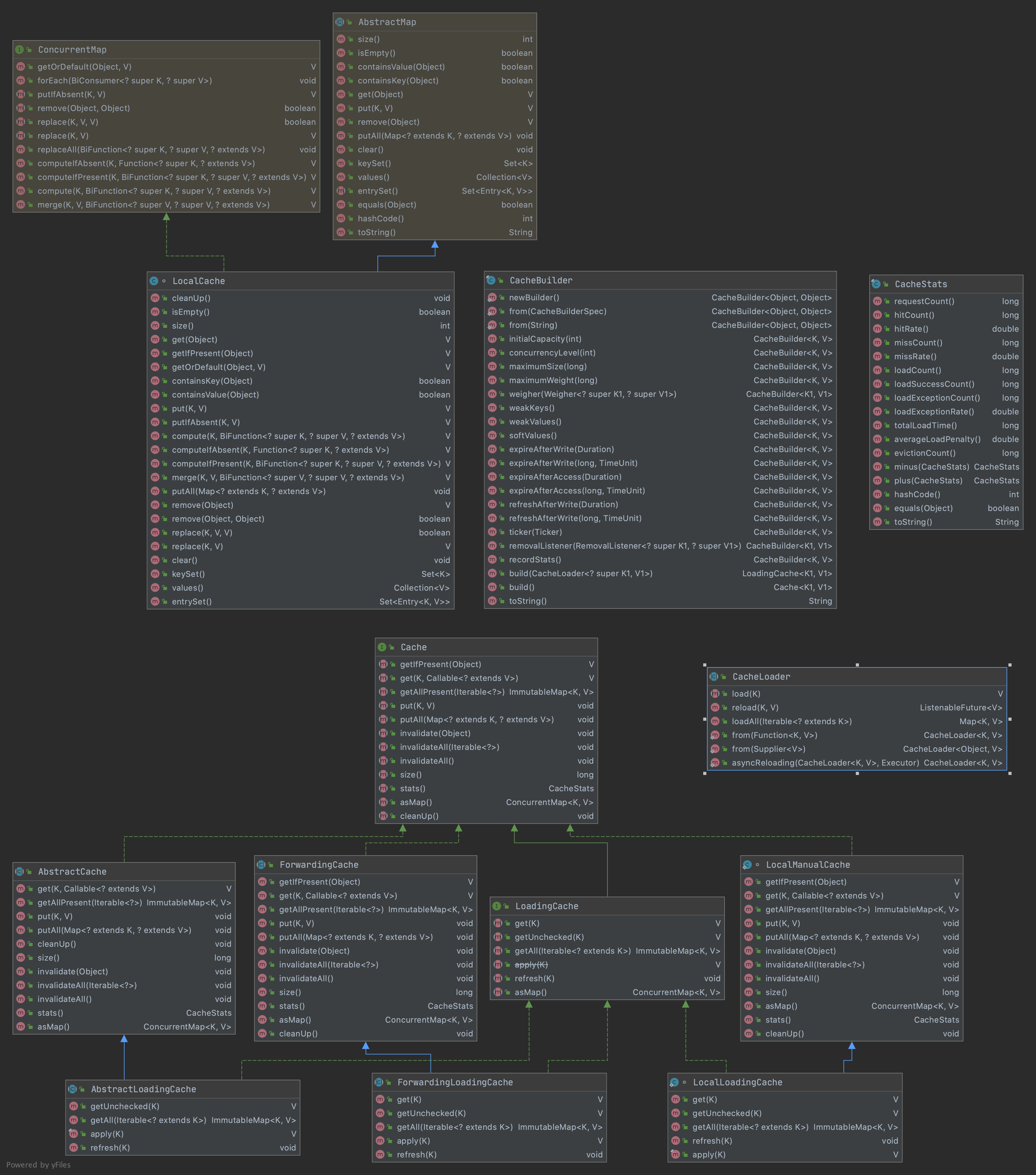
核心类及接口的说明,简单的理解如下:
- Cache接口是Guava对外暴露的缓存接口,提供以下动作:
public interface Cache<K, V> {
/**
* 当key存在缓存中的时候返回value,否则返回null
*/
@Nullable
V getIfPresent(@CompatibleWith("K") Object key);
/**
* 如果key存在缓存中返回value,否则通过loader获取value
* 如果已缓存返回,否则创建,缓存,返回。
*/
V get(K key, Callable<? extends V> loader) throws ExecutionException;
/**
* 返回一个map,这个map包含所有存在缓存中的entries
*/
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAllPresent(Iterable<?> keys);
/**
* 添加一个缓存entry
* @since 11.0
*/
void put(K key, V value);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
/**
* 移除给定的key的缓存entry
* */
void invalidate(@CompatibleWith("K") Object key);
/**
* 移除给定的keys的缓存entries
* @since 11.0
*/
void invalidateAll(Iterable<?> keys);
/**
* 移除所有的缓存
* */
void invalidateAll();
/**
* 返回缓存个数
* */
@CheckReturnValue
long size();
/**
* 统计
*/
@CheckReturnValue
CacheStats stats();
/**
* 返回所有缓存entries的一个视图,一个线程安全的map
*/
@CheckReturnValue
ConcurrentMap<K, V> asMap();
/**
* 根据实现策略,主动清除无效缓存
*/
void cleanUp();
}
-
LoadingCache接口继承自Cache接口,增加了获取不到缓存自动加载的特性。
通过CacheBuilder构造传入自动加载策略CacheLoader
LoadingCache<String, String> loadingCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() .build( new CacheLoader<String, String>() { @Override public String load(String key) throws Exception { //创建加载缓存 return key; } });
public interface LoadingCache<K, V> extends Cache<K, V>, Function<K, V> {
/**
* 获取缓存,获取不到就 创建 缓存 返回
* 显示声明异常ExecutionException 需要手动捕获处理
*/
V get(K key) throws ExecutionException;
/**
* 未检查的获取方法,加载缓存过程中可能抛出异常
* 获取缓存,获取不到就 创建 缓存 返回
*/
V getUnchecked(K key);
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws ExecutionException;
@Deprecated
@Override
V apply(K key);
void refresh(K key);
@Override
ConcurrentMap<K, V> asMap();
}
- LocalManualCache是Cache接口的标准实现,顾名思义手动的获取缓存,当加载不到缓存需手动传入Callable<? extends V> loader 手动加载。在实现细节中,Callable接口也是被封装成匿名CacheLoader,负责加载key到缓存。
@Override
public V get(K key, final Callable<? extends V> valueLoader) throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(valueLoader);
return localCache.get(
key,
new CacheLoader<Object, V>() {
@Override
public V load(Object key) throws Exception {
return valueLoader.call();
}
});
}
- LocalLoadingCache实现LoadingCache接口并继承LocalManualCache,实现自动加载缓存特性。
static class LocalLoadingCache<K, V> extends LocalManualCache<K, V>
implements LoadingCache<K, V> {
LocalLoadingCache(
CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
super(new LocalCache<K, V>(builder, checkNotNull(loader)));
}
// LoadingCache methods
@Override
public V get(K key) throws ExecutionException {
return localCache.getOrLoad(key);
}
@Override
public V getUnchecked(K key) {
try {
return get(key);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(e.getCause());
}
}
@Override
public ImmutableMap<K, V> getAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws ExecutionException {
return localCache.getAll(keys);
}
@Override
public void refresh(K key) {
localCache.refresh(key);
}
@Override
public final V apply(K key) {
return getUnchecked(key);
}
// Serialization Support
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1;
@Override
Object writeReplace() {
return new LoadingSerializationProxy<>(localCache);
}
}
-
LocalCache是核心存储层,是真正意义上数据存放的地方,继承了java.util.AbstractMap同时也实现了ConcurrentMap接口,实现方式参照了1.7版本的ConcurrentHashMap,使用多个segments方式的细粒度锁,在保证线程安全的同时,支持高并发场景需求。LocalCache类似于Map,它是存储键值对的集合,不同的是它还需要处理evict、expire、dynamic load等算法逻辑,需要一些额外信息来实现这些操作。如下图cache的内存数据模型,可以看到,使用ReferenceEntry接口来封装一个键值对,而用ValueReference来封装Value值,之所以用Reference命令,是因为Cache要支持WeakReference Key和SoftReference、WeakReference value。同时每一个segment中维护了writeQueue,accessQueue,keyReferenceQueue,valueReferenceQueue,recencyQueue队列来支持不同回收策略。
大致看一下LocalCache和Segment的成员变量和构造方法(LocalCache这个类实在是太庞大了,里面嵌入了大量的内部类 - -)
-
class LocalCache<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements ConcurrentMap<K, V> { // Constants 常量 /** * 最大容量 1073741824 */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** * 最大允许的segment数 * 65536 */ static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16; // slightly conservative /** * 获取锁最大重试次数 static final int CONTAINS_VALUE_RETRIES = 3; /** * 每个segment在访问操作结束会缓冲一定的次数后执行回收缓存操作 * 驱除阀值 * 它只在每次第 64 次调用postReadCleanup()时执行 * 63 */ static final int DRAIN_THRESHOLD = 0x3F; /** * 每次驱除reference queues队列时 最大驱除个数 */ // TODO(fry): empirically optimize this static final int DRAIN_MAX = 16; // Fields 成员变量 static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(LocalCache.class.getName()); /** * Mask value for indexing into segments. The upper bits of a key's hash code are used to choose * the segment. */ final int segmentMask; /** * Shift value for indexing within segments. Helps prevent entries that end up in the same segment * from also ending up in the same bucket. */ final int segmentShift; /** The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table. */ final Segment<K, V>[] segments; /** The concurrency level. * 最大并发数 * */ final int concurrencyLevel; /** Strategy for comparing keys. * * 比较keys的工具类 * */ final Equivalence<Object> keyEquivalence; /** Strategy for comparing values. * 比较值的工具类 * */ final Equivalence<Object> valueEquivalence; /** Strategy for referencing keys. * * key引用强度 * */ final Strength keyStrength; /** Strategy for referencing values. * * value引用强度 * */ final Strength valueStrength; /** The maximum weight of this map. UNSET_INT if there is no maximum. * 最大容纳大小 * */ final long maxWeight; /** Weigher to weigh cache entries. * 计算每个cache的权重 由用户自己实现 * */ final Weigher<K, V> weigher; /** How long after the last access to an entry the map will retain that entry. * 访问过期时间 * */ final long expireAfterAccessNanos; /** How long after the last write to an entry the map will retain that entry. * 写过期时间 * */ final long expireAfterWriteNanos; /** How long after the last write an entry becomes a candidate for refresh. * 刷新时间 * */ final long refreshNanos; /** Entries waiting to be consumed by the removal listener. * * 移除通知队列 等待被removal listener消费 * */ // TODO(fry): define a new type which creates event objects and automates the clear logic final Queue<RemovalNotification<K, V>> removalNotificationQueue; /** * A listener that is invoked when an entry is removed due to expiration or garbage collection of * soft/weak entries. * * 监听一个entry因为到期回收或被垃圾回收器回收而触发的动作 */ final RemovalListener<K, V> removalListener; /** Measures time in a testable way. * 时间工具 * */ final Ticker ticker; /** Factory used to create new entries. */ final EntryFactory entryFactory; /** * Accumulates global cache statistics. Note that there are also per-segments stats counters which * must be aggregated to obtain a global stats view. * * 统计 */ final StatsCounter globalStatsCounter; /** The default cache loader to use on loading operations. * 缓存自动加载策略 * */ final @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> defaultLoader; /** * Creates a new, empty map with the specified strategy, initial capacity and concurrency level. */ LocalCache( CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) { concurrencyLevel = Math.min(builder.getConcurrencyLevel(), MAX_SEGMENTS); keyStrength = builder.getKeyStrength(); valueStrength = builder.getValueStrength(); keyEquivalence = builder.getKeyEquivalence(); valueEquivalence = builder.getValueEquivalence(); maxWeight = builder.getMaximumWeight(); weigher = builder.getWeigher(); expireAfterAccessNanos = builder.getExpireAfterAccessNanos(); expireAfterWriteNanos = builder.getExpireAfterWriteNanos(); refreshNanos = builder.getRefreshNanos(); removalListener = builder.getRemovalListener(); removalNotificationQueue = (removalListener == NullListener.INSTANCE) ? LocalCache.<RemovalNotification<K, V>>discardingQueue() : new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RemovalNotification<K, V>>(); ticker = builder.getTicker(recordsTime()); entryFactory = EntryFactory.getFactory(keyStrength, usesAccessEntries(), usesWriteEntries()); globalStatsCounter = builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get(); defaultLoader = loader; int initialCapacity = Math.min(builder.getInitialCapacity(), MAXIMUM_CAPACITY); if (evictsBySize() && !customWeigher()) { initialCapacity = (int) Math.min(initialCapacity, maxWeight); } // Find the lowest power-of-two segmentCount that exceeds concurrencyLevel, unless // maximumSize/Weight is specified in which case ensure that each segment gets at least 10 // entries. The special casing for size-based eviction is only necessary because that eviction // happens per segment instead of globally, so too many segments compared to the maximum size // will result in random eviction behavior. int segmentShift = 0; int segmentCount = 1; while (segmentCount < concurrencyLevel && (!evictsBySize() || segmentCount * 20 <= maxWeight)) { ++segmentShift; segmentCount <<= 1; } this.segmentShift = 32 - segmentShift; segmentMask = segmentCount - 1; this.segments = newSegmentArray(segmentCount); int segmentCapacity = initialCapacity / segmentCount; if (segmentCapacity * segmentCount < initialCapacity) { ++segmentCapacity; } int segmentSize = 1; while (segmentSize < segmentCapacity) { segmentSize <<= 1; } if (evictsBySize()) {//使用按大小回收策略 // Ensure sum of segment max weights = overall max weights //计算每个segment平分下来的大小 long maxSegmentWeight = maxWeight / segmentCount + 1; long remainder = maxWeight % segmentCount; for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) { if (i == remainder) { maxSegmentWeight--; } this.segments[i] = createSegment(segmentSize, maxSegmentWeight, builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get()); } } else { for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) { this.segments[i] = createSegment(segmentSize, UNSET_INT, builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get()); } } }// Inner Classes @SuppressWarnings("serial") // This class is never serialized. static class Segment<K, V> extends ReentrantLock { @Weak final LocalCache<K, V> map; /** * 当前segment中生效的元素的个数 * */ volatile int count; /** * 当前segment中生效元素的大小的总和 * */ @GuardedBy("this") long totalWeight; /** * 修改次数 */ int modCount; /** * 扩容阀值 threshold = table.length * loadFactor(0.75) */ int threshold; /** * 当前segment中存放元素的表 * */ volatile @Nullable AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table; /** 允许segment最大大小 */ final long maxSegmentWeight; /** * 存放key已经被垃圾回收的entries的队列 * 根据引用强度(强引用 软引用 虚引用)清除元素策略 */ final @Nullable ReferenceQueue<K> keyReferenceQueue; /** * 存放value已经被垃圾回收的entries的队列 */ final @Nullable ReferenceQueue<V> valueReferenceQueue; /** * recencyQueue 启用条件和accessQueue一样。 * 每次访问操作都会将该entry加入到队列尾部,并更新accessTime。 * 如果遇到写入操作,则将该队列内容排干,如果accessQueue队列中持有该这些 entry,然后将这些entry add到accessQueue队列。 * 注意,因为accessQueue是非线程安全的,所以如果每次访问entry时就将该entry加入到accessQueue队列中,就会导致并发问题。 * 所以这里每次访问先将entry临时加入到并发安全的ConcurrentLinkedQueue队列中,也就是recencyQueue中。 * 在写入的时候通过加锁的方式,将recencyQueue中的数据添加到accessQueue队列中。 * 如此看来,recencyQueue是为 accessQueue服务的 */ final Queue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> recencyQueue; /** * A counter of the number of reads since the last write, used to drain queues on a small * fraction of read operations. */ final AtomicInteger readCount = new AtomicInteger(); /** * 写队列 */ @GuardedBy("this") final Queue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> writeQueue; /** * 访问队列 */ @GuardedBy("this") final Queue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> accessQueue; /** Accumulates cache statistics. */ final StatsCounter statsCounter; Segment( LocalCache<K, V> map, int initialCapacity, long maxSegmentWeight, StatsCounter statsCounter) { this.map = map; this.maxSegmentWeight = maxSegmentWeight; this.statsCounter = checkNotNull(statsCounter); initTable(newEntryArray(initialCapacity)); keyReferenceQueue = map.usesKeyReferences() ? new ReferenceQueue<K>() : null; valueReferenceQueue = map.usesValueReferences() ? new ReferenceQueue<V>() : null; recencyQueue = map.usesAccessQueue() ? new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>() : LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue(); writeQueue = map.usesWriteQueue() ? new WriteQueue<K, V>() : LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue(); accessQueue = map.usesAccessQueue() ? new AccessQueue<K, V>() : LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue(); } ... } -
CacheLoader是一个抽象类,是用户自己实现的缓存加载策略,即负责在获取不到缓存的时候根据策略创建缓存返回。
-
CacheBuilder 由于cache配置项众多,典型的builder模式场景,复杂对象的构造与其对应配置属性表示的分离。
它提供三种方式加载到缓存中。分别是:
- 在构建缓存的时候,使用build方法内部调用CacheLoader方法加载数据;
- callable 、callback方式加载数据;
- 使用粗暴直接的方式,直接Cache.put 加载数据,但自动加载是首选的,因为它可以更容易的推断所有缓存内容的一致性。
build生成器的两种方式都实现了一种逻辑:从缓存中取key的值,如果该值已经缓存过了则返回缓存中的值,如果没有缓存过可以通过某个方法来获取这个值,不同的地方在于cacheloader的定义比较宽泛,是针对整个cache定义的,可以认为是统一的根据key值load value的方法,而callable的方式较为灵活,允许你在get的时候指定load方法。
Guava Cache数据结构图
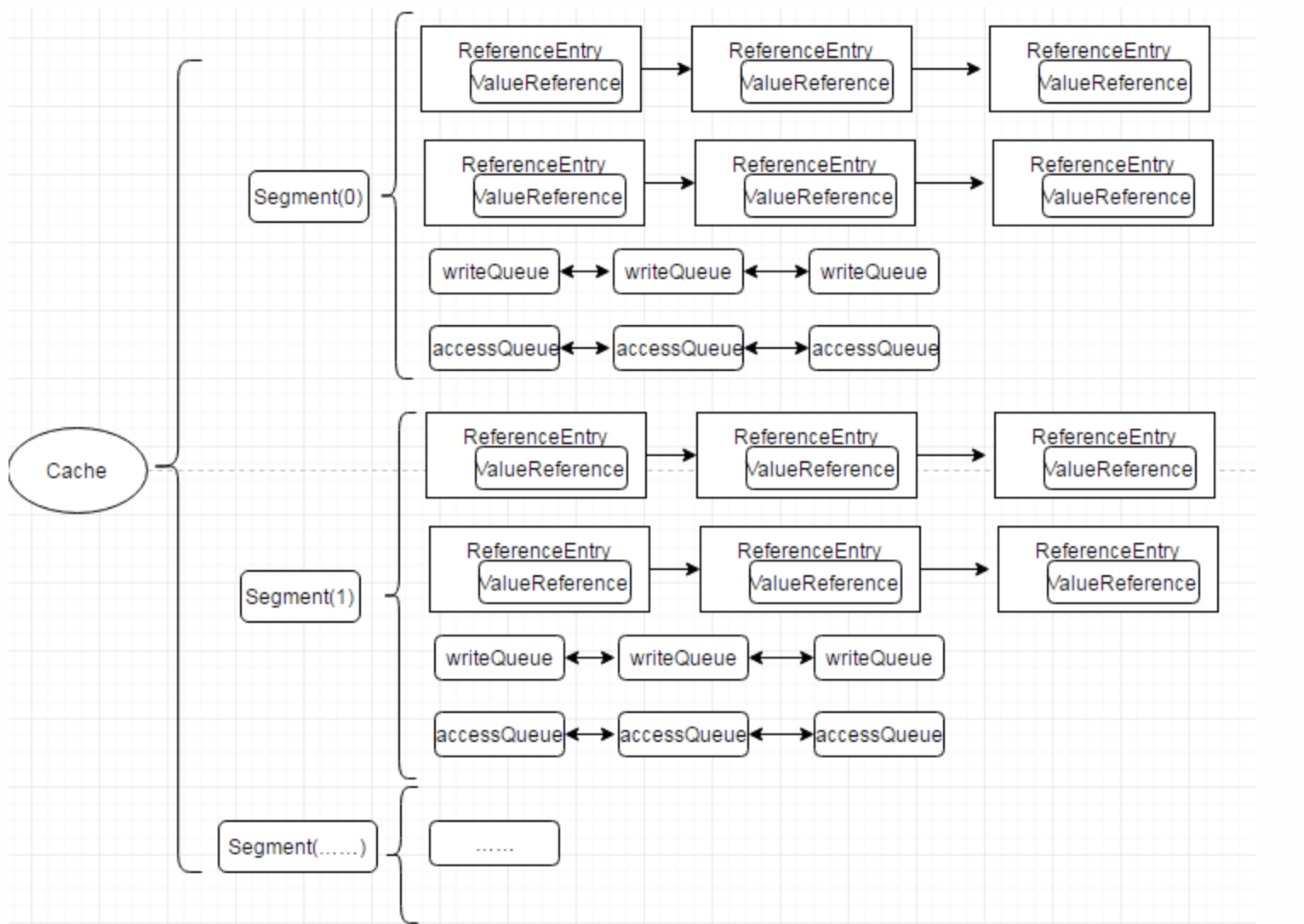
ReferenceEntry是对一个键值对节点的抽象,它包含了key和值的ValueReference抽象类,Cache由多个Segment组成,而每个Segment包含一个ReferenceEntry数组,每个ReferenceEntry数组项都是一条ReferenceEntry链,且一个ReferenceEntry包含key、hash、valueReference、next字段。除了在ReferenceEntry数组项中组成的链,在一个Segment中,所有ReferenceEntry还组成access链(accessQueue)和write链(writeQueue)(后面会介绍链的作用)。ReferenceEntry可以是强引用类型的key,也可以WeakReference类型的key,为了减少内存使用量,还可以根据是否配置了expireAfterWrite、expireAfterAccess、maximumSize来决定是否需要write链和access链确定要创建的具体Reference:StrongEntry、StrongWriteEntry、StrongAccessEntry、StrongWriteAccessEntry等。
对于ValueReference,因为Cache支持强引用的Value、SoftReference Value以及WeakReference Value,因而它对应三个实现类:StrongValueReference、SoftValueReference、WeakValueReference。为了支持动态加载机制,它还有一个LoadingValueReference,在需要动态加载一个key的值时,先把该值封装在LoadingValueReference中,以表达该key对应的值已经在加载了,如果其他线程也要查询该key对应的值,就能得到该引用,并且等待改值加载完成,从而保证该值只被加载一次,在该值加载完成后,将LoadingValueReference替换成其他ValueReference类型。ValueReference对象中会保留对ReferenceEntry的引用,这是因为在Value因为WeakReference、SoftReference被回收时,需要使用其key将对应的项从Segment的table中移除。
WriteQueue和AccessQueue :为了实现最近最少使用算法,Guava Cache在Segment中添加了两条链:write链(writeQueue)和access链(accessQueue),这两条链都是一个双向链表,通过ReferenceEntry中的previousInWriteQueue、nextInWriteQueue和previousInAccessQueue、nextInAccessQueue链接而成,但是以Queue的形式表达。WriteQueue和AccessQueue都是自定义了offer、add(直接调用offer)、remove、poll等操作的逻辑,对offer(add)操作,如果是新加的节点,则直接加入到该链的结尾,如果是已存在的节点,则将该节点链接的链尾;对remove操作,直接从该链中移除该节点;对poll操作,将头节点的下一个节点移除,并返回。
了解了cache的整体数据结构后,再来看下针对缓存的相关操作就简单多了:
- Segment中的evict清除策略操作,是在每一次调用操作的开始和结束时触发清理工作,这样比一般的缓存另起线程监控清理相比,可以减少开销,但如果长时间没有调用方法的话,会导致不能及时的清理释放内存空间的问题。evict主要处理四个Queue:1. keyReferenceQueue;2. valueReferenceQueue;3. writeQueue;4. accessQueue。前两个queue是因为WeakReference、SoftReference被垃圾回收时加入的,清理时只需要遍历整个queue,将对应的项从LocalCache中移除即可,这里keyReferenceQueue存放ReferenceEntry,而valueReferenceQueue存放的是ValueReference,要从Cache中移除需要有key,因而ValueReference需要有对ReferenceEntry的引用,这个前面也提到过了。而对后面两个Queue,只需要检查是否配置了相应的expire时间,然后从头开始查找已经expire的Entry,将它们移除即可。
- Segment中的put操作:put操作相对比较简单,首先它需要获得锁,然后尝试做一些清理工作,接下来的逻辑类似ConcurrentHashMap中的rehash,查找位置并注入数据。需要说明的是当找到一个已存在的Entry时,需要先判断当前的ValueRefernece中的值事实上已经被回收了,因为它们可以是WeakReference、SoftReference类型,如果已经被回收了,则将新值写入。并且在每次更新时注册当前操作引起的移除事件,指定相应的原因:COLLECTED、REPLACED等,这些注册的事件在退出的时候统一调用Cache注册的RemovalListener,由于事件处理可能会有很长时间,因而这里将事件处理的逻辑在退出锁以后才做。最后,在更新已存在的Entry结束后都尝试着将那些已经expire的Entry移除。另外put操作中还需要更新writeQueue和accessQueue的语义正确性。
- Segment带CacheLoader的get操作:1. 先查找table中是否已存在没有被回收、也没有expire的entry,如果找到,并在CacheBuilder中配置了refreshAfterWrite,并且当前时间间隔已经超过这个时间,则重新加载值,否则,直接返回原有的值;2. 如果查找到的ValueReference是LoadingValueReference,则等待该LoadingValueReference加载结束,并返回加载的值;3. 如果没有找到entry,或者找到的entry的值为null,则加锁后,继续在table中查找已存在key对应的entry,如果找到并且对应的entry.isLoading()为true,则表示有另一个线程正在加载,因而等待那个线程加载完成,如果找到一个非null值,返回该值,否则创建一个LoadingValueReference,并调用loadSync加载相应的值,在加载完成后,将新加载的值更新到table中,即大部分情况下替换原来的LoadingValueReference。
测试构建实现不同回收策略的LoadingCache的实例,分析put和get的实现的细节。
- put操作过程解析:
1.测试入口:构建一个实现支持缓存最大个数缓存策略且有自动加载特性的本地缓存LoadingCache。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
debugMaximumSize();
// debugExpireAfterWrite();
// debugExpireAfterAccess();
}
private static void debugMaximumSize() throws Exception{
LoadingCache<String, String> loadingCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(4)
.build(
new CacheLoader<String, String>() {
@Override
public String load(String key) throws Exception {
System.out.println("key:" + key + " is not exist. do nothing.");
return "111";
}
});
loadingCache.put("zhangtianci","good");
loadingCache.get("zhangtianci");
}
2.进入到实现标准接口Cache的LocalManualCache的put的方法,实际通过拥有一个LocalCache的成员变量调用其put方法。
static class LocalManualCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V>, Serializable {
//拥有一个LocalCache的成员变量
final LocalCache<K, V> localCache;
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
localCache.put(key, value);
}
}
3.进入到LocalCache的put方法,对key进行hash定位到segment[]的下标,调用具体对应segment实例的put方法。
class LocalCache{
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
checkNotNull(key);
checkNotNull(value);
int hash = hash(key);
return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, false);
}
..
}
* Callable
*/
public void callablex() throws ExecutionException
{
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000).build();
String result = cache.get("key", new Callable<String>()
{
public String call()
{
return "result";
}
});
System.out.println(result);
}
4.进入到segment的put方法
1.上锁,写前清理操作,回收被垃圾回收的entries和过期的entries
2.判断segment是否需要扩容
3.确定写入元素在table中的下标并拿到该下标的头元素,遍历该链表找到这个entry,覆盖或不做处理或新增。
4.解锁,写后清理操作,将removalNotificationQueue队列里面注册的移除事件,一一触发相应的动作。
@Nullable
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
lock();
try {
long now = map.ticker.read();
//写操作前
// 1.驱逐参考队列
// 2.驱逐过期entries
preWriteCleanup(now);
//判断segment是否需要扩容
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (newCount > this.threshold) { // ensure capacity
expand();
newCount = this.count + 1;
}
//确定写入元素在table中的下标并拿到该下标的头元素
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
// Look for an existing entry.
//遍历该链表 找到这个entry
for (ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = e.getKey();
if (e.getHash() == hash
&& entryKey != null
&& map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
// We found an existing entry.
//找到该entry
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
V entryValue = valueReference.get();
if (entryValue == null) {//entryValue被垃圾回收了
++modCount;
if (valueReference.isActive()) {
enqueueNotification(
key, hash, entryValue, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.COLLECTED);
setValue(e, key, value, now);
newCount = this.count; // count remains unchanged
} else {
setValue(e, key, value, now);
newCount = this.count + 1;
}
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
evictEntries(e);
return null;
} else if (onlyIfAbsent) {
// Mimic
// "if (!map.containsKey(key)) ...
// else return map.get(key);
//仅更新access queue队列的顺序
recordLockedRead(e, now);
return entryValue;
} else {
// clobber existing entry, count remains unchanged
//覆盖现有条目,计数保持不变
++modCount;
enqueueNotification(
key, hash, entryValue, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.REPLACED);
setValue(e, key, value, now);
evictEntries(e);
return entryValue;
}
}
}
// Create a new entry.
//没有找到entry 创建一个新的entry
++modCount;
ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry = newEntry(key, hash, first);
setValue(newEntry, key, value, now);
table.set(index, newEntry);
newCount = this.count + 1;
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
evictEntries(newEntry);
return null;
} finally {
unlock();
//并且在每次更新时注册当前操作引起的移除事件,指定相应的原因:COLLECTED、REPLACED等,
// 这些注册的事件在退出的时候统一调用Cache注册的RemovalListener,
// 由于事件处理可能会有很长时间,因而这里将事件处理的逻辑在退出锁以后才做。
postWriteCleanup();
}
}
看看写前清理操作的实现细节:
加锁,驱逐参考队列和驱逐过期entries
@GuardedBy("this")
void preWriteCleanup(long now) {
runLockedCleanup(now);
}
void runLockedCleanup(long now) {
if (tryLock()) {
try {
//驱逐参考队列
drainReferenceQueues();
//驱逐过期entries
expireEntries(now); // calls drainRecencyQueue
readCount.set(0);
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}
驱逐参考队列实现细节
/**
* 驱逐参考队列
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainReferenceQueues() {
if (map.usesKeyReferences()) {
drainKeyReferenceQueue();
}
if (map.usesValueReferences()) {
drainValueReferenceQueue();
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainKeyReferenceQueue() {
Reference<? extends K> ref;
int i = 0;
while ((ref = keyReferenceQueue.poll()) != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry = (ReferenceEntry<K, V>) ref;
map.reclaimKey(entry);
if (++i == DRAIN_MAX) { //此次操作最多清除16个
break;
}
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainValueReferenceQueue() {
Reference<? extends V> ref;
int i = 0;
while ((ref = valueReferenceQueue.poll()) != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = (ValueReference<K, V>) ref;
map.reclaimValue(valueReference);
if (++i == DRAIN_MAX) {
break;
}
}
}
驱逐过期entries实现细节
/**
* 驱逐过期entries
* @param now
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
void expireEntries(long now) {
//清空最近使用队列
//recencyQueue 是在访问时维护的一个并发安全的最近使用队列
drainRecencyQueue();
//清空writeQueue所有过期的entry
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
while ((e = writeQueue.peek()) != null && map.isExpired(e, now)) {
if (!removeEntry(e, e.getHash(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
//清空accessQueue所有过期的entry
while ((e = accessQueue.peek()) != null && map.isExpired(e, now)) {
if (!removeEntry(e, e.getHash(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}
/**
* 排干最近使用队列,将队列放到accessQueue中
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainRecencyQueue() {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
while ((e = recencyQueue.poll()) != null) {
if (accessQueue.contains(e)) {
accessQueue.add(e);
}
}
}
移除entry实现细节:
@VisibleForTesting
@GuardedBy("this")
boolean removeEntry(ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, int hash, RemovalCause cause) {
//获取entry当前segement中所属链表的头元素
int newCount = this.count - 1;
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
//遍历链表
for (ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
if (e == entry) {
++modCount;
ReferenceEntry<K, V> newFirst =
removeValueFromChain(
first,
e,
e.getKey(),
hash,
e.getValueReference().get(),
e.getValueReference(),
cause);
newCount = this.count - 1;
table.set(index, newFirst);
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@GuardedBy("this")
@Nullable
ReferenceEntry<K, V> removeValueFromChain(
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first,
ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry,
@Nullable K key,
int hash,
V value,
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference,
RemovalCause cause) {
enqueueNotification(key, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), cause);
writeQueue.remove(entry); //维护writeQueue
accessQueue.remove(entry); //维护accessQueue
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
valueReference.notifyNewValue(null);
return first;
} else {
return removeEntryFromChain(first, entry);//从实际存放数据的table中移除该entry
}
}
put操作替换value实现细节:
@GuardedBy("this")
void setValue(ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, K key, V value, long now) {
ValueReference<K, V> previous = entry.getValueReference();
int weight = map.weigher.weigh(key, value);
checkState(weight >= 0, "Weights must be non-negative");
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference =
map.valueStrength.referenceValue(this, entry, value, weight);//根据回收策略(value的强/弱/软引用)new 一个ValueReference
entry.setValueReference(valueReference);
recordWrite(entry, weight, now);//记录写,是否需要记录访问时间和写时间,并往加入到accessQueue和writeQueue
previous.notifyNewValue(value);
}
/**
记录写操作,是否需要记录访问时间和写时间,并往加入到accessQueue和writeQueue
*/
void recordWrite(ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, int weight, long now) {
// we are already under lock, so drain the recency queue immediately
drainRecencyQueue();
totalWeight += weight;
if (map.recordsAccess()) {
entry.setAccessTime(now);
}
if (map.recordsWrite()) {
entry.setWriteTime(now);
}
accessQueue.add(entry);
writeQueue.add(entry);
}
写后清理操作实现细节:
void postWriteCleanup() {
runUnlockedCleanup();
}
void runUnlockedCleanup() {
// locked cleanup may generate notifications we can send unlocked
if (!isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
map.processPendingNotifications();
}
}
}
void processPendingNotifications() {
RemovalNotification<K, V> notification;
while ((notification = removalNotificationQueue.poll()) != null) {
try {
removalListener.onRemoval(notification);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Exception thrown by removal listener", e);
}
}
}
- get操作过程解析:
进入到实现LoadingCache接口的有自动加载特性的LocalLoadingCache的get方法
static class LocalLoadingCache<K, V> extends LocalManualCache<K, V>
implements LoadingCache<K, V> {
LocalLoadingCache(
CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
super(new LocalCache<K, V>(builder, checkNotNull(loader)));
}
// LoadingCache methods
@Override
public V get(K key) throws ExecutionException {
return localCache.getOrLoad(key);
}
其实是调用成员变量localCache的getOrLoad(key)方法,对key进行hash,定位到segment[]下标,调用segment的get方法
V get(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
int hash = hash(checkNotNull(key));
return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash, loader);
}
V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(key);
checkNotNull(loader);
try {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile
// don't call getLiveEntry, which would ignore loading values
//获取该entry
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getEntry(key, hash);
if (e != null) {
long now = map.ticker.read();
V value = getLiveValue(e, now);//判断entry的value是否有效
if (value != null) {
recordRead(e, now);
statsCounter.recordHits(1);
return scheduleRefresh(e, key, hash, value, now, loader);
}
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {//是否正在加载
return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
}
}
}
// at this point e is either null or expired;
//创建 缓存 返回
return lockedGetOrLoad(key, hash, loader);
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
Throwable cause = ee.getCause();
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw new ExecutionError((Error) cause);
} else if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause);
}
throw ee;
} finally {
postReadCleanup();//读后清理操作
}
}
未完待续...
总体来看,Guava Cache基于ConcurrentHashMap的优秀设计借鉴,在高并发场景支持和线程安全上都有相应的改进策略,使用Reference引用命令,提升高并发下的数据……访问速度并保持了GC的可回收,有效节省空间;同时,write链和access链的设计,能更灵活、高效的实现多种类型的缓存清理策略,包括基于容量的清理、基于时间的清理、基于引用的清理等;编程式的build生成器管理,让使用者有更多的自由度,能够根据不同场景设置合适的模式。