前提
之前在写一个通用HTTP组件的时候遇到过媒体(Media)类型multipart/form-data的封装问题,这篇文章主要简单介绍一下HTTP协议中媒体类型multipart/form-data的定义、应用和简单实现。
multipart/form-data的定义
媒体类型multipart/form-data遵循multipart MIME数据流定义(该定义可以参考Section 5.1 - RFC2046),大概含义就是:媒体类型multipart/form-data的数据体由多个部分组成,这些部分由一个固定边界值(Boundary)分隔。
multipart/form-data请求体布局
multipart/form-data请求体的布局如下:
# 请求头 - 这个是必须的,需要指定Content-Type为multipart/form-data,指定唯一边界值
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=${Boundary}
# 请求体
--${Boundary}
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name of file"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
bytes of file
--${Boundary}
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name of pdf"; filename="pdf-file.pdf"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
bytes of pdf file
--${Boundary}
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="key"
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8
text encoded in UTF-8
--${Boundary}--
媒体类型multipart/form-data相对于其他媒体类型如application/x-www-form-urlencoded等来说,最明显的不同点是:
- 请求头的
Content-Type属性除了指定为multipart/form-data,还需要定义boundary参数 - 请求体中的请求行数据是由多部分组成,
boundary参数的值模式--${Boundary}用于分隔每个独立的分部 - 每个部分必须存在请求头
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="${PART_NAME}";,这里的${PART_NAME}需要进行URL编码,另外filename字段可以使用,用于表示文件的名称,但是其约束性比name属性低(因为并不确认本地文件是否可用或者是否有异议) - 每个部分可以单独定义
Content-Type和该部分的数据体 - 请求体以
boundary参数的值模式--${Boundary}--作为结束标志
{% note warning flat %}
RFC7578中提到两个multipart/form-data过期的使用方式,其一是Content-Transfer-Encoding请求头的使用,这里也不展开其使用方式,其二是请求体中单个表单属性传输多个二进制文件的方式建议换用multipart/mixed(一个"name"对应多个二进制文件的场景)
{% endnote %}
特殊地:
- 如果某个部分的内容为文本,其的
Content-Type为text/plain,可指定对应的字符集,如Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8 - 可以通过
_charset_属性指定默认的字符集,用法如下:
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="_charset_"
UTF-8
--ABCDE--
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="field"
...text encoded in UTF-8...
ABCDE--
Boundary参数取值规约
Boundary参数取值规约如下:
Boundary的值必须以英文中间双横杠--开头,这个--称为前导连字符Boundary的值除了前导连字符以外的部分不能超过70个字符Boundary的值不能包含HTTP协议或者URL禁用的特殊意义的字符,例如英文冒号:等- 每个
--${Boundary}之前默认强制必须为CRLF,如果某一个部分的文本类型请求体以CRLF结尾,那么在请求体的二级制格式上,必须显式存在两个CRLF,如果某一个部分的请求体不以CRLF结尾,可以只存在一个CRLF,这两种情况分别称为分隔符的显式类型和隐式类型,说的比较抽象,见下面的例子:
# 请求头
Content-type: multipart/data; boundary="--abcdefg"
--abcdefg
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="x"
Content-type: text/plain; charset=ascii
It does NOT end with a linebreak # <=== 这里没有CRLF,隐式类型
--abcdefg
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="y"
Content-type: text/plain; charset=ascii
It DOES end with a linebreak # <=== 这里有CRLF,显式类型
--abcdefg
## 直观看隐式类型的CRLF
It does NOT end with a linebreak CRLF --abcdefg
## 直观看显式类型的CRLF
It DOES end with a linebreak CRLF CRLF --abcdefg
实现multipart/form-data媒体类型的POST请求
这里只针对低JDK版本的HttpURLConnection和高JDK版本内置的HttpClient编写multipart/form-data媒体类型的POST请求的HTTP客户端,其他如自定义Socket实现可以依照类似的思路完成。先引入org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:2.6.0做一个简单的控制器方法:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@PostMapping(path = "/test")
public ResponseEntity<?> test(MultipartHttpServletRequest request) {
return ResponseEntity.ok("ok");
}
}
Postman的模拟请求如下:

后台控制器得到的请求参数如下:
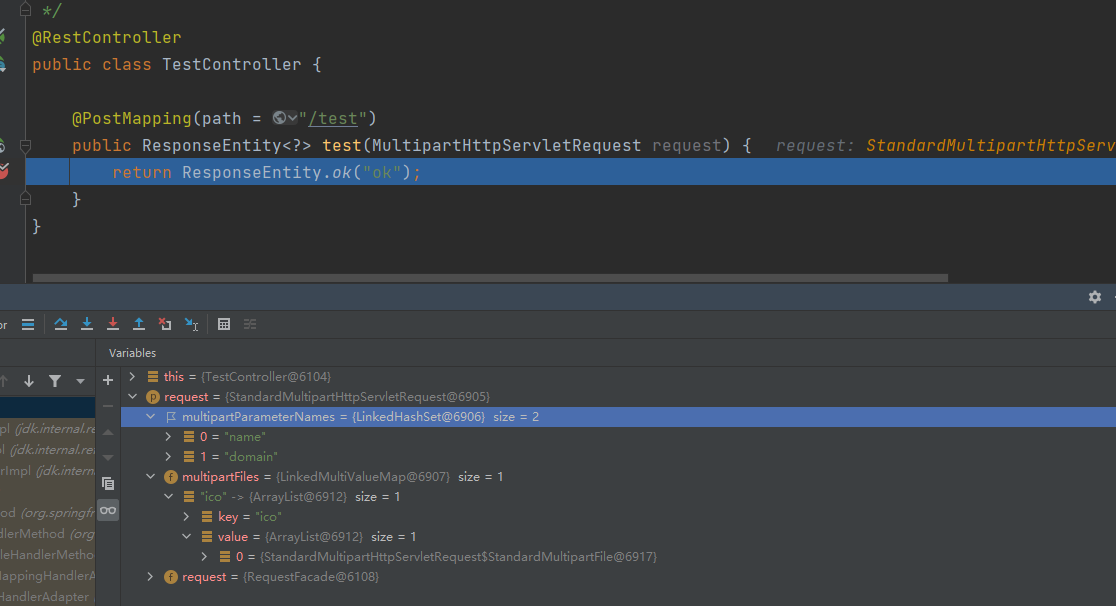
后面编写的客户端可以直接调用此接口进行调试。
封装请求体转换为字节容器的模块
这里的边界值全用显式实现,边界值直接用固定前缀加上UUID生成即可。简单实现过程中做了一些简化:
- 只考虑提交文本表单数据和二进制(文件)表单数据
- 基于上一点,每个部分都明确指定
Content-Type这个请求头 - 文本编码固定为
UTF-8
编写一个MultipartWriter:
public class MultipartWriter {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
private static final byte[] FIELD_SEP = ": ".getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
private static final byte[] CR_LF = "\r\n".getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
private static final String TWO_HYPHENS_TEXT = "--";
private static final byte[] TWO_HYPHENS = TWO_HYPHENS_TEXT.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
private static final String CONTENT_DISPOSITION_KEY = "Content-Disposition";
private static final String CONTENT_TYPE_KEY = "Content-Type";
private static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = "multipart/form-data; boundary=";
private static final String DEFAULT_BINARY_CONTENT_TYPE = "application/octet-stream";
private static final String DEFAULT_TEXT_CONTENT_TYPE = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8";
private static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_DISPOSITION_VALUE = "form-data; name=\"%s\"";
private static final String FILE_CONTENT_DISPOSITION_VALUE = "form-data; name=\"%s\"; filename=\"%s\"";
private final Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>(8);
private final List<AbstractMultipartPart> parts = new ArrayList<>();
private final String boundary;
private MultipartWriter(String boundary) {
this.boundary = Objects.isNull(boundary) ? TWO_HYPHENS_TEXT +
UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "") : boundary;
this.headers.put(CONTENT_TYPE_KEY, DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE + this.boundary);
}
public static MultipartWriter newMultipartWriter(String boundary) {
return new MultipartWriter(boundary);
}
public static MultipartWriter newMultipartWriter() {
return new MultipartWriter(null);
}
public MultipartWriter addHeader(String key, String value) {
if (!CONTENT_TYPE_KEY.equalsIgnoreCase(key)) {
headers.put(key, value);
}
return this;
}
public MultipartWriter addTextPart(String name, String text) {
parts.add(new TextPart(String.format(DEFAULT_CONTENT_DISPOSITION_VALUE, name), DEFAULT_TEXT_CONTENT_TYPE, this.boundary, text));
return this;
}
public MultipartWriter addBinaryPart(String name, byte[] bytes) {
parts.add(new BinaryPart(String.format(DEFAULT_CONTENT_DISPOSITION_VALUE, name), DEFAULT_BINARY_CONTENT_TYPE, this.boundary, bytes));
return this;
}
public MultipartWriter addFilePart(String name, File file) {
parts.add(new FilePart(String.format(FILE_CONTENT_DISPOSITION_VALUE, name, file.getName()), DEFAULT_BINARY_CONTENT_TYPE, this.boundary, file));
return this;
}
private static void writeHeader(String key, String value, OutputStream out) throws IOException {
writeBytes(key, out);
writeBytes(FIELD_SEP, out);
writeBytes(value, out);
writeBytes(CR_LF, out);
}
private static void writeBytes(String text, OutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.write(text.getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET));
}
private static void writeBytes(byte[] bytes, OutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.write(bytes);
}
interface MultipartPart {
void writeBody(OutputStream os) throws IOException;
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public static abstract class AbstractMultipartPart implements MultipartPart {
protected final String contentDispositionValue;
protected final String contentTypeValue;
protected final String boundary;
protected String getContentDispositionValue() {
return contentDispositionValue;
}
protected String getContentTypeValue() {
return contentTypeValue;
}
protected String getBoundary() {
return boundary;
}
public final void write(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
writeBytes(TWO_HYPHENS, out);
writeBytes(getBoundary(), out);
writeBytes(CR_LF, out);
writeHeader(CONTENT_DISPOSITION_KEY, getContentDispositionValue(), out);
writeHeader(CONTENT_TYPE_KEY, getContentTypeValue(), out);
writeBytes(CR_LF, out);
writeBody(out);
writeBytes(CR_LF, out);
}
}
public static class TextPart extends AbstractMultipartPart {
private final String text;
public TextPart(String contentDispositionValue,
String contentTypeValue,
String boundary,
String text) {
super(contentDispositionValue, contentTypeValue, boundary);
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public void writeBody(OutputStream os) throws IOException {
os.write(text.getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET));
}
@Override
protected String getContentDispositionValue() {
return contentDispositionValue;
}
@Override
protected String getContentTypeValue() {
return contentTypeValue;
}
}
public static class BinaryPart extends AbstractMultipartPart {
private final byte[] content;
public BinaryPart(String contentDispositionValue,
String contentTypeValue,
String boundary,
byte[] content) {
super(contentDispositionValue, contentTypeValue, boundary);
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public void writeBody(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.write(content);
}
}
public static class FilePart extends AbstractMultipartPart {
private final File file;
public FilePart(String contentDispositionValue,
String contentTypeValue,
String boundary,
File file) {
super(contentDispositionValue, contentTypeValue, boundary);
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public void writeBody(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file)) {
final byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int l;
while ((l = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, l);
}
out.flush();
}
}
}
public void forEachHeader(BiConsumer<String, String> consumer) {
headers.forEach(consumer);
}
public void write(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
if (!parts.isEmpty()) {
for (AbstractMultipartPart part : parts) {
part.write(out);
}
}
writeBytes(TWO_HYPHENS, out);
writeBytes(this.boundary, out);
writeBytes(TWO_HYPHENS, out);
writeBytes(CR_LF, out);
}
}
这个类已经封装好三种不同类型的部分请求体实现,forEachHeader()方法用于遍历请求头,而最终的write()方法用于把请求体写入到OutputStream中。
HttpURLConnection实现
实现代码如下(只做最简实现,没有考虑容错和异常处理):
public class HttpURLConnectionApp {
private static final String URL = "http://localhost:9099/test";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MultipartWriter writer = MultipartWriter.newMultipartWriter();
writer.addTextPart("name", "throwable")
.addTextPart("domain", "vlts.cn")
.addFilePart("ico", new File("I:\\doge_favicon.ico"));
DataOutputStream requestPrinter = new DataOutputStream(System.out);
writer.write(requestPrinter);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) new java.net.URL(URL).openConnection();
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");
connection.addRequestProperty("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
// 设置请求头
writer.forEachHeader(connection::addRequestProperty);
connection.setDoInput(true);
connection.setDoOutput(true);
connection.setConnectTimeout(10000);
connection.setReadTimeout(10000);
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream());
// 设置请求体
writer.write(out);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String line;
while (Objects.nonNull(line = reader.readLine())) {
builder.append(line);
}
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
reader.close();
out.close();
connection.disconnect();
System.out.printf("响应码:%d,响应内容:%s\n", responseCode, builder);
}
}
执行响应结果:
响应码:200,响应内容:ok
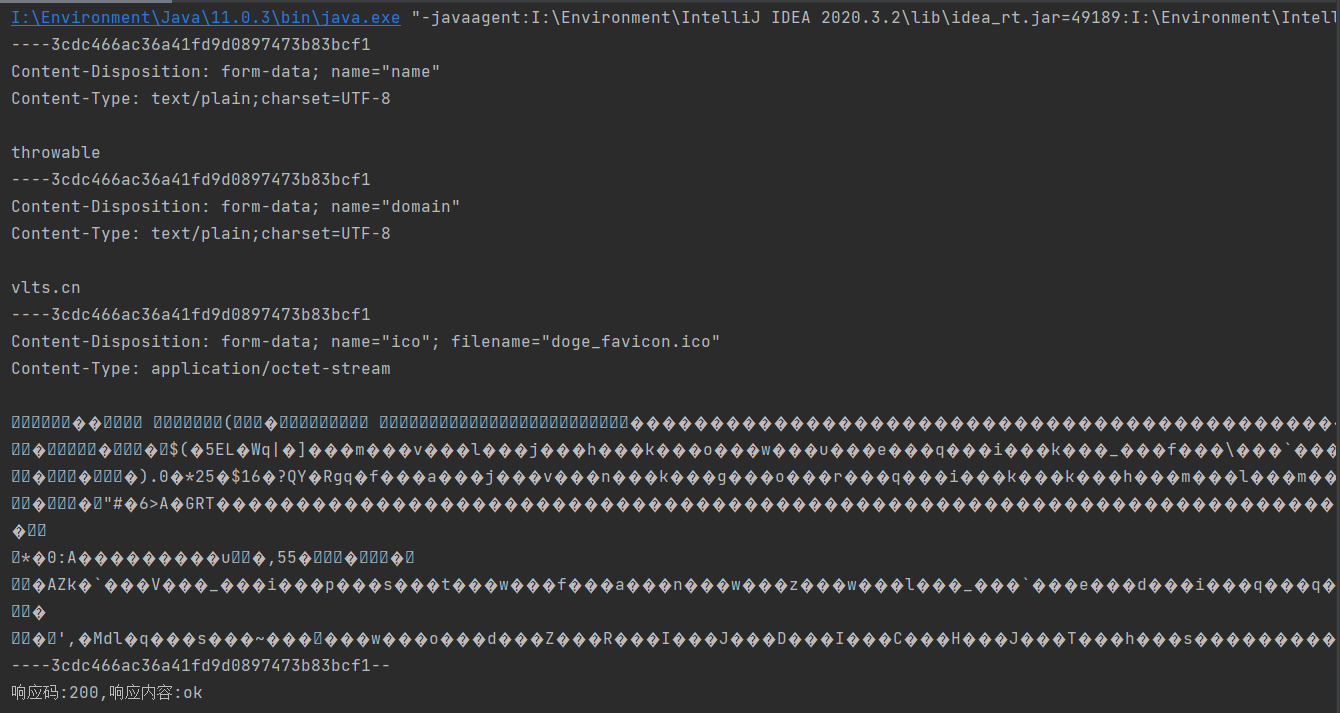
可以尝试加入两行代码打印请求体:
MultipartWriter writer = MultipartWriter.newMultipartWriter();
writer.addTextPart("name", "throwable")
.addTextPart("domain", "vlts.cn")
.addFilePart("ico", new File("I:\\doge_favicon.ico"));
DataOutputStream requestPrinter = new DataOutputStream(System.out);
writer.write(requestPrinter);
控制台输出如下;
JDK内置HttpClient实现
JDK11+内置了HTTP客户端实现,具体入口是java.net.http.HttpClient,实现编码如下:
public class HttpClientApp {
private static final String URL = "http://localhost:9099/test";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient.newBuilder()
.connectTimeout(Duration.of(10, ChronoUnit.SECONDS))
.build();
MultipartWriter writer = MultipartWriter.newMultipartWriter();
writer.addTextPart("name", "throwable")
.addTextPart("domain", "vlts.cn")
.addFilePart("ico", new File("I:\\doge_favicon.ico"));
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
writer.write(out);
HttpRequest.Builder requestBuilder = HttpRequest.newBuilder();
writer.forEachHeader(requestBuilder::header);
HttpRequest request = requestBuilder.uri(URI.create(URL))
.method("POST", HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofByteArray(out.toByteArray()))
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = httpClient.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
System.out.printf("响应码:%d,响应内容:%s\n", response.statusCode(), response.body());
}
}
内置的HTTP组件几乎都是使用Reactive编程模型,使用的API都是相对底层,灵活性比较高但是易用性不高。
小结
媒体类型multipart/form-data常用于POST方法下的HTTP请求,至于作为HTTP响应的场景相对少见。
参考资料:
(本文完 c-1-d e-a-20211226 写完后发现了Boundary前导多加了中横杠,不过看了Postman的请求也多加了很多个,懒得改)