一、Expect自动化交互程序
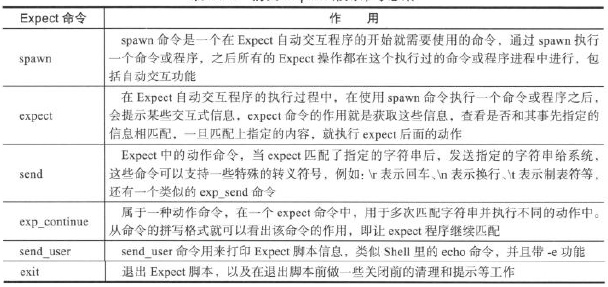
1.spawn命令
通过spawn执行一个命令或程序,之后所有的Expect操作都会在这个执行过的命令或程序进程中进行,包括自动交互功能。
语法:
spawn [ 选项 ] [ 需要自动交互的命令或程序 ]
- -open 表示启动文件进程
- -ignore 表示忽略某些信号
spawn ssh root@192.168.1.1 uptime
2.expect命令
获取spawn命令执行后的信息,看卡是否和其事先指定的相匹配,一旦匹配上指定的内容就执行expect
语法:
expect 表达式 [ 动作 ]
spawn ssh root@192.168.1.1 uptime
expect "*password" {sshd "123456
"}
3.expect实践
(1)执行ssh命令远程获取服务器负载,并实现自动输入密码
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 18_1.sh
#!/bin/expect
#Author:xiaoda
#Time:2017-09-06 11:53:30
#Name:18_1.sh
#Version:V1.0
#Description:This is a test script
spawn ssh -p12541 test@192.168.1.22 uptime
expect "*password" {send "123456
"}
expect eof
[root@codis-178 ~]# expect 18_1.sh
spawn ssh -p12541 test@192.168.1.22 uptime
Address 192.168.1.22 maps to localhost, but this does not map back to the address - POSSIBLE BREAK-IN ATTEMPT!
test@192.168.1.22's password:
11:56:01 up 1754 days, 23:53, 0 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
说明:
通过spawn执行ssh后,系统会提示输入密码,expect按照匹配password字符串,之后根据send或exp_send动作执行。
(2)执行ssh命令远程获取服务器负载,并自动输入“yes”及用户密码
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 18_2.sh
#!/bin/expect
#Author:xiaoda
#Time:2017-09-06 11:53:30
#Name:18_1.sh
#Version:V1.0
#Description:This is a test script
spawn ssh -p12541 test@192.168.1.22 uptime
expect {
"yes/no" {exp_send "yes
";exp_continue}
"*password" {exp_send "12345465
"}
}
expect eof
[root@codis-178 ~]# expect 18_2.sh
spawn ssh -p12541 test@192.168.1.22 uptime
Address 192.168.1.22 maps to localhost, but this does not map back to the address - POSSIBLE BREAK-IN ATTEMPT!
test@192.168.1.22's password:
12:03:18 up 1755 days, 1 min, 0 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
(3)利用expect响应Shell脚本中的多个read读入
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 18_3_1.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Author:xiaoda
#Time:2017-09-06 12:05:38
#Name:18_3_1.sh
#Version:V1.0
#Description:This is a test script
read -p 'Please input your username:' name
read -p 'Please input your password:' pass
read -p 'Please input your email:' email
echo -n "your name is $name."
echo -n "your password is $pass."
echo "your email is $email."
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat 18_3_2.sh
#!/bin/expect
#Author:xiaoda
#Time:2017-09-06 12:07:37
#Name:18_3_2.sh
#Version:V1.0
#Description:This is a test script
spawn /bin/sh 18_3_1.sh
expect {
"username" {exp_send "oldboy
";exp_continue}
"*pass*" {send "123456
";exp_continue}
"*email*" {exp_send "12313@.qq.com
"}
}
expect eof'
[root@codis-178 ~]# expect 18_3_2.sh
spawn /bin/sh 18_3_1.sh
Please input your username:oldboy
Please input your password:123456
Please input your email:12313@.qq.com
your name is oldboy.your password is 123456.your email is 12313@.qq.com.
4.命令简介
(1)send命令
发送指定的字符串给系统
(2)exp_continue命令
让Expect程序继续匹配
(3)send_user命令
用来打印Expect脚本信息,类似echo
(4)exit命令
直接退出Expect脚本
5.Expect关键字
(1)eof
用于匹配结束符
(2)timeout
控制时间,是一个全局性的时间控制开关,可以通过为这个变量赋值来规定整个Expect操作的时间
(即使命令没有任何错误,到了时间仍然会激活这个变量)
spqwn ssh root@192.168.1.1 uptime
set timeout 30
expect "yes/no" {exp_send "yes
";exp_continue}
expect timeout {puts "Request timeout by oldboy.";return}
spqwn ssh root@192.168.1.1 uptime
expect {
-timeout 3
expect "yes/no" {exp_send "yes
";exp_continue}
expect timeout {puts "Request timeout by oldboy.";return}
}
6.企业应用
(1)实现Expect自动交互
#!/usr/bin/expect
if [ $argc != 2 ] {
puts "usage: expect $argv0 ip command"
exit
}
set ip [lindex $argv 0]
set cmd [lindex $argv 1]
set password "123456"
spawn ssh root@192.168.1.1 $cmd
expect {
expect "yes/no" {exp_send "yes
";exp_continue}
"*password" {send "$password
"}
}
export eof
(2)批量发送文件
#!/usr/bin/expect
if [ $argc != 3 ] {
puts "usage: expect $argv0 file host dir"
exit
}
set file [lindex $argv 0]
set host [lindex $argv 1]
set dir [lindex $argv 2]
set password "123456"
spawn ssh -P22 root@192.168.1.1 $cmd
expect {
expect "yes/no" {exp_send "yes
";exp_continue}
"*password" {send "$password
"}
}
export eof
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -ne 2 ];then
echo $"Usage:$0 file dir"
exit 1
fi
file=$1
dir=$2
for n in 128 129 130
do
expect 18_13_1.exp $file 192.168.1.$n $dir
done