本示例已升级到Spring Boot 2.x
源码地址:https://github.com/smltq/spring-boot-demo/tree/master/template-thymeleaf
国际化介绍
web开发中,国际化是需要考虑的一个问题,而且这个问题一般是越早敲定越好(不然等到系统大了,翻译是个问题).下面是结合实际项目(Spring MVC+Velocity)对实现国际化的一些总结.github地址
Spring国际化
I18N:作为"国际化"的简称,其来源是英文单词internationalization的首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数.
Spring做国际化的配置主要有3个关键点:
- ResourceBundleMessageSource:实现国际化资源的定义.
- LocaleResolver:实现本地化信息的解析.
- LocaleChangeInterceptor:实现本地化信息的监听(来实现url参数动态指定locale).
LocaleResolver
LocaleResolver是指用什么策略来检测请求是哪一种locale,Spring MVC提供了一下几种策略:
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
根据浏览器Http Header中的accept-language域判定浏览器的语言环境,可以通过HttpServletRequest.getLocale获得域的内容,但是无法调用LocaleResolver接口的setLocale设置locale.基于这个策略,在后面的demo中可以实现基于浏览器的国际化案例.
SessionLocaleResolver
根据用户本次会话过程中的语言设定决定语言种类,session级别的,在此session周期内可以修改语言种类,但是session失效后,语言设定失效.基于这个策略,在后面的demo中可以实现基于session的国际化案例.
CookiedLocaleResolver
根据Cookie判定用于的语言设定(Cookie中保存着用户前一次的语言设定参数).
FixedLocaleResolver
一直使用固定的Locale,改变locale是不支持的.
如果需要使用哪一种策略,只需要在DispatcherServlet制定的Spring配置文件中配置就行,DispatchServlet将在初始化的时候调用initLocaleResolver(context)方法去配置文件中找名字为localeResolver的bean,如果有就使用配置文件的,没有就使用默认的AcceptHeaderLocaleResovler
通过上面,了解了Spring实现国际化的相关概念,下面结合demo实例,看看Spring MVC是如何实现国际化的
- 配置文件
<!--国际化配置 start-->
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="classpath:i18n/messages"/>
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
<bean id="localeChangeInterceptor"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor">
<property name="paramName" value="lang"/>
</bean>
<!--语言选择-->
<bean id="localeResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver">
<property name="defaultLocale" value="en"/>
</bean>
<!--国际化配置 end-->
- demo里准备两份语言文件分别是messages_cn.properties和messages_en.properties,内容分别如下:
Hello=Hello
HelloWorld=Hello World
SpringMvcBootstrap=Spring MVC Bootstrap
Greetings=I deeply greet you!
Hello=你好,现在是中文版
HelloWorld=你好,现在是中文版
SpringMvcBootstrap=中文版头部
Greetings=中文版欢迎你
- 前端界面通过使用spring针对不同view视图提供的标记处理国际化信息.velocity标记,比如demo中的hello.vm文件
#define($content)
#springMessage("Hello")
#end
-
最后运行结果会根据defaultLocale的配置显示英语版本或中文版本,显示效果如下:

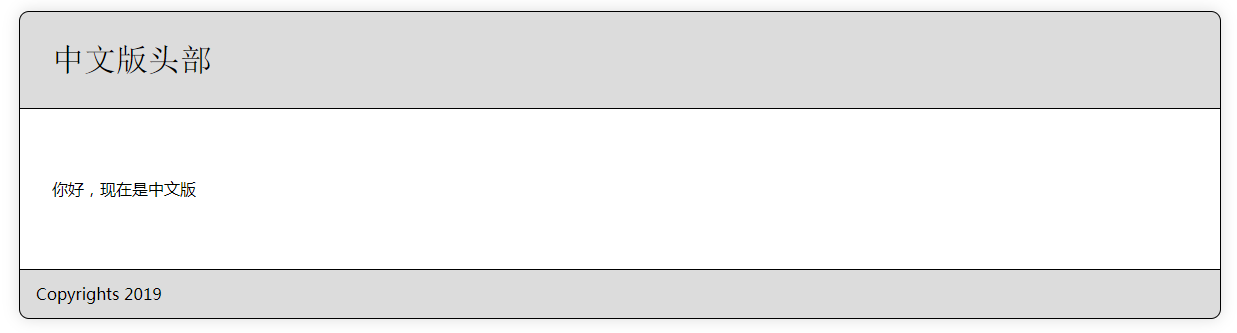
-
以上配置示例是基于Cookie的国际化实现,国际化根据实际需求,实现方式有很多比如:
- 基于浏览器请求的国际化
- 基于Session的国际化实现
- 基于ULR请求的国际化实现
Velocity简单使用
- pom.xml增加Velocity 依赖
<!-- Velocity 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity</artifactId>
<version>1.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-tools</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>
- xml增加模板引擎配置
<!--模板引擎配置 start-->
<bean id="velocityConfig"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.velocity.VelocityConfigurer">
<property name="configLocation">
<value>/WEB-INF/velocity/velocity.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.velocity.VelocityLayoutViewResolver">
<property name="cache" value="false"/>
<property name="layoutUrl" value="/layout/main.vm"/>
<property name="prefix" value="/templates/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".vm"/>
<property name="exposeSpringMacroHelpers" value="true"/>
<property name="contentType" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8"/>
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.velocity.VelocityLayoutView"/>
</bean>
<!--模板引擎配置 end-->
- controller代码,hello方法会显示hello.vm内容,helloWorld方法显示hello-world.vm内容,入口是main.vm
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello-world", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloWorld() {
return "hello-world";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello-redirect", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloRedirect() {
return "redirect:/hello-world";
}
}
- 我们看看main.vm代码
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>$!page_title</title>
<link href="#springUrl('/resources/css/reset.css')" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
<link href="#springUrl('/resources/css/style.css')" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
</head>
<body>
<article>
<header>#parse('/layout/header.vm')</header>
<section>$!content</section>
<footer>#parse('/layout/footer.vm')</footer>
</article>
</body>
</html>
SpringMVC和REST服务API的基本用法示例
- pom.xml增加json和xml依赖
<!-- JSON 转换器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-mapper-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- XML 转换器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>
- controller代码
@Controller
public class UserServiceController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{name}/{surname}.json", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public @ResponseBody
User getUserJson(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String surname) {
User user = new User(name, surname);
return user;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{name}/{surname}.xml", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE)
public @ResponseBody
User getUserXml(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String surname) {
User user = new User(name, surname);
return user;
}
}
@XmlRootElement(name = "user")
public class User {
private String name;
private String surname;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, String surname) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.surname = surname;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSurname() {
return surname;
}
public void setSurname(String surname) {
this.surname = surname;
}
}
- json数据结果
浏览器输入http://localhost:9080/testweb/user/tq/lin.json,结果显示如下:
{
name: "tq",
surname: "lin"
}
- xml数据结果
浏览器输入http://localhost:9080/testweb/user/tq/lin.xml,结果显示如下:
<user>
<name>tq</name>
<surname>lin</surname>
</user>