1.f.read(), f.readline(), f.readlines()
##### 1. f.read() 整体读 返回字符串 In [2]: f = open("aaa.py") In [3]: f.read() Out[3]: 'this is the file then,we want to copy this file to other file end '
#### 2. f.readline() 1行1行读 返回字符串 In [5]: f = open("aaa.py") In [6]: f.read() Out[6]: 'this is the file then,we want to copy this file to other file end ' In [7]: f.readline() #文件指针到末尾 Out[7]: '' In [9]: f = open("aaa.py") In [10]: f.readline() Out[10]: 'this is the file ' In [11]: f.readline() Out[11]: 'then,we want to copy this file to other file '
#### 3. f.readlines() 整体读 返回list列表 In [16]: f = open("aaa.py") In [17]: f.readlines() Out[17]: ['this is the file ', 'then,we want to copy this file to other file ', 'end ']
2. 5G大文件 读入
一丁点一丁点的倒水
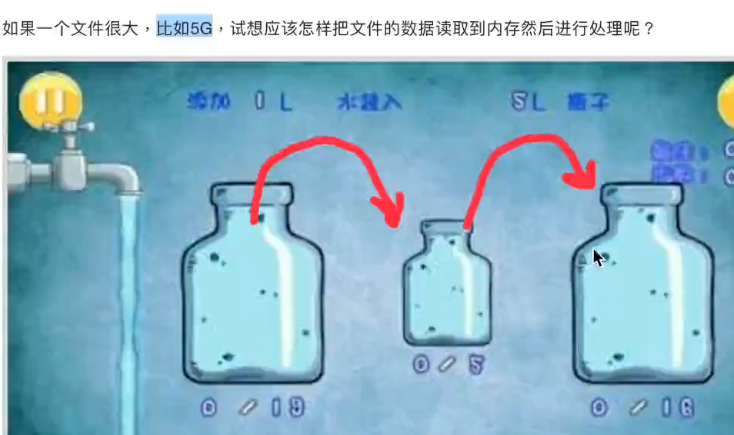
思路:while循环
f.read() f.readlines()不可用
#1.获取用户要复制的文件名 file_name = input("请输入文件名:") #2. 打开原文件 f1 = open(file_name,"r") #3.打开新文件 #获取文件名 字符串操作 position = file_name.rfind(".") new_file_name = file_name[0:position] + "[大文件]" + file_name[position:] f2 = open(new_file_name,"w") #4.读取原文件的内容 #切记不可以用f.read() f.readlines() while True: result = f1.read(1024) if len(result) == 0: break #5。写到新文件中 f2.write(result) #6.关闭文件 f1.close() f2.close()