2020年11月5日11:46:45-王凯玉
python format 格式化函数
Python2.6 开始,新增了一种格式化字符串的函数 str.format(),它增强了字符串格式化的功能。
基本语法是通过 {} 和 : 来代替以前的 %
-
format 函数可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序。
# 不设置指定位置,按默认顺序 "{} {}".format("hello", "world") >'hello world' # 设置指定位置 "{0} {1}".format("hello", "world") >'hello world' # 设置指定位置 "{1} {0} {1}".format("hello", "world") >'world hello world' -
也可以设置参数
print("网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(name="菜鸟教程", url="www.runoob.com")) # 通过字典设置参数 site = {"name": "菜鸟教程", "url": "www.runoob.com"} print("网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(**site)) # 通过列表索引设置参数 my_list = ['菜鸟教程', 'www.runoob.com'] print("网站名:{0[0]}, 地址 {0[1]}".format(my_list)) # "0" 是必须的 # 输出的结果为 网站名:菜鸟教程, 地址 www.runoob.com 网站名:菜鸟教程, 地址 www.runoob.com 网站名:菜鸟教程, 地址 www.runoob.com -
也可以向 str.format() 传入对象:
class AssignValue(object): def __init__(self, value): self.value = value my_value = AssignValue(6) print('value 为: {0.value}'.format(my_value)) # "0" 是可选的 # 输出结果为 value 为: 6 -
数字格式化
print("{:.2f}".format(3.1415926)); 3.14str.format()格式化数字的多种方法
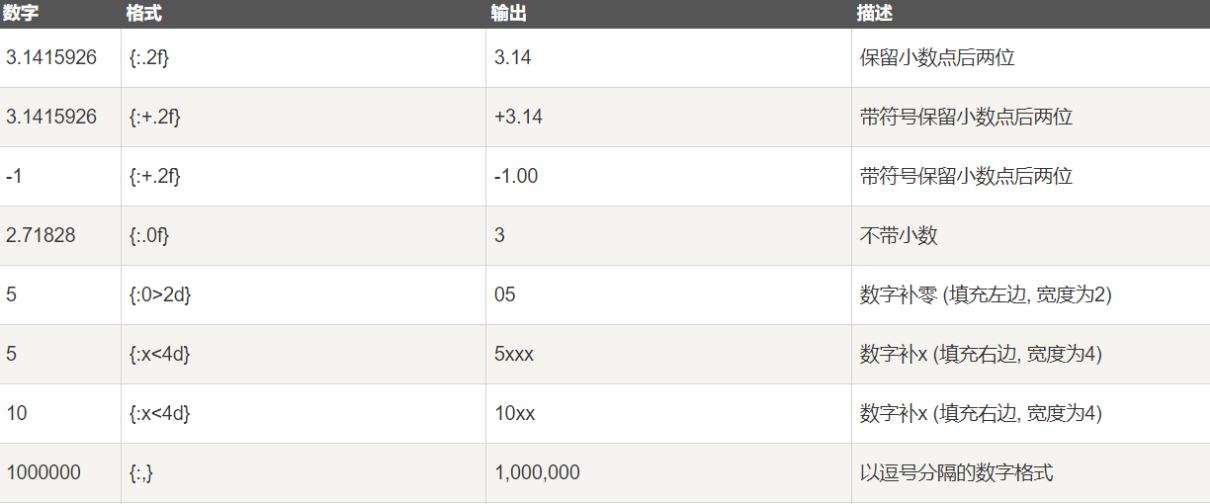
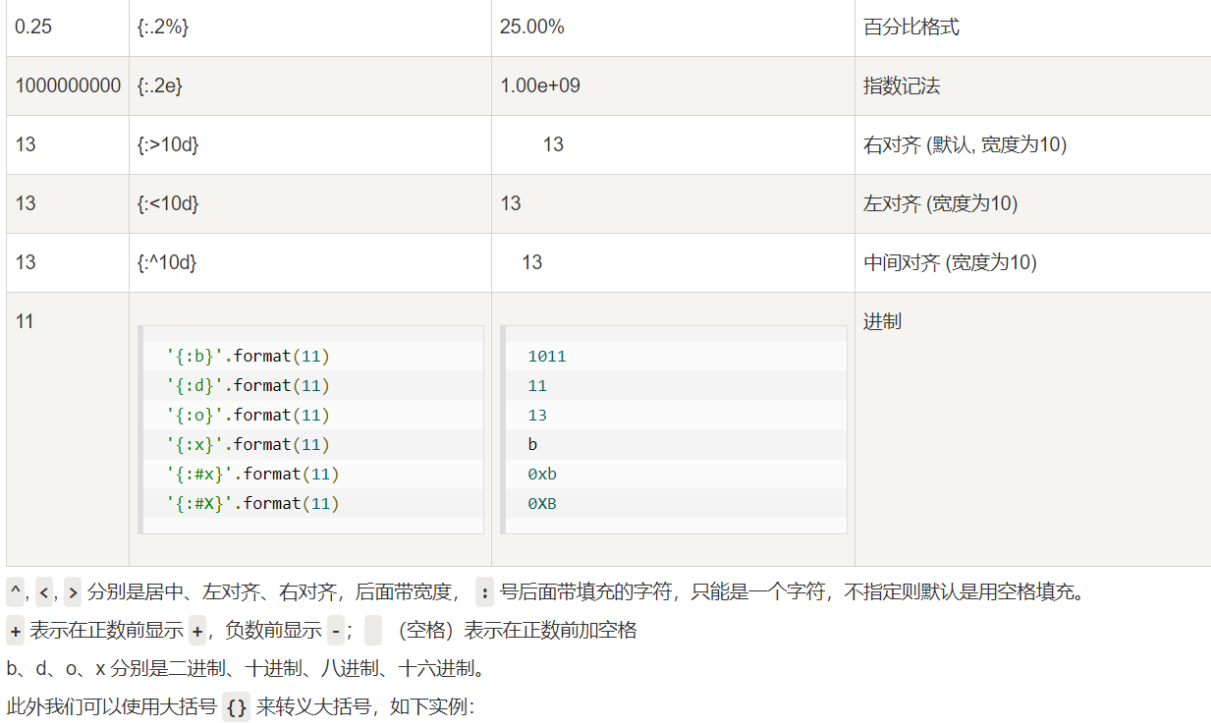
-
此外我们可以使用大括号 {} 来转义大括号,如下实例:
print ("{} 对应的位置是 {{0}}".format("runoob")) # 输出结果为 runoob 对应的位置是 {0}