1.栈与队列
栈与队列是程序设计中广泛使用的两种重要的线性数据结构。
栈是LIFO(Last In First Out),先存进去的数据只能最后被取出来,进出顺序逆序,即先进后出,后进先出。
队列是FIFO(First In First Out),它保持进出顺序一致,即先进先出,后进后出。
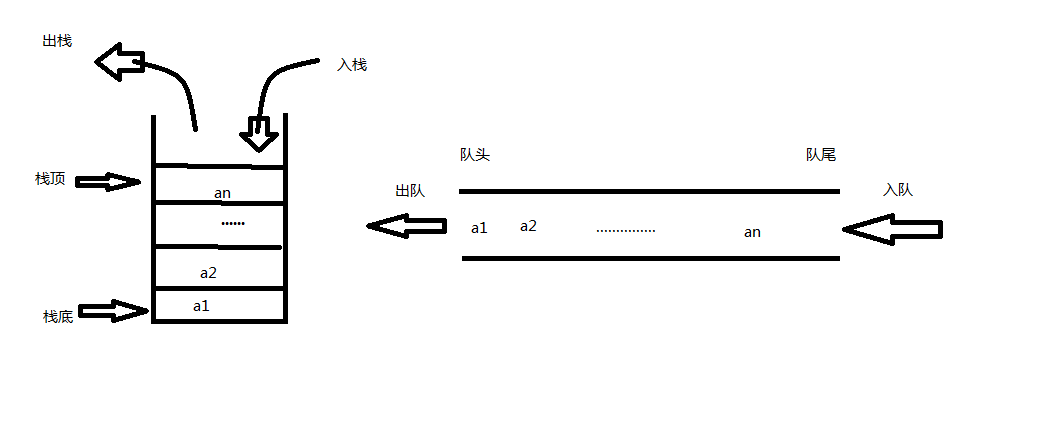
2.如何实现栈

两种方式实现,数组和链表
1 public class MyStack<E> { 2 3 /* 4 * 用数组实现栈 先进后出,后进先出 5 * 思路:定义一个数组,用来保存入栈的数据,数组初始化大小为10 6 * 用size表示入栈数据的个数 而size-1则是对应的数组下标 7 * (由于是数组,需要考虑扩容的问题) 8 * 入栈时,需要判断数据个数是否超出数组大小,如果超出 使用Arrays.copyOf(,)来扩容 9 * 10 * 出栈时,则直接获取栈顶数据,即根据size-1获取后进的数据元素的数组下标,然后将对应出栈 11 * 的数据元素的数组下标处置空。 12 * 13 */ 14 private Object[] stack; 15 private int size; //初始化为0 16 private int newLen; 17 18 public MyStack(){ 19 stack = new Object[10]; 20 } 21 //判读是否栈为空 22 public boolean isEmpty(){ 23 return size==0; 24 } 25 //查看堆栈顶部的对象,而不将其从堆栈中移除。 26 public E peek(){ 27 if(isEmpty()) 28 { 29 return null; 30 } 31 return (E)stack[size-1]; 32 } 33 //栈顶元素 出栈 34 public E pop(){ 35 E e = peek(); 36 stack[size-1]=null; 37 size--; 38 return e; 39 } 40 41 //入栈 42 public E push(E item){ 43 ensureCapacity(size+1); 44 stack[size++] = item; 45 return item; 46 } 47 // 48 private void ensureCapacity(int size) { 49 int len = stack.length; 50 if(size>len) 51 { 52 int newLen = 10; 53 //copy stack to newLen+len of length ’s array 54 stack = Arrays.copyOf(stack, newLen+len); 55 } 56 } 57 58 59 public static void main(String[] args) { 60 MyStack<Integer> ms = new MyStack<>(); 61 System.out.println(ms.size); 62 ms.push(1); 63 ms.push(2); 64 65 System.out.println(ms.size); 66 System.out.println("栈顶元素:"+ms.pop()); 67 System.out.println("栈顶元素:"+ms.pop()); 68 69 }
1 /* 2 * 使用链表实现栈 先进后出 后进先出 3 * 思路: 栈顶位置top 根据链表 进行前插法 将入栈的元素放在链表头部 4 * 出栈的时候,就直接可以从链表头部取出 5 */ 6 class Node<E>{ 7 Node<E> next = null; 8 E data; 9 Node(E data){ 10 this.data = data; 11 } 12 } 13 class Stack<E>{ 14 Node<E> top = null; 15 16 //判读是否栈空 17 public boolean isEmpty(){ 18 return top==null; 19 } 20 //读栈顶元素 21 public E peek(){ 22 if(isEmpty()){ 23 return null; 24 } 25 return top.data; 26 } 27 28 //取出栈顶元素 29 public E pop(){ 30 if(isEmpty()){ 31 return null; 32 } 33 E data = top.data; 34 top = top.next; 35 return data; 36 } 37 38 39 40 //元素入栈 41 public void push(E data){ 42 Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(data); 43 newNode.next = top; 44 top = newNode; 45 } 46 }
3.如何实现队列
Java中是实现了Queue队列的接口,具体实例化的时候需要用到LinkedList等其他实例化类


使用LinkedList和链表
1 public class MyQueue<E> { 2 /* 3 * 使用(list)实现队列 先进先出 后进后出 4 * 思路使用LinkedList 本质是双向链表 5 * 入队 链表后插入 6 * 出队 获取链表头部元素 并remove掉 7 */ 8 private LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<E>(); 9 private int size ; 10 public synchronized void push(E e){ 11 list.add(e); 12 //list.addLast(e); 13 size++; 14 } 15 public synchronized E pop(){ 16 E e = list.removeFirst(); 17 size--; 18 return e; 19 } 20 21 public synchronized boolean empty(){ 22 return size==0; 23 } 24 25 public synchronized int size(){ 26 return size; 27 } 28 29 30 public static void main(String[] args) { 31 32 33 MyQueue<Integer> mq = new MyQueue<>(); 34 mq.push(4);// 35 mq.push(2); 36 37 System.out.println(mq.size); 38 System.out.println(mq.pop()); 39 System.out.println(mq.size); 40 } 41 42 }
class Queue<E>{ Node<E> head = null; Node<E> tail = null; //判读是否队空 public boolean isEmpty(){ if(head == null && tail==null){ return true; } else return false; } //读队头 public E peek(){ if(isEmpty()) return null; return head.data; } //从队头 出队 public E pop(){ if(isEmpty()) return null; E e = head.data; head= head.next; return e; } //进队尾 public void push(E data){ Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(data); if(head==null && tail == null) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; }else{ tail.next = newNode; tail = newNode; } } //队长 public int size(){ if(head == null) return 0; int len = 1 ; Node<E> l = head; while(l.next!=null){ len++; l = l.next; } return len; } public static void main(String[] args) { //使用链表实现队列 Queue<Integer> q = new Queue(); q.push(1); q.push(2); q.push(3); System.out.println(q.size()); System.out.println(q.pop()); System.out.println(q.peek()); } } class Node<E>{ Node<E> next = null; E data; Node(E data){ this.data = data; } }
4.如何使用两个栈模拟队列操作
1 public class TwoStackForQueue<E> { 2 3 /* 4 * 用法两个stack 实现队列操作 队列是先进先出的 5 * 思想:设置两个stack A,B, stackA为入队的栈,stackB为出队的栈 6 * 入队直接进栈A,出栈需要判断栈B是否为空,如果为空,需要将栈A中的元素放入栈B中 7 * 如果不为空 直接获取栈B的栈顶元素 8 */ 9 Stack<E> A = new Stack<>(); 10 Stack<E> B = new Stack<>(); 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 TwoStackForQueue<Integer> queue = new TwoStackForQueue<>(); 13 queue.put(1); 14 queue.put(2); 15 queue.put(3); 16 // int i = queue.pop(); 17 // System.out.println(i); 18 // i = queue.pop(); 19 // System.out.println(i); 20 // i = queue.pop(); 21 // System.out.println(i); 22 while(!queue.empty()){ 23 int i = queue.pop(); 24 System.out.println(i); 25 } 26 27 } 28 //判断是否队空 29 public boolean empty(){ 30 return A.isEmpty() && B.isEmpty(); 31 } 32 33 //出队 34 public synchronized E pop(){ 35 /*if(B.isEmpty()){ 36 if(A.isEmpty()) 37 return null; 38 while(!A.isEmpty()) 39 { 40 B.push(A.pop()); 41 } 42 return B.pop(); 43 } 44 return B.pop();*/ 45 //优化 46 if(B.isEmpty()){ 47 while(!A.isEmpty()) 48 { 49 B.push(A.pop()); 50 } 51 } 52 return B.pop(); 53 } 54 //入队 55 public synchronized void put(E e){ 56 A.push(e); 57 } 58 59 60 61 62 }
5.如果使用两个队列模拟栈操作
1 public class TwoQueueForStack<E> { 2 3 /* 4 * 使用两个队列实现栈 栈的特点是先进后出,后进先出 5 * 思路:两个Queue 使用LinkedList实例化 LinkedList实际上是一个双向链表 6 * q1作为入栈的队列 即直接将入栈的数据放入q1 7 * q2作为出栈的队列 即需要出栈时,如果q1只有一个元素 直接出栈 8 * 如果q1不止一个元素,即可以将q1队列中的数据依次放入q2,最后一个不放入,最后一个元素输出 9 * 再将q2中的元素依次放回q1 10 */ 11 private Queue<E> q1 = new LinkedList<E>(); 12 private Queue<E> q2 = new LinkedList<E>();; 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 TwoQueueForStack<Integer> stack = new TwoQueueForStack<>(); 15 stack.put(1); 16 stack.put(2); 17 stack.put(3); 18 while(!stack.empty()){ 19 int i = stack.pop(); 20 System.out.println(i); 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 //判断是否栈空 26 public boolean empty(){ 27 return q1.isEmpty() && q2.isEmpty(); 28 } 29 30 //出栈 31 public synchronized E pop(){ 32 int size = q1.size(); 33 if(size==1) 34 return q1.poll(); 35 36 int i=1; 37 while(!(i==size)){ 38 q2.add(q1.poll()); 39 i++; 40 } 41 E e = q1.poll(); 42 43 while(!q2.isEmpty()){ 44 q1.add(q2.poll()); 45 } 46 return e; 47 } 48 //入栈 49 public synchronized void put(E e){ 50 q1.add(e); 51 } 52 53 }