题意: 判断凸包是否稳定。
解法: 稳定凸包每条边上至少有三个点。
这题就在于求凸包的细节了,求凸包有两种算法:
1.基于水平序的Andrew算法
2.基于极角序的Graham算法
两种算法都有一个类似下面的语句:
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
while(m > 1 && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2], p[i]-ch[m-2]) <= 0) m--;
ch[m++] = p[i];
}
这样的话,求出来就是最简凸包,即点数尽量少的凸包,因为Cross == 0的情况也被出栈了,所以一条凸包边上就会三点共线了。
我们把语句改下,把Cross.. <=0 改成 Cross.. < 0 ,那么求的就是最繁凸包,即可能一条凸包边上包含很多点也属于凸包的点。
即下面的情况:
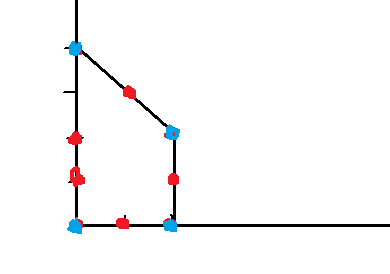
最简凸包即为蓝色的四个点。 最繁凸包求出的是所有蓝点和红点。
作为这个题,我们怎么求其实都可以:
1.如果求最简凸包,我们只需判断总共有多少个点在该凸包边上即可(端点也算),如果 < 3 ,则不符。
2.如果求的是最繁的凸包,就不能用上面的判法,因为怎么判都只有两个点了,这时候可以采用下面的方法:
假设要判断的边i,那么判断边i和边i-1,边i和边i+1的夹角是否都为0(180)。 ----XDruid
代码: (这里我用的是Andrew算法)

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define eps 1e-8
using namespace std;
struct Point{
double x,y;
Point(double x=0, double y=0):x(x),y(y) {}
void input() { scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y); }
};
typedef Point Vector;
int dcmp(double x) {
if(x < -eps) return -1;
if(x > eps) return 1;
return 0;
}
template <class T> T sqr(T x) { return x * x;}
Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B) { return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); }
Vector operator - (Vector A, Vector B) { return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); }
Vector operator * (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x*p, A.y*p); }
Vector operator / (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x/p, A.y/p); }
bool operator < (const Point& a, const Point& b) { return a.x < b.x || (a.x == b.x && a.y < b.y); }
bool operator >= (const Point& a, const Point& b) { return a.x >= b.x && a.y >= b.y; }
bool operator <= (const Point& a, const Point& b) { return a.x <= b.x && a.y <= b.y; }
bool operator == (const Point& a, const Point& b) { return dcmp(a.x-b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y-b.y) == 0; }
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x*B.x + A.y*B.y; }
double Length(Vector A) { return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); }
double Angle(Vector A, Vector B) { return acos(Dot(A, B) / Length(A) / Length(B)); }
double Cross(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x*B.y - A.y*B.x; }
double angle(Vector v) { return atan2(v.y, v.x); }
bool OnSegment(Point P, Point A, Point B) { //端点不算
return dcmp(Cross(A-P,B-P)) == 0 && dcmp(Dot(A-P,B-P)) <= 0;
}
int ConvexHull(Point* p, int n, Point* ch) {
sort(p,p+n);
int m = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
while(m > 1 && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2], p[i]-ch[m-2]) <= 0) m--;
ch[m++] = p[i];
}
int k = m;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--) {
while(m > k && Cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2], p[i]-ch[m-2]) <= 0) m--;
ch[m++] = p[i];
}
if(n > 1) m--;
return m;
}
Point ch[1006],p[1006];
int main()
{
int t,n,i,j;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++) p[i].input();
if(n <= 5) { puts("NO"); continue; }
int m = ConvexHull(p,n,ch);
if(m <= 2) { puts("NO"); continue; }
for(i=0;i<m;i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(OnSegment(p[j],ch[i],ch[(i+1)%m]))
cnt++;
if(cnt < 3) break;
}
if(i == m) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
现在终于对自己的凸包版有了全面的了解了,妈妈再也不用担心我用错凸包了。哈哈。
