环境
系统环境:Win10
编程语言:Go 1.17
知识点:
- Go语言结构体定义及初始化
- 序列化与反序列化
- bolt.DB 数据库
- 哈希算法
- pow工作量证明创建区块
功能:
实现一个简单的区块链,采用作量证明(PoW)方式创建新的区块;数据序列化与反序列化;持久化存储(存入数据库中)
PoW:就要定义一个挖矿难度,hash(data)<pow.target,并要验证该获得哈希是否有效
序列化与反序列化:序列化是便于数据的传输与存储,反序列化是方便人去查看数据
采用的技术是Go语言中encode包中gob("encode/gob")
持久化存储:即存储至数据库中,数据库采用的是bolt
数据的流程大致如下:
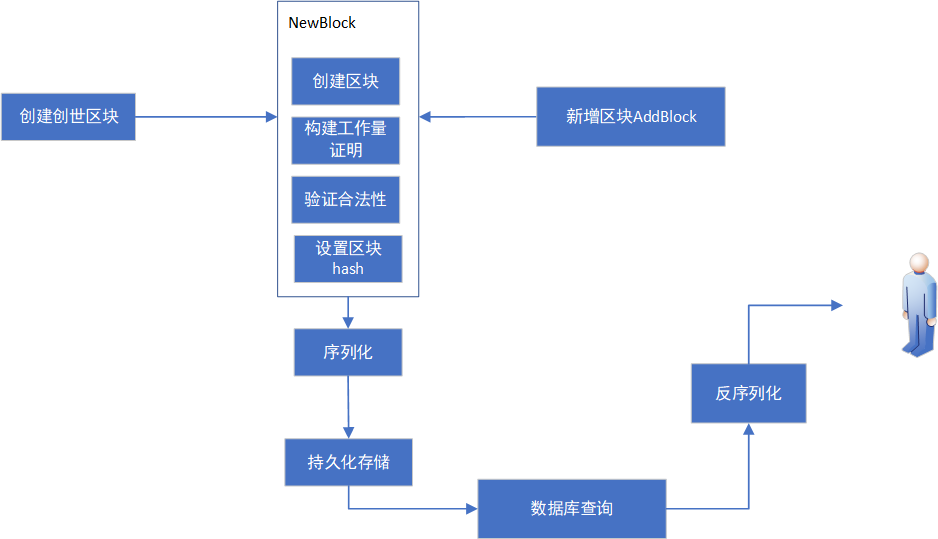
具体实现
区块结构体定义:
type Block struct {
//时间戳,创建区块的时间
TimeStamp int64
//上个区块的hash
PrevBlockHash []byte
//Data 交易数据
Data []byte
// Hash 当前区块的hash
Hash []byte
// Nonce随机数
Nonce int
}
序列化与反序列化:
func (b *Block) Serialize() []byte {
var result bytes.Buffer
encoder := gob.NewEncoder(&result)
err := encoder.Encode(b)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return result.Bytes()
}
func DeSerialBlock(d []byte) *Block {
var block Block
decoder := gob.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(d))
err := decoder.Decode(&block)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return &block
}
工作量证明POW:
package BLC
import (
"fmt"
"math/big"
"bytes"
"math"
"crypto/sha256"
)
var (
//define Nonce max
maxNonce = math.MaxInt64
)
const targetBits = 20
type ProofOfWork struct{
block *Block //current block to validate
target *big.Int //Big number storage, block difficulty
}
func (pow *ProofOfWork) prepareData(nonce int) []byte{
data := bytes.Join(
[][]byte{
pow.block.PrevBlockHash,
pow.block.Data,
IntToHex(pow.block.TimeStamp),
IntToHex(int64(targetBits)),
IntToHex(int64(nonce)),
},
[]byte{},
)
return data
}
// ProofOfWork object function
func (pow *ProofOfWork) Run() (int, []byte){
fmt.Printf("RUN....")
var hashInt big.Int
var hash [32]byte
nonce := 0
fmt.Printf("Mining the block containing \"%s\"\n",pow.block.Data)
for nonce < maxNonce{
data := pow.prepareData(nonce)
hash = sha256.Sum256(data)
fmt.Printf("\r%x",hash)
hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:])
if hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1 {
break
}else{
nonce++
}
}
fmt.Printf("\n\n")
return nonce,hash[:]
}
func NewProofOfWork(block *Block) *ProofOfWork{
target := big.NewInt(1)
// fmt.Printf("--------------")
// fmt.Printf("%b\n", target)
//fmt.Printf("--------------")
target.Lsh(target,uint(256-targetBits))
//fmt.Printf("------target.Lsh------")
//fmt.Printf("%b\n", target)
pow := &ProofOfWork{block,target}
return pow
}
哈希验证:
func (pow *ProofOfWork) Validate() bool{
var hashInt big.Int
data := pow.prepareData(pow.block.Nonce)
hash := sha256.Sum256(data)
hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:])
isValid := hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1
return isValid
}
新增区块并存储至boltdb中:
//新增区块
func (blockChain *BlockChain) AddBlock(data string) {
//1、创建区块
newBlock := NewBlock(data, blockChain.Tip)
//2、update数据
err := blockChain.DB.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
//获取数据表
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
if b != nil {
err := b.Put(newBlock.Hash, newBlock.Serialize())
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
//更新l对应的hash
err = b.Put([]byte("l"), newBlock.Hash)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
//将最新的区块的hash存储到blockchain的Tip中
blockChain.Tip = newBlock.Hash
return nil
} else {
fmt.Println("AddBlock failed ....")
return nil
}
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
}
查询数据库中数据:通过迭代器访问
//迭代器
type BlockchainIterator struct {
CurrentHash []byte // 当前正在遍历的区块的Hash
DB *bolt.DB // 数据库
}
//迭代器
func (blockchain *BlockChain) Iterator() *BlockchainIterator {
return &BlockchainIterator{blockchain.Tip, blockchain.DB}
}
//下一个迭代器
func (bi *BlockchainIterator) Next() *BlockchainIterator {
var nextHash []byte
//查询数据
err := bi.DB.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
//获取表
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
//通过当前的hash获取Block
currentHashbytes := b.Get(bi.CurrentHash)
//反序列化
currentBlock := DeSerialBlock(currentHashbytes)
nextHash = currentBlock.PrevBlockHash
return nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return &BlockchainIterator{nextHash, bi.DB}
}
在main.go中调用:
var blockchainIterator *BLC.BlockchainIterator
blockchainIterator = blockchain.Iterator()
var hashInt big.Int
for {
fmt.Printf("%x\n", blockchainIterator.CurrentHash)
// 获取下一个迭代器
blockchainIterator = blockchainIterator.Next()
// 将迭代器中的hash存储到hashInt
hashInt.SetBytes(blockchainIterator.CurrentHash)
/*
// Cmp compares x and y and returns:
//
// -1 if x < y
// 0 if x == y
// +1 if x > y
*/
if hashInt.Cmp(big.NewInt(0)) == 0 {
break
}
}
详细代码可参考:https://github.com/NGLHarry/Blockchainer/tree/main/part13-seriAndDeserialBlock_cli_queryDatabase