摘要:
本章介绍了二叉查找树的概念及操作。主要内容包括二叉查找树的性质,如何在二叉查找树中查找最大值、最小值和给定的值,如何找出某一个元素的前驱和后继,如何在二叉查找树中进行插入和删除操作。在二叉查找树上执行这些基本操作的时间与树的高度成正比,一棵随机构造的二叉查找树的期望高度为O(lgn),从而基本动态集合的操作平均时间为θ(lgn)。
1、二叉查找树
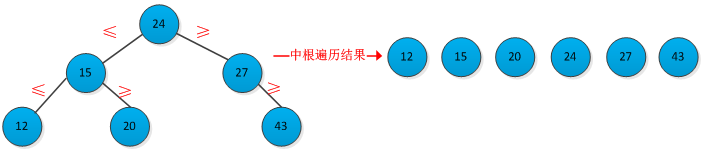
二叉查找树是按照二叉树结构来组织的,因此可以用二叉链表结构表示。二叉查找树中的关键字的存储方式满足的特征是:设x为二叉查找树中的一个结点。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y]≤key[x]。如果y是x的右子树中的一个结点,则key[x]≤key[y]。根据二叉查找树的特征可知,采用中根遍历一棵二叉查找树,可以得到树中关键字有小到大的序列。一棵二叉树查找及其中根遍历结果如下图所示:
书中给出了一个定理:如果x是一棵包含n个结点的子树的根,则其中根遍历运行时间为θ(n)。
问题:二叉查找树性质与最小堆之间有什么区别?能否利用最小堆的性质在O(n)时间内,按序输出含有n个结点的树中的所有关键字?
2、查询二叉查找树
二叉查找树中最常见的操作是查找树中的某个关键字,除了基本的查询,还支持最大值、最小值、前驱和后继查询操作,书中就每种查询进行了详细的讲解。
(1)查找SEARCH
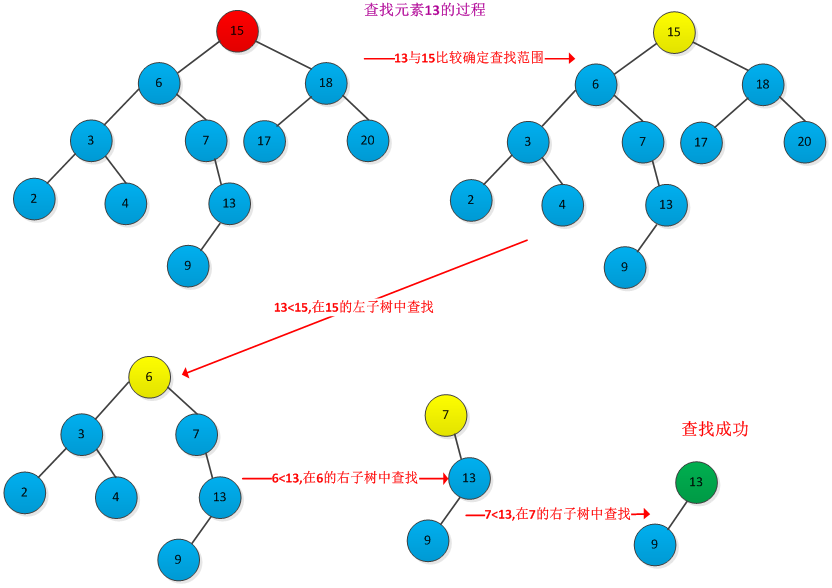
在二叉查找树中查找一个给定的关键字k的过程与二分查找很类似,根据二叉查找树在的关键字存放的特征,很容易得出查找过程:首先是关键字k与树根的关键字进行比较,如果k大比根的关键字大,则在根的右子树中查找,否则在根的左子树中查找,重复此过程,直到找到与遇到空结点为止。例如下图所示的查找关键字13的过程:(查找过程每次在左右子树中做出选择,减少一半的工作量)
书中给出了查找过程的递归和非递归形式的伪代码:
TREE_SEARCH(x,k) if x=NULL or k=key[x] then return x if(k<key[x]) then return TREE_SEARCH(left[x],k) else then return TREE_SEARCH(right[x],k)
非递归
ITERATIVE_TREE_SEARCH(x,k) while x!=NULL and k!=key[x] do if k<key[x] then x=left[x] else then x=right[x] return x
(2)查找最大关键字和最小关键字
根据二叉查找树的特征,很容易查找出最大和最小关键字。查找二叉树中的最小关键字:从根结点开始,沿着各个节点的left指针查找下去,直到遇到NULL时结束。如果一个结点x无左子树,则以x为根的子树中,最小关键字就是key[x]。查找二叉树中的最大关键字:从根结点开始,沿着各个结点的right指针查找下去,直到遇到NULL时结束。书中给出了查找最大最小关键字的伪代码:
查找最小关键字
TREE_MINMUM(x) while left[x] != NULL do x=left[x] return x
查找最大关键字
TREE_MAXMUM(x) while right[x] != NULL do x= right[x] return x
(3)前驱和后继
给定一个二叉查找树中的结点,找出在中序遍历顺序下某个节点的前驱和后继。如果树中所有关键字都不相同,则某一结点x的前驱就是小于key[x]的所有关键字中最大的那个结点,后继即是大于key[x]中的所有关键字中最小的那个结点。根据二叉查找树的结构和性质,不用对关键字做任何比较,就可以找到某个结点的前驱和后继。
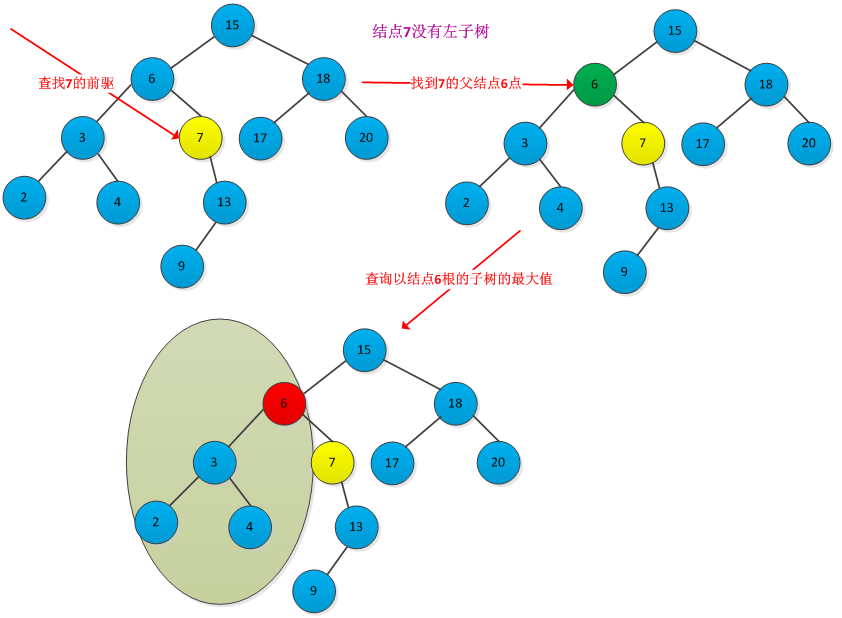
查找前驱步骤:先判断x是否有左子树,如果有则在left[x]中查找关键字最大的结点,即是x的前驱。如果没有左子树,则从x继续向上执行此操作,直到遇到某个结点是其父节点的右孩子结点。例如下图查找结点7的前驱结点6过程:
查找后继步骤:先判断x是否有右子树,如果有则在right[x]中查找关键字最小的结点,即使x的后继。如果没有右子树,则从x的父节点开始向上查找,直到遇到某个结点是其父结点的左儿子的结点时为止。例如下图查找结点13的后继结点15的过程:
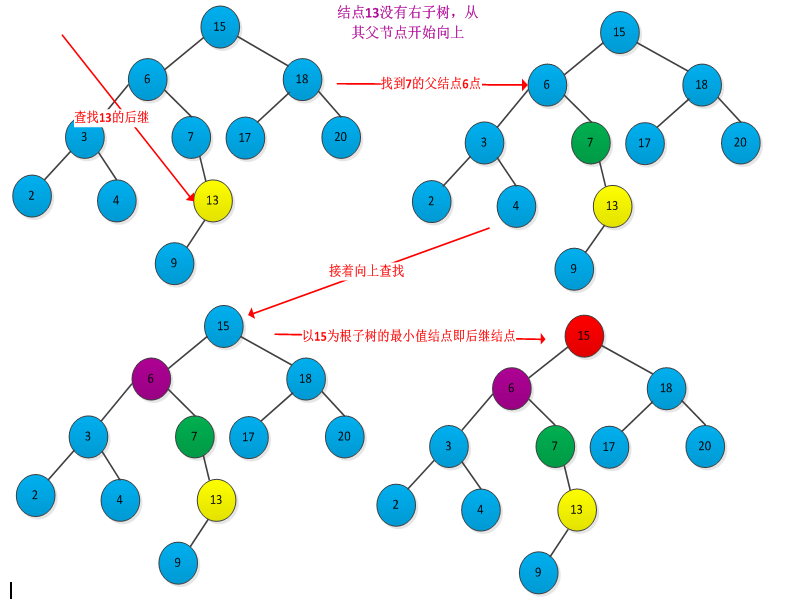
书中给出了求x结点后继结点的伪代码:
TREE_PROCESSOR(x) if right[x] != NULL then return TREE_MINMUM(right(x)) y=parent[x] while y!= NULL and x ==right[y] do x = y y=parent[y] return y
定理:对一棵高度为h的二叉查找,动态集合操作SEARCH、MINMUM、MAXMUM、SUCCESSOR、PROCESSOR等的运行时间均为O(h)。
3、插入和删除
插入和删除会引起二叉查找表示的动态集合的变化,难点在在插入和删除的过程中要保持二叉查找树的性质。插入过程相当来说要简单一些,删除结点比较复杂。
(1)插入
插入结点的位置对应着查找过程中查找不成功时候的结点位置,因此需要从根结点开始查找带插入结点位置,找到位置后插入即可。下图所示插入结点过程:
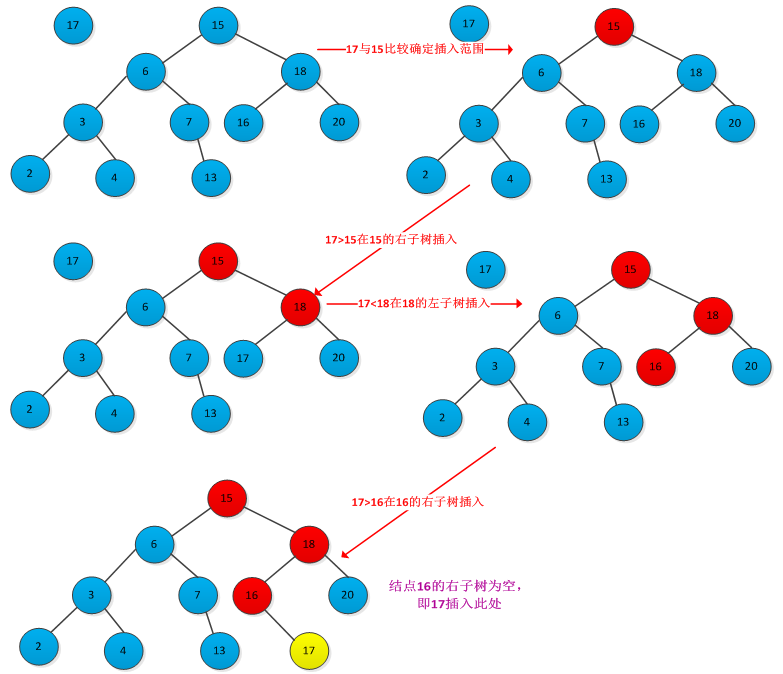
书中给出了插入过程的伪代码:
TREE_INSERT(T,z) y = NULL; x =root[T] while x != NULL do y =x if key[z] < key[x] then x=left[x] else x=right[x] parent[z] =y if y=NULL then root[T] =z else if key[z]>key[y] then keft[y] = z else right[y] =z
插入过程运行时间为O(h),h为树的高度。
(2)删除
从二叉查找树中删除给定的结点z,分三种情况讨论:
<1>结点z没有左右子树,则修改其父节点p[z],使其为NULL。删除过程如下图所示: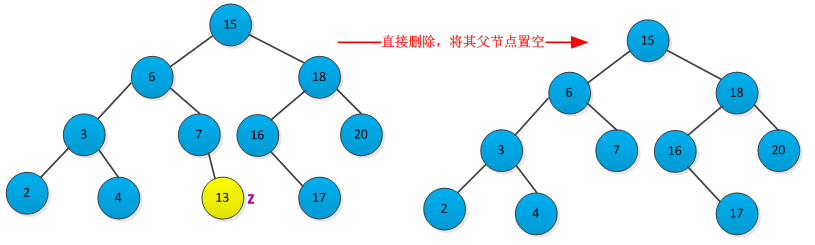
<2>如果结点z只有一个子树(左子树或者右子树),通过在其子结点与父节点建立一条链来删除z。删除过程如下图所示: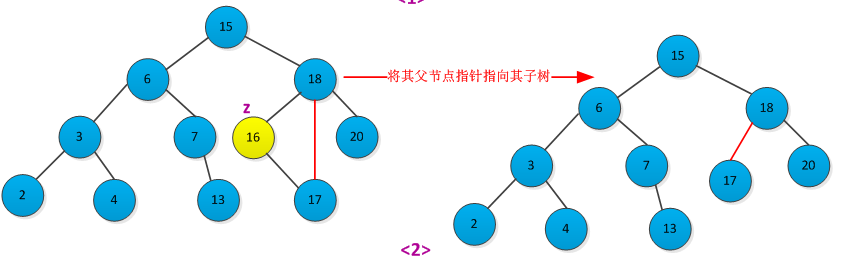
<3>如果z有两个子女,则先删除z的后继y(y没有左孩子),在用y的内容来替代z的内容。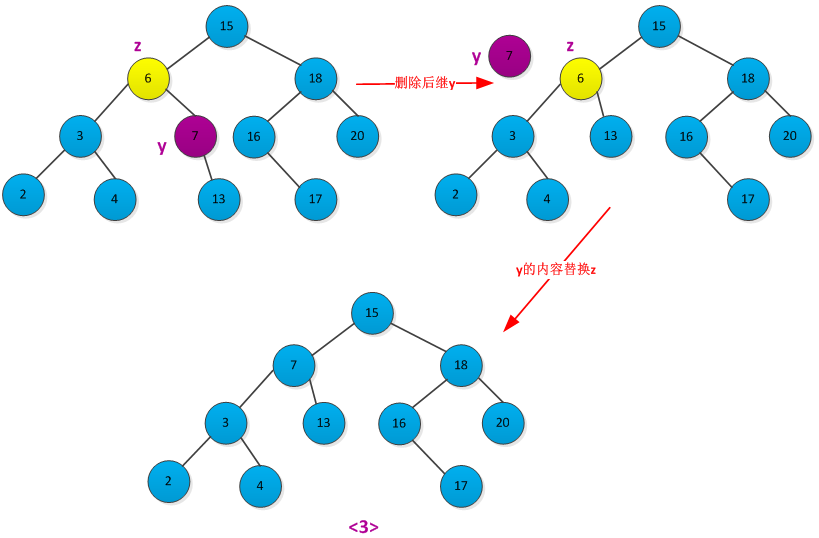
书中给出了删除过程的伪代码:
TREE_DELETE(T,z) if left[z] ==NULL or right[z] == NULL then y=z else y=TREE_SUCCESSOR(z) if left[y] != NULL then x=left[y] else x=right[y] if x!= NULL then parent[x] = parent[y] if p[y] ==NULL then root[T] =x else if y = left[[prarnt[y]] then left[parent[y]] = x else right[parent[y]] =x if y!=z then key[z] = key[y] copy y's data into z return y
定理:对高度为h的二叉查找树,动态集合操作INSERT和DELETE的运行时间为O(h)。
4、实现测试
采用C++语言实现一个简单的二叉查找树,支持动态集合的基本操作:search、minmum、maxmum、predecessor、successor、insert和delete。设计的二叉查找树结构如下所示:

#include<iostream> #include<stack> #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; typedef struct BinarySearchTreeNode { int elem; struct BinarySearchTreeNode *parent; struct BinarySearchTreeNode *left; struct BinarySearchTreeNode *right; }BinarySearchTreeNode,*BinarySearchTree; //初始化二叉树 void init_binary_tree(BinarySearchTree *root) { *root=NULL; } //非递归 void TreeInsert(BinarySearchTree *root,int z) { BinarySearchTree y=NULL,x; if(*root==NULL) { *root=(BinarySearchTree)malloc(sizeof(BinarySearchTreeNode)); (*root)->elem=z; (*root)->left=(*root)->right=NULL; (*root)->parent=NULL; return; } x=*root; while(x) { //y用来记录父节点 y=x; if(z<x->elem) x=x->left; else x=x->right; } BinarySearchTree p=(BinarySearchTree)malloc(sizeof(BinarySearchTreeNode)); p->elem=z; p->parent=y; p->left=p->right=NULL; if(z<y->elem) y->left=p; else y->right=p; } //递归 void tree_insert(BinarySearchTree *root,int z) { if(*root==NULL) { *root=(BinarySearchTree)malloc(sizeof(BinarySearchTreeNode)); (*root)->elem=z; (*root)->left=(*root)->right=(*root)->parent=NULL; return; } if((*root)->left==NULL&&z<(*root)->elem) { BinarySearchTree p=(BinarySearchTree)malloc(sizeof(BinarySearchTreeNode)); p->elem=z; p->left=p->right=NULL; p->parent=*root; (*root)->left=p; return; } if((*root)->right==NULL&&z>(*root)->elem) { BinarySearchTree p=(BinarySearchTree)malloc(sizeof(BinarySearchTreeNode)); p->elem=z; p->left=p->right=NULL; p->parent=*root; (*root)->right=p; return; } if(z<(*root)->elem) TreeInsert(&((*root)->left),z); else TreeInsert(&((*root)->right),z); } void CreateBSTree(BinarySearchTree *root,int length) { cout<<"create BST tree:"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<length;i++) { int key; cin>>key; tree_insert(root,key); } } //递归 void inorder_tree_walk(BinarySearchTree root) { if(root) { inorder_tree_walk(root->left); cout<<root->elem<<" "; inorder_tree_walk(root->right); } } //非递归中序遍历 void inoder(BinarySearchTree root) { stack<BinarySearchTree> s; while(root||!s.empty()) { if(root) { s.push(root); root=root->left; } else { BinarySearchTree tmpnode=s.top(); cout<<tmpnode->elem<<" "; s.pop(); root=root->right; } } } //递归查找 BinarySearchTree tree_search(BinarySearchTree root,int key) { if(root==NULL||root->elem==key) return root; if(key<root->elem) return tree_search(root->left,key); else return tree_search(root->right,key); } //非递归查找 BinarySearchTree TreeSearch(BinarySearchTree root,int key) { if(root==NULL||root->elem==key) return root; while(root&&root->elem!=key) { if(key<root->elem) { root=root->left; } else root=root->right; } return root; } //非递归查找最小值 BinarySearchTree TreeMinimum(BinarySearchTree root) { if(root==NULL||!root->left) return root; while(root->left) root=root->left; return root; } //非递归查找最大值 BinarySearchTree TreeMaximum(BinarySearchTree root) { if(root==NULL||root->left) return root; while(root->right) root=root->right; return root; } //找后继 BinarySearchTree TreeSuccessor(BinarySearchTree x) { if(x->right) return TreeMinimum(x->right); BinarySearchTree parent; parent=x->parent; while(parent&&parent->right==x) { x=parent; parent=parent->parent; } return parent; } //找前驱 BinarySearchTree TreePredecessor(BinarySearchTree x) { if(x->left) return TreeMaximum(x->left); BinarySearchTree parent; parent=x->parent; while(parent&&x==parent->left) { x=parent; parent=parent->parent; } return parent; } //删除 int TreeDelete(BinarySearchTree *root,int z) { BinarySearchTree pnode,snode; pnode=TreeSearch(*root,z); if(pnode!=NULL) { BinarySearchTree parentnode=pnode->parent; if(pnode->left==NULL||pnode->right==NULL) { if(pnode->left) { if(parentnode->left==pnode) parentnode->left=pnode->left; else parentnode->right=pnode->left; pnode->left->parent=parentnode; } else if(pnode->right) { if(parentnode->left==pnode) parentnode->left=pnode->right; else parentnode->right=pnode->right; pnode->right->parent=parentnode; } else { if(parentnode->left==pnode) parentnode->left=NULL; else parentnode->right=NULL; } free(pnode); } else { snode=TreeSuccessor(pnode); pnode->elem=snode->elem; if(snode==snode->parent->left) { snode->parent->left=snode->right; snode->right->parent=snode->parent; cout<<"delete left:"<<endl; cout<<snode->right->parent->elem<<endl; } if(snode==snode->parent->right) { snode->parent->right=snode->right; snode->right->parent=snode->parent; cout<<"delete right:"<<endl; cout<<snode->right->parent->elem<<endl; } free(snode); } return(0); } return(1); } int main() { BinarySearchTree root; init_binary_tree(&root); CreateBSTree(&root,10); cout<<"中序遍历:"; inorder_tree_walk(root); cout<<endl; cout<<"delete node:"<<endl; TreeDelete(&root,4); cout<<endl; inorder_tree_walk(root); }
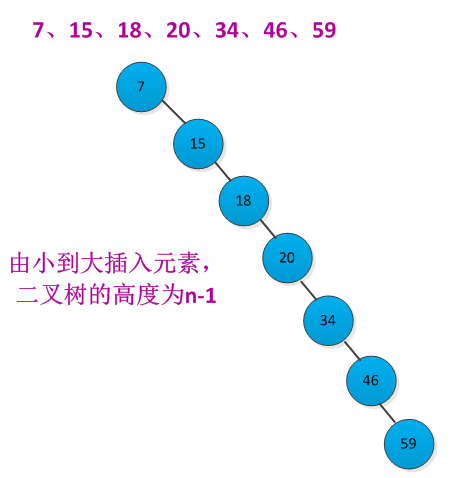
5、随机构造二叉查找树
二叉查找上各种基本操作的运行时间都是O(h),h为树的高度。但是在元素插入和删除过程中,树的高度会发生改变。如果n个元素按照严格增长的顺序插入,那个构造出的二叉查找树的高度为n-1。例如按照先后顺序插入7、15、18、20、34、46、59元素构造二叉查找树,二叉查找树结构如下所示: