对于一个给定的随机粗糙面,对光波来说可能呈现很粗糙,而对微波来说却可能呈现的很光滑,这主要是因为随机表面的粗糙度是以波长为度量单位的统计参数来表征的。而描述粗糙面的统计量除功率谱密度外,还有高度起伏的概率密度函数和均方高,相关函数和相关长度,结构函数,特征函数,均方斜度与曲率半径等。下面将逐一介绍它们统计描述,并说明它们和功率谱密度间的相互关系。
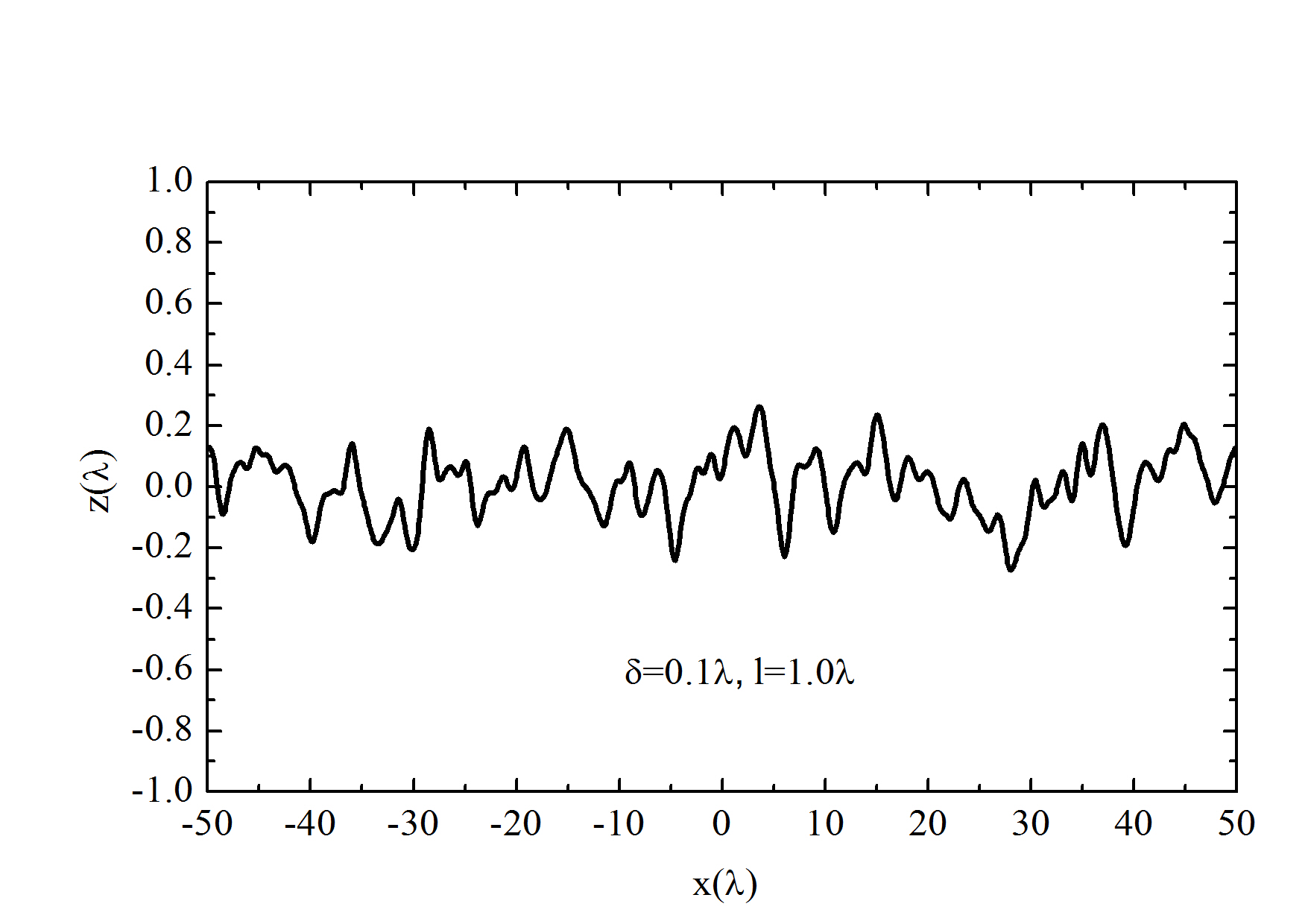 图1 一维粗糙表面的模拟图(其中x轴和y轴都是以入射波长$lambda$为单位的)
图1 一维粗糙表面的模拟图(其中x轴和y轴都是以入射波长$lambda$为单位的)
1 粗糙面中各个基本参量
图1为一个一维粗糙表面,其高度起伏$z=f(x)$,概率密度函数$p(f)$表征高度起伏的分布情况;均方根高度$delta $又称为表面高度标准离差,对于无限长度的粗糙面,其均方根高度表示为$delta =sqrt{E[{{f}^{2}}(x)]-{{{E[f(x)]}}^{2}}}=sqrt{int_{-infty }^{infty }{ {{f}^{2}}p(f)\,df-{{[int_{-infty }^{infty }{ fp(f)\,df}]}^{2}}}}$
$E$表示沿整个粗糙面取均值,一般以$z=0$的平面作为参考面。对于有限长度$L$的粗糙面,需要将上式积分上下限改为$-L/2 ilde{ }L/2$,对该有限表面进行离散,设离散采样点数$N$个,离散采样间隔$Delta x$一般在1/10波长范围内,然后通过下式计算$delta =sqrt{frac{1}{N-1} [sumlimits_{i=1}^{N}{{{({{f}_{i}})}^{2}}-Ncdot {{(E(f))}^{2}}]}}$
粗糙面上任意两点间的关联程度,称为相关函数$C$,定义为$C({{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}})=(1/{{delta }^{2}})E[f({{x}_{1}})\,f({{x}_{2}})]$,其中$delta $为均方根高度,${{x}_{1}}$和${{x}_{2}}$为表面上任意两点横坐标,常用的相关函数有高斯相关函数和指数相关函数,分别如下
$C({{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}})=exp (-{{({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})}^{2}}/{{l}^{2}})$(高斯),$C({{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}})=exp (-left| {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}}
ight|/l)$(指数)
其中$l$为相关长度,$D={{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}}$为表面上两点间水平距离,当$C({{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}})=1/e$时需要${{({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})}^{2}}/{{l}^{2}}=1$,即此时$D={{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}}=l$,即为相关长度$l$。
对表面高度相关函数作傅立叶变换,即得到其功率谱密度函数,表示为$W(k)=frac{1}{2pi }int_{-infty }^{infty }{C(D)exp (-ikD)dD}$
对高斯相关函数和指数相关函数分别作如上傅立叶变换,得到高斯谱密度函数和指数谱密度函数,分别如下$W(k)=frac{{{delta }^{2}}l}{2sqrt{pi }}exp (-{{k}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}/4)$(高斯),$W(k)=frac{{{delta }^{2}}l}{pi (1+{{k}^{2}}{{l}^{2}})}$(指数)
均方根斜率$s$表示为$s=sqrt{E[{{(df/dx)}^{2}}]}$,均方根斜率$s$与功率谱密度函数间有如下关系$s=[int{{{k}^{2}}S(k)dk{{]}^{1/2}}}$,对于高斯谱密度粗糙面,$s=sqrt{2}h/l$;对于指数谱密度粗糙面,因通常表面边缘形状较尖锐,积分不可积,均方根斜率$s$通常不存在。
结构函数定义为表面上两点高度差的均值,即
$D({{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}})=E[{{[f({{x}_{1}})-f({{x}_{2}})]}^{2}}]$
上面费了好长时间,公式神马的实在是太麻烦了,真心想了解的同学可以下载下面的附件,我在这里就直接贴出代码了
http://files.cnblogs.com/xd-jinjian/%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%8C%E7%AB%A0%EF%BC%88%E5%BB%BA%E6%A8%A1%EF%BC%89.pdf
第一种方法 不使用傅里叶变换,直接叠加法
// OneDimensionRoughSurface.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
const complex<double> unit_i(0.0,1.0);
const complex<double> unit_r(1.0,0.0);
const double wavespeed=3.0*pow(10.0,8); //波速
const double frequence=1.0*pow(10.0,9); //频率
const double lamda=wavespeed/frequence; //波长
const double delta=0.2*lamda; //均方根高度
const double lcor=lamda; //相关长度
const int M=1024; //总采样点数
const double m=8; //一个波长内的采样点数
const double dx=lamda/m; //x方向的间隔
const double L=(M-1)*dx;
//const double L=102.4*lamda;
const double pi=3.1415926;
void random(double start,double end,double seed,double size,double *myrand);
double gaussrand();
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
double *x=new double [M];
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
x[i]=(-0.5*M+i)*dx;
double *kj=new double [M];
complex<double> *Fkj=new complex<double> [M];
double *S=new double [M];
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
{
kj[i]=(-0.5*M+i)*2*pi/L;
S[i]=delta*delta*lcor/(2*sqrt(pi))*exp(-kj[i]*kj[i]*lcor*lcor/4);
}
double *myrand=new double [M];
random(0.0,1.0,time(0),M,myrand);
Fkj[0]=sqrt(2*pi*L*S[0])*myrand[0];
Fkj[M/2]=sqrt(2*pi*L*S[M/2])*myrand[1];
for(int i=1;i<M/2;++i)
{
Fkj[i]=sqrt(2*pi*L*S[i])*(myrand[2*i]+unit_i*myrand[2*i+1])/sqrt(2.0);
Fkj[M-i]=conj(Fkj[i]);
}
complex<double> *res=new complex<double> [M];
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
{
double xn=(-0.5*M+i)*dx;
//double xn=(i)*dx;
for(int j=0;j<M;++j)
{
res[i]+=Fkj[j]*exp(unit_i*kj[j]*xn);
}
res[i]/=L;
}
ofstream sout("diejia.dat",ios::out);
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
sout<<res[i].real()/lamda<<" "<<res[i].imag()/lamda<<endl;
sout.close();
delete [] res;
delete [] x;
delete [] S;
delete [] myrand;
delete [] kj;
delete [] Fkj;
return 0;
}
void random(double start,double end,double seed,double size,double *myrand) //在用二维数组作为形参时,必须指明列数
{
double s=65536.0;
double w=2053.0;
double v=13849.0;
double T=0.0;
int m;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
T=0.0;
for(int k=0;k<12;k++)
{
seed=w*seed+v;
m=seed/s;
seed=seed-m*s;
T=T+seed/s;
}
myrand[i]=start+end*(T-6.0);
}
}
第二种,使用傅里叶变换
// OneDimensionRoughSurface.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
const complex<double> unit_i(0.0,1.0);
const complex<double> unit_r(1.0,0.0);
const double wavespeed=3.0*pow(10.0,8); //波速
const double frequence=1.0*pow(10.0,9); //频率
const double lamda=wavespeed/frequence; //波长
const double delta=0.2*lamda; //均方根高度
const double lcor=lamda; //相关长度
const int M=1024; //总采样点数
const double m=8; //一个波长内的采样点数
const double dx=lamda/m; //x方向的间隔
const double L=(M-1)*dx;
const double pi=3.1415926;
void random(double start,double end,double seed,double size,double *myrand);
double gaussrand();
inline void swap (float &a, float &b);
void bitrp (float xreal [], float ximag [], int n);
void IFFT (float xreal [], float ximag [], int n);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
double *x=new double [M];
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
x[i]=-L/2+i*dx;
double *kj=new double [M];
complex<double> *Fkj=new complex<double> [M];
double *S=new double [M];
for(int i=0;i<=M/2;++i)
{
kj[i]=i*2*pi/L;
S[i]=delta*delta*lcor/(2*sqrt(pi))*exp(-kj[i]*kj[i]*lcor*lcor/4);
}
double *myrand=new double [M];
random(0.0,1.0,time(0),M,myrand);
Fkj[0]=sqrt(2*pi*L*S[0])*myrand[0];
Fkj[M/2]=sqrt(2*pi*L*S[M/2])*myrand[1];
for(int i=1;i<M/2;++i)
{
Fkj[i]=sqrt(2*pi*L*S[i])*(myrand[2*i]+unit_i*myrand[2*i+1])/sqrt(2.0);
Fkj[M-i]=conj(Fkj[i]);
}
float xreal [M] = {}, ximag [M] = {};
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
{
xreal[i]=Fkj[i].real();
ximag[i]=Fkj[i].imag();
}
IFFT (xreal, ximag, M);
ofstream sout("fft.dat",ios::out);
for(int i=0;i<M;++i)
{
sout<<xreal[i]*M/L/lamda<<" "<<ximag[i]*M/L/lamda<<endl;
}
sout.close();
delete [] x;
delete [] S;
delete [] myrand;
delete [] kj;
delete [] Fkj;
return 0;
}
void random(double start,double end,double seed,double size,double *myrand) //在用二维数组作为形参时,必须指明列数
{
double s=65536.0;
double w=2053.0;
double v=13849.0;
double T=0.0;
int m;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
T=0.0;
for(int k=0;k<12;k++)
{
seed=w*seed+v;
m=seed/s;
seed=seed-m*s;
T=T+seed/s;
}
myrand[i]=start+end*(T-6.0);
}
}
inline void swap (float &a, float &b)
{
float t;
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
void bitrp (float xreal [], float ximag [], int n)
{
// 位反转置换 Bit-reversal Permutation
int i, j, a, b, p;
for (i = 1, p = 0; i < n; i *= 2)
{
p ++;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
a = i;
b = 0;
for (j = 0; j < p; j ++)
{
b = (b << 1) + (a & 1); // b = b * 2 + a % 2;
a >>= 1; // a = a / 2;
}
if ( b > i)
{
swap (xreal [i], xreal [b]);
swap (ximag [i], ximag [b]);
}
}
}
void IFFT (float xreal [], float ximag [], int n)
{
// 快速傅立叶逆变换
float wreal [M / 2], wimag [M / 2], treal, timag, ureal, uimag, arg;
int m, k, j, t, index1, index2;
bitrp (xreal, ximag, n);
// 计算 1 的前 n / 2 个 n 次方根 Wj = wreal [j] + i * wimag [j] , j = 0, 1, , n / 2 - 1
arg = 2 * pi / n;
treal = cos (arg);
timag = sin (arg);
wreal [0] = 1.0;
wimag [0] = 0.0;
for (j = 1; j < n / 2; j ++)
{
wreal [j] = wreal [j - 1] * treal - wimag [j - 1] * timag;
wimag [j] = wreal [j - 1] * timag + wimag [j - 1] * treal;
}
for (m = 2; m <= n; m *= 2)
{
for (k = 0; k < n; k += m)
{
for (j = 0; j < m / 2; j ++)
{
index1 = k + j;
index2 = index1 + m / 2;
t = n * j / m; // 旋转因子 w 的实部在 wreal [] 中的下标为 t
treal = wreal [t] * xreal [index2] - wimag [t] * ximag [index2];
timag = wreal [t] * ximag [index2] + wimag [t] * xreal [index2];
ureal = xreal [index1];
uimag = ximag [index1];
xreal [index1] = ureal + treal;
ximag [index1] = uimag + timag;
xreal [index2] = ureal - treal;
ximag [index2] = uimag - timag;
}
}
}
for (j=0; j < n; j ++)
{
xreal [j] /= n;
ximag [j] /= n;
}
}
结果如上图所示