Problem Description
定义一个二维数组:
它表示一个迷宫,其中的1表示墙壁,0表示可以走的路,只能横着走或竖着走,不能斜着走,要求编程序找出从左上角到右下角的最短路线。
int maze[5][5] = {
0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
};
它表示一个迷宫,其中的1表示墙壁,0表示可以走的路,只能横着走或竖着走,不能斜着走,要求编程序找出从左上角到右下角的最短路线。
Input
一个5 × 5的二维数组,表示一个迷宫。数据保证有唯一解。
Output
左上角到右下角的最短路径,格式如样例所示。
Sample Input
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
Sample Output
(0, 0) (1, 0) (2, 0) (2, 1) (2, 2) (2, 3) (2, 4) (3, 4) (4, 4)
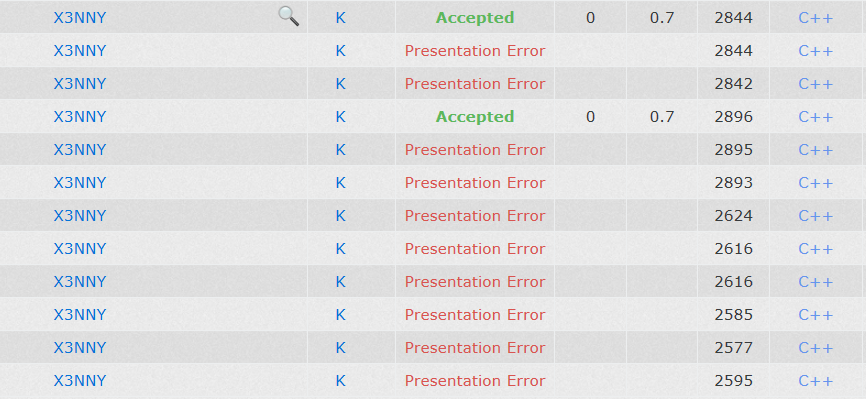
也是kuangbin搜索专题里面的,说起这道题,也是满满的恶意,先看图吧
整整花了一个小时去找到底哪里PE了。
题目思路很明确,BFS或者DFS都可以,但其实这个题目没必要DFS,简单BFS标记一下前驱就行了,何为前驱,就是说你走到了下一步你上一步 是从哪里走来的,然后用优先队列保证每次优先走距离右下角最近的路。那么问题来了,如何输出,因为我们存的是前驱,所以可以先把所有前驱 入栈,再依次出栈输出就行了,但最开始我想到了另一种更好的方法,因为我发现
ostringstream outt; outt << 2 << 1 << 3; string s = outt.str(); reverse(s.begin(), s.end()); cout << s << endl;
利用ostringstream流,最后倒过来就可以实现直接顺序输出了,提交PE。找了半天发现是<<endl;倒序后变成先输出了,那么我第一个不加endl,再次提交PE、PE、PE、PE。到这里我觉得可能是ostringstream影响缓冲区,不能这样,改成栈模拟,还是PE =7=,直到最后我发现,(a, b)中间 逗号后面 有个空格 /微笑/微笑。然后改了两种方法都AC了;
AC代码
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <sstream> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <deque> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <set> 13 #include <list> 14 #include <cstring> 15 #include <cctype> 16 #include <algorithm> 17 #include <iterator> 18 #include <cmath> 19 #include <bitset> 20 #include <ctime> 21 #include <fstream> 22 #include <limits.h> 23 #include <numeric> 24 25 using namespace std; 26 27 #define F first 28 #define S second 29 #define mian main 30 #define ture true 31 32 #define MAXN 1000000+5 33 #define MOD 1000000007 34 #define PI (acos(-1.0)) 35 #define EPS 1e-6 36 #define MMT(s) memset(s, 0, sizeof s) 37 typedef unsigned long long ull; 38 typedef long long ll; 39 typedef double db; 40 typedef long double ldb; 41 typedef stringstream sstm; 42 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 43 44 int mp[5][5],vis[5][5]; 45 int fx[4][2] = {1,0,-1,0,0,-1,0,1}; 46 vector< pair< int, pair<int,int> > >bj(40); //记录前驱和位置 47 ostringstream outt; 48 class cmp{ //优先队列使得曼哈顿距离小的优先出队 49 public: 50 bool operator() (const pair<int,int>a,const pair<int,int>b) const{ 51 int ax = 4 - a.F + 4 - a.S; 52 int bx = 4 - b.F + 4 - b.S; 53 return ax > bx; 54 } 55 }; 56 57 void bfs(){ 58 priority_queue< pair<int,int>,vector< pair<int,int> >, cmp >q; 59 //queue< pair<int,int> >q; 60 q.push(make_pair(0,0)); 61 vis[0][0] = 1; 62 while(!q.empty()){ 63 pair<int,int>nx = q.top(); 64 q.pop(); 65 //cout << nx.F << " " << nx.S << endl; 66 if(8 - (nx.F + nx.S) == 1){ 67 bj[24].F = nx.F*5+nx.S; 68 bj[24].S.F = 4, bj[24].S.S = 4; 69 break; 70 } 71 72 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ 73 int nxx = nx.F + fx[i][0]; 74 int nxy = nx.S + fx[i][1]; 75 if(nxx < 0 || nxx > 4 || nxy < 0 || nxy > 4 || mp[nxx][nxy] == 1 || vis[nxx][nxy]) 76 continue; 77 vis[nxx][nxy] = 1; 78 q.push(make_pair(nxx,nxy)); 79 bj[nxx*5+nxy].F = nx.F*5+nx.S; 80 bj[nxx*5+nxy].S.F = nxx, bj[nxx*5+nxy].S.S = nxy; 81 } 82 } 83 int nex = 24; 84 /* //这是用栈模拟的方式 85 stack<int>p; 86 while(nex){ 87 p.push(nex); 88 nex = bj[nex].F; 89 } 90 p.push(0); 91 while(!p.empty()){ 92 nex = p.top(); 93 p.pop(); 94 cout << "(" << bj[nex].S.F << ", " << bj[nex].S.S << ")"<< endl; 95 } 96 */ 97 while(1){ //反向输出到ostringstream中 98 //cout << nex << endl; 99 if(nex == 0){ 100 outt << ")" << bj[nex].S.S << " ," << bj[nex].S.F << "("; 101 break; 102 } 103 outt << ")" << bj[nex].S.S << " ," << bj[nex].S.F << "(" << " "; 104 nex = bj[nex].F; 105 } 106 107 } 108 109 int main(){ 110 ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); 111 cout.tie(0); 112 cin.tie(0); 113 fill(vis[0],vis[0]+5*5,0); 114 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 115 for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){ 116 cin>>mp[i][j]; 117 } 118 } 119 bfs(); 120 string s = outt.str(); 121 reverse(s.begin(),s.end()); //再次逆序 122 cout << s << endl; 123 124 return 0; 125 }
其他就是一个简单的BFS,值得注意就是优先队列的使用,当然用DFS也行 ,而且DFS就不需要这么多繁杂的逆序了,直接记录从起点到终点的路径输出就好了。