参考指南:
Web API入门指南
http://www.cnblogs.com/guyun/p/4589115.html
用Python写一个简单的Web框架
http://www.cnblogs.com/russellluo/p/3338616.html
WSGI接口 def application(environ, start_response)
https://blog.csdn.net/tycoon1988/article/details/40394555
GET和POST两种基本请求方法的区别
https://www.cnblogs.com/logsharing/p/8448446.html
Web API :
面向如浏览器,移动设备等各种客户端,提供Http服务的框架。
支持基于HTTP的各种操作(get,post,put,delete)。
请求的回复格式支持JSON,XML,CSV等。
使用场景:
1)服务在http协议之上,利用http协议的各种功能;
2)服务需被各种客户端(尤其是移动客户端)调用。
WISG(Web Server Gateway Interface):
在Python中,WSGI(Web Server Gateway Interface)定义了Web服务器与Web应用(或Web框架)之间的标准接口.
利用WSGI,可以很方便写一个Web框架。
引用方式是:from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server。
application()函数就是符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,它接收两个参数:
1)environ:一个包含所有HTTP请求信息的dict对象;
2)start_response:一个发送HTTP响应的函数。
urlparse解析URL参数模块:
可以对URL按照一定格式进行拆分或拼接。
urlparse.parse_qs()方法返回解析URL后的字典
Json(JavaScriptObject Notation, JS 对象标记):
是轻量级的数据交换格式
格式:双引号 "" 包裹健名,使用冒号 : 分隔,然后紧接着值:
如 {"firstName": "Json"}
优点:使用的字符比xml与html等少,大大节约传输数据占用的带宽;
语法格式与层次结构比较清晰,容易阅读。
json.dumps()函数是将字典转化为字符串.
get/post请求:
get:请求参数都是通过url传递,如url?param1=xxx¶m2=xxx
post:请求参数通过request body传递,需要知道请求参数类型(如application/json、application/x-www-form-urlencoded、multipart/form-data、text/html等),url,返回结果格式,是否有是否有header、cookie等
实例:
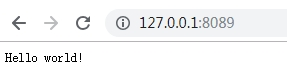
实例1:启动一个简单web,访问时返回hello world!字符串

1 # coding:utf-8 2 3 #导入WISG(Web Server Gateway Interface) 4 from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server 5 6 #application()函数是Python中符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,返回是一个字符串 7 def application(environ,start_response): 8 #start_response如下调用就会发送HTTP响应的Header,注意只能调用一次start_response()函数发送Header。 9 #start_response()函数两个参数,一是HTTP响应码,一是一组list表示的HTTP Header,每个Header用一个包含两个str的数组表示 10 status='200 OK' 11 response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/plain')] 12 start_response(status,response_headers) 13 return ['Hello world! '] 14 15 ip='0.0.0.0' 16 port=8089 17 httpd =make_server(ip,port,application) 18 print("server is started, port is 8089....") 19 httpd.serve_forever() 20 21
运行结果:
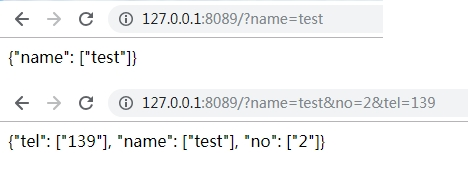
实例2:启动一个简单web,访问接口,返回解析URL的值
# coding:utf-8 #导入WISG(Web Server Gateway Interface) from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server import urlparse #application()函数是Python中符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,返回是一个字符串 def application(environ,start_response): #start_response如下调用就会发送HTTP响应的Header,注意只能调用一次start_response()函数发送Header。 #start_response()函数两个参数,一是HTTP响应码,一是一组list表示的HTTP Header,每个Header用一个包含两个str的数组表示 status='200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/html')] start_response(status,response_headers) #调用urlparse的parse_qs解析URL参数,并返回字典 query_args=environ['QUERY_STRING'] params = urlparse.parse_qs(environ['QUERY_STRING']) print(str(params)) return [str(params)] ip='0.0.0.0' port=8089 httpd =make_server(ip,port,application) print("server is started, port is 8089....") httpd.serve_forever()
运行结果:

实例3:启动一个简单web,访问接口,返回解析URL的值(n个变量),JSON格式
# coding:utf-8 #导入WISG(Web Server Gateway Interface) from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server import urlparse import json #application()函数是Python中符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,返回是一个字符串 def application(environ,start_response): #start_response如下调用就会发送HTTP响应的Header,注意只能调用一次start_response()函数发送Header。 #start_response()函数两个参数,一是HTTP响应码,一是一组list表示的HTTP Header,每个Header用一个包含两个str的数组表示 status='200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/html')] start_response(status,response_headers) #调用urlparse的parse_qs解析URL参数,并返回字典 query_args=environ['QUERY_STRING'] params = urlparse.parse_qs(environ['QUERY_STRING']) #返回的字段,需要转换为字符串作为函数的输出 print(str(params)) #json.dumps()函数是将字典转化为字符串 result=json.dumps(params) return [result] ip='0.0.0.0' port=8089 httpd =make_server(ip,port,application) print("server is started, port is 8089....") httpd.serve_forever()
返回结果:
实例4:启动一个简单web,get方法访问接口,根据输入的值返回判断结果(JSON格式)
# coding:utf-8 #导入WISG(Web Server Gateway Interface) from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server import urlparse import json #application()函数是Python中符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,返回是一个字符串 def application(environ,start_response): #start_response如下调用就会发送HTTP响应的Header,注意只能调用一次start_response()函数发送Header。 #start_response()函数两个参数,一是HTTP响应码,一是一组list表示的HTTP Header,每个Header用一个包含两个str的数组表示 status='200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/html')] start_response(status,response_headers) #调用urlparse的parse_qs解析URL参数,并返回字典 query_args=environ['QUERY_STRING'] params = urlparse.parse_qs(query_args) # 获取get中key为name的值 name = params.get('name', [''])[0] # 获取get中key为passwd的值 passwd = params.get('passwd', [''])[0] # 获取get中key为tel的值 tel = params.get('tel', [''])[0] if name=='admin' and passwd=='123456' and tel=='139': result={'code':200,'message':"You get the flag"} return json.dumps(result) elif passwd!='123456': result={'code':404,'message':"oh, passwd is wrong!"} return json.dumps(result) elif name!='admin': result={'code':404,'message':"oh, name is wrong!"} return json.dumps(result) else: result={'code':404,'message':"oh,what are you doing???"} return json.dumps(result) #返回的字段,需要转换为字符串作为函数的输出 print(str(params)) #json.dumps()函数是将字典转化为字符串 #result=json.dumps(params) return [result] ip='0.0.0.0' port=8089 httpd =make_server(ip,port,application) print("server is started, port is 8089....") httpd.serve_forever()
返回结果:

实例5:启动一个简单web,post方法访问接口,根据输入的值返回结果(JSON格式)
# coding:utf-8 #导入WISG(Web Server Gateway Interface) from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server import json from cgi import parse_qs, escape #application()函数是Python中符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,返回是一个字符串 def application(environ,start_response): #start_response如下调用就会发送HTTP响应的Header,注意只能调用一次start_response()函数发送Header。 #start_response()函数两个参数,一是HTTP响应码,一是一组list表示的HTTP Header,每个Header用一个包含两个str的数组表示 status='200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-type', 'application/json')] start_response(status,response_headers) #environ是当前请求的所有数据,包括Header和URL,body #当请求方法是POST的时候,查询字符串将从HTTP请求体中传递而不是通过URL。 #请求体是WSGI服务器提供的类似于环境变量的wsgi.input文件 #有必要知道应答体的大小,以便从wsgi.input中读出它。WSGI明细规定,CONTENT_LENGTH变量来存储大小,它可以为空或者被忽略,所以读它的时候把它放到一个try/except块中。 try: request_body_size = int(environ.get('CONTENT_LENGTH', 0)) except (ValueError): request_body_size = 0 print("request_body_size is:"+str(request_body_size)) request_body = environ["wsgi.input"].read(request_body_size) print("request_body is:"+request_body) # 获取get中key为name的值 name=parse_qs(request_body).get("name", [""])[0] # 获取get中key为passwd的值 passwd = parse_qs(request_body).get('passwd', [''])[0] print(name,passwd) #返回的字段,需要转换为字符串作为函数的输出 #json.dumps()函数是将字典转化为字符串 #result=json.dumps(params) return [request_body] ip='0.0.0.0' port=8089 httpd =make_server(ip,port,application) print("server is started, port is 8089....") httpd.serve_forever()
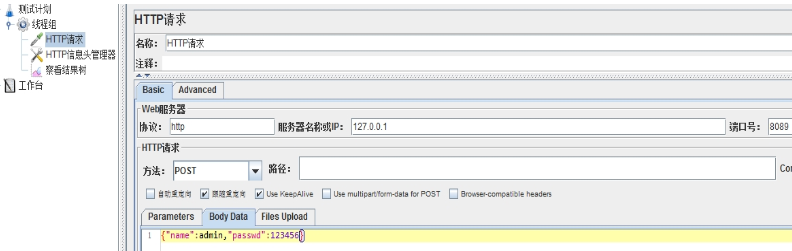
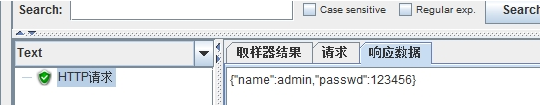
请求与应答:
Jmeter发送post请求,并查看结果