Interpolator 被用来修饰动画效果,定义动画的变化率。在Android源码中对应的接口类为TimeInterpolator,通过输入均匀变化的0~1之间的值,可以得到匀速、正加速、负加速、无规则变加速等0~1之间的变化曲线。
曲线举例:
如下图所示,为Android源码中OvershootInterpolator插值器变化率曲线。
输入为均匀变化0~1.0f之间浮点值,输出为先加速超过临界值1.0f 再慢慢又回落到1.0f 连续变化的浮点值。
效果举例:
使用OvershootInterpolator动画插值器后,动画的运行效果如下所示:

上图中,旋转放大效果中,旋转动画就是使用了OvershootInterpolator动画插值器。
可以看到3D勋章 360度旋转时,旋转角度先超过了360度,然后慢慢又回到了360度位置,从而呈现一个回弹的视觉效果。

注:
了解 3D勋章具体实现,参考文章《3D勋章实现方案》:
https://xiaxl.blog.csdn.net/article/details/77048507
- Android 源码中的动画插值器
- Easing 经典动画插值器
一、Android中的插值器
Android源码中使用 TimeInterpolator 接口修饰动画效果,定义动画的变化率。
代码位于android.animation包下,只包含一个抽象方法为getInterpolation(float input)。
// 位于android.animation包下
package android.animation;
// Android源码中的 动画插值器
public interface TimeInterpolator {
// 差值计算(输入为0~1.0f之间的浮点值,输出为连续的变化率曲线)
float getInterpolation(float input);
}
TimeInterpolator接口类中,只有一个方法float getInterpolation(float input),根据输入的浮点值input(0~1.0f之间),输出为连续的变化率曲线。
Android中动画插值器的使用方式如下:
// view 位移动画
AnimatorSet localAnimatorSet = new AnimatorSet();
float[] arrayOfFloat = new float[2];
arrayOfFloat[0] = y0;
arrayOfFloat[1] = y1;
// 位移动画使用了 DecelerateInterpolator() 动画插值器
// 动画效果:先位移超过临界值,再回到临界值
ObjectAnimator localObjectAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view,
"translationY", arrayOfFloat);
localObjectAnimator.setDuration(240L);
localObjectAnimator.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
localAnimatorSet.play(localObjectAnimator);
localAnimatorSet.start();
TimeInterpolator为接口类,其有如下接口实现类。
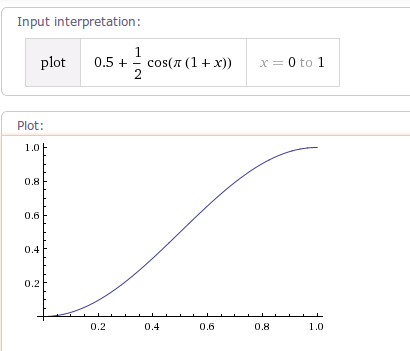
1.1 AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 两边慢 中间快,其运动曲线如下图所示:
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change starts and ends slowly but
* accelerates through the middle.
* 两边慢 中间快
*/
public class AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator
implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator() {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return (float)(Math.cos((input + 1) * Math.PI) / 2.0f) + 0.5f;
}
}
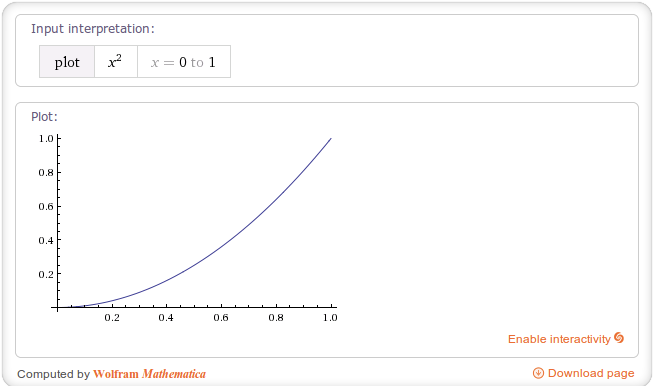
1.2 AccelerateInterpolator
AccelerateInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 先慢 后快,其运动曲线如下图所示(factor值为1):
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change starts out slowly and
* and then accelerates.
* 先慢 后快
*/
public class AccelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mFactor;
private final double mDoubleFactor;
public AccelerateInterpolator() {
mFactor = 1.0f;
mDoubleFactor = 2.0;
}
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param factor Degree to which the animation should be eased. Seting
* factor to 1.0f produces a y=x^2 parabola. Increasing factor above
* 1.0f exaggerates the ease-in effect (i.e., it starts even
* slower and ends evens faster)
*/
public AccelerateInterpolator(float factor) {
mFactor = factor;
mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor;
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
if (mFactor == 1.0f) {
return input * input;
} else {
return (float)Math.pow(input, mDoubleFactor);
}
}
}
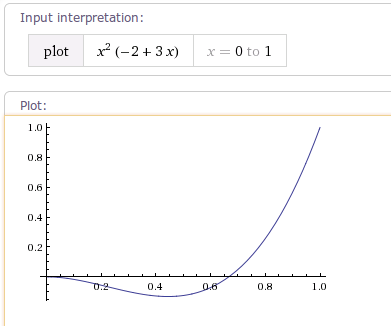
1.3 AnticipateInterpolator
AnticipateInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 先向后超过临界值,再快速向前,像一个回荡的秋千,因此被称为回荡秋千插值器曲线图如下:
/**
* An interpolator where the change starts backward then flings forward.
* 先向后 再向前
*/
public class AnticipateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mTension;
public AnticipateInterpolator() {
mTension = 2.0f;
}
/**
* @param tension Amount of anticipation. When tension equals 0.0f, there is
* no anticipation and the interpolator becomes a simple
* acceleration interpolator.
*/
public AnticipateInterpolator(float tension) {
mTension = tension;
}
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
// a(t) = t * t * ((tension + 1) * t - tension)
return t * t * ((mTension + 1) * t - mTension);
}
}
1.4 AnticipateOvershootInterpolator
AnticipateOvershootInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 先向后运动 超过临界值,再快速向前运动到达临界值,其运动曲线如下图所示:
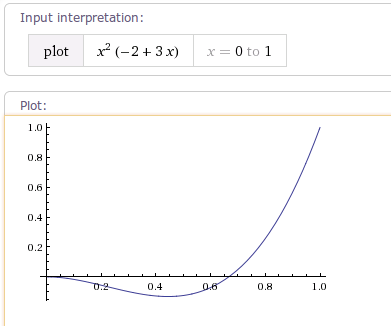
/**
* An interpolator where the change starts backward then flings forward and overshoots
* the target value and finally goes back to the final value.
* 先向后运动 超过临界值,再快速向前运动超过临界值,最后慢慢回到临界值
*/
public class AnticipateOvershootInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator
implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mTension;
public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator() {
mTension = 2.0f * 1.5f;
}
/**
* @param tension Amount of anticipation/overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f,
* there is no anticipation/overshoot and the interpolator becomes
* a simple acceleration/deceleration interpolator.
*/
public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(float tension) {
mTension = tension * 1.5f;
}
/**
* @param tension Amount of anticipation/overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f,
* there is no anticipation/overshoot and the interpolator becomes
* a simple acceleration/deceleration interpolator.
* @param extraTension Amount by which to multiply the tension. For instance,
* to get the same overshoot as an OvershootInterpolator with
* a tension of 2.0f, you would use an extraTension of 1.5f.
*/
public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(float tension, float extraTension) {
mTension = tension * extraTension;
}
private static float a(float t, float s) {
return t * t * ((s + 1) * t - s);
}
private static float o(float t, float s) {
return t * t * ((s + 1) * t + s);
}
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
// a(t, s) = t * t * ((s + 1) * t - s)
// o(t, s) = t * t * ((s + 1) * t + s)
// f(t) = 0.5 * a(t * 2, tension * extraTension), when t < 0.5
// f(t) = 0.5 * (o(t * 2 - 2, tension * extraTension) + 2), when t <= 1.0
if (t < 0.5f) return 0.5f * a(t * 2.0f, mTension);
else return 0.5f * (o(t * 2.0f - 2.0f, mTension) + 2.0f);
}
}
1.5 BounceInterpolator
BounceInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 快速运动到临界值后,进行几次回跳,类似一个从高空坠落篮球的运动曲线,其运动曲线如下图所示:
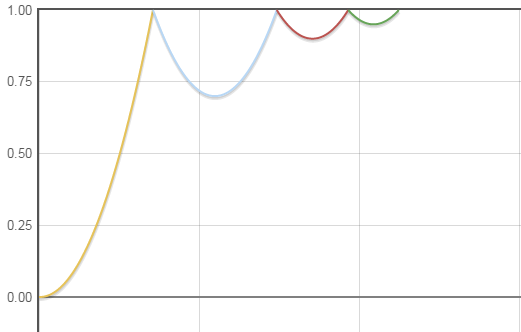
/**
* An interpolator where the change bounces at the end.
* 快速运动到临界值后,进行几次回跳,类似一个从高空坠落篮球的运动曲线。
*/
public class BounceInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
public BounceInterpolator() {
}
private static float bounce(float t) {
return t * t * 8.0f;
}
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
// _b(t) = t * t * 8
// bs(t) = _b(t) for t < 0.3535
// bs(t) = _b(t - 0.54719) + 0.7 for t < 0.7408
// bs(t) = _b(t - 0.8526) + 0.9 for t < 0.9644
// bs(t) = _b(t - 1.0435) + 0.95 for t <= 1.0
// b(t) = bs(t * 1.1226)
t *= 1.1226f;
if (t < 0.3535f) return bounce(t);
else if (t < 0.7408f) return bounce(t - 0.54719f) + 0.7f;
else if (t < 0.9644f) return bounce(t - 0.8526f) + 0.9f;
else return bounce(t - 1.0435f) + 0.95f;
}
}
1.6 CycleInterpolator
CycleInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 正弦变化曲线,其运动曲线如下图所示:
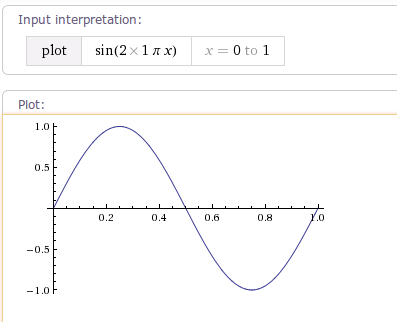
/**
* Repeats the animation for a specified number of cycles. The
* rate of change follows a sinusoidal pattern.
* sin正弦变化曲线
*/
@HasNativeInterpolator
public class CycleInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private float mCycles;
public CycleInterpolator(float cycles) {
mCycles = cycles;
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return (float)(Math.sin(2 * mCycles * Math.PI * input));
}
}
1.7 DecelerateInterpolator
DecelerateInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 减速插值器变化曲线,其算法为AccelerateInterpolator的完全倒置,同样有DecelerateInterpolator(float factor)构造函数来指定mFactor运动曲线如下图所示(factor值为1):
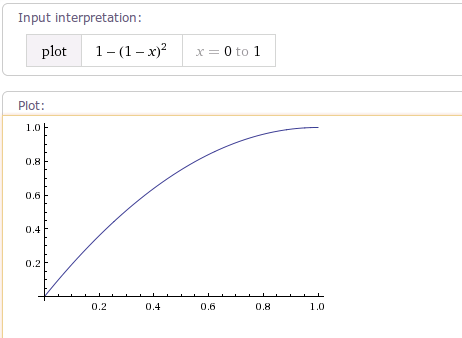
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change starts out quickly and
* and then decelerates.
* 减速插值器变化曲线,其算法为AccelerateInterpolator的完全倒置。
*/
public class DecelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private float mFactor = 1.0f;
public DecelerateInterpolator() {
}
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param factor Degree to which the animation should be eased. Setting factor to 1.0f produces
* an upside-down y=x^2 parabola. Increasing factor above 1.0f exaggerates the
* ease-out effect (i.e., it starts even faster and ends evens slower).
*/
public DecelerateInterpolator(float factor) {
mFactor = factor;
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
float result;
if (mFactor == 1.0f) {
result = (float)(1.0f - (1.0f - input) * (1.0f - input));
} else {
result = (float)(1.0f - Math.pow((1.0f - input), 2 * mFactor));
}
return result;
}
}
1.8 LinearInterpolator
LinearInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 为0~1之间匀速变化的一条直线,其运动曲线如下图所示:
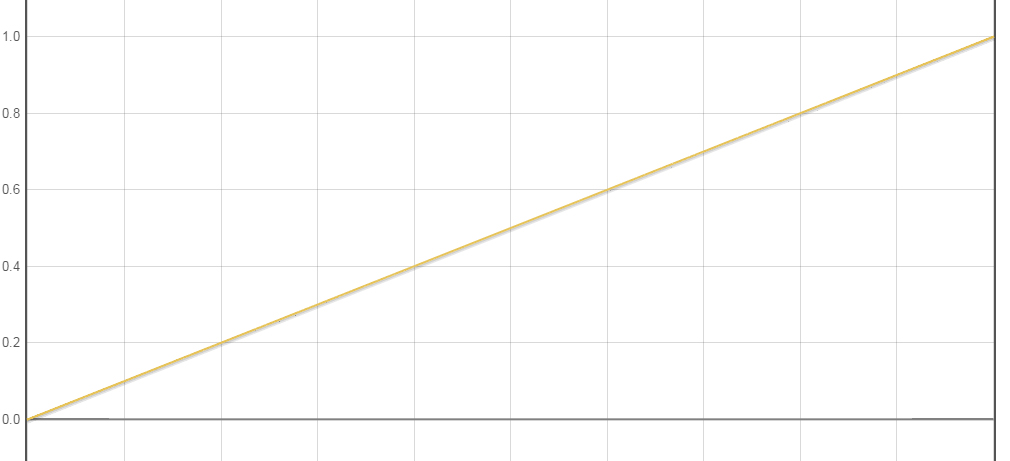
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change starts out quickly and
* and then decelerates.
* 为0~1之间匀速变化的一条直线。
*/
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change is constant
*/
public class LinearInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
public LinearInterpolator() {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return input;
}
}
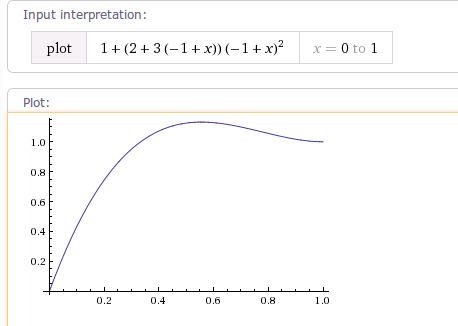
1.9 OvershootInterpolator
OvershootInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 先加速超过临界值1.0f 再慢慢又回落到1.0f,有一个回弹的效果。
可使用OvershootInterpolator(float tension)构造函数设置mTension弹力值,mTension值越大,超出目标值的时间点越靠前,超出目标值的回弹距离越大,回弹越明显。
其运动曲线如下图所示:
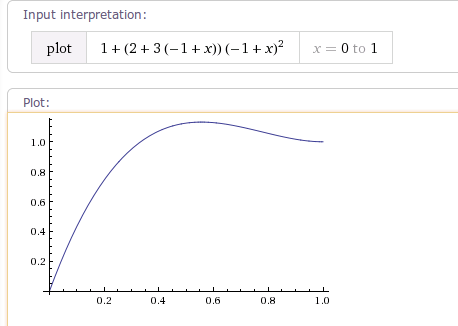
/**
* An interpolator where the change flings forward and overshoots the last value
* then comes back.
* 先超过临界值 再慢慢回到临界值
*/
public class OvershootInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mTension;
public OvershootInterpolator() {
mTension = 2.0f;
}
/**
* @param tension Amount of overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f, there is
* no overshoot and the interpolator becomes a simple
* deceleration interpolator.
*/
public OvershootInterpolator(float tension) {
mTension = tension;
}
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
// _o(t) = t * t * ((tension + 1) * t + tension)
// o(t) = _o(t - 1) + 1
t -= 1.0f;
return t * t * ((mTension + 1) * t + mTension) + 1.0f;
}
}
1.10 PathInterpolator
PathInterpolator 可以称之为万能插值器,可以通过PathInterpolator构造一个Path路径 或 通过传入点来构造一个贝塞尔曲线(通过这个贝塞尔曲线,我们可以构造任意的变化曲线)。
//创建一个任意Path的插值器
PathInterpolator(Path path)
//创建一个二阶贝塞尔曲线的插值器
PathInterpolator(float controlX, float controlY)
//创建一个三阶贝塞尔曲线的插值器
PathInterpolator(float controlX1, float controlY1, float controlX2, float controlY2)
贝塞尔曲线的构建,可以使用如下辅助工具 cubic-bezier:
https://cubic-bezier.com/
/**
* An interpolator that can traverse a Path that extends from <code>Point</code>
* <code>(0, 0)</code> to <code>(1, 1)</code>. The x coordinate along the <code>Path</code>
* is the input value and the output is the y coordinate of the line at that point.
* This means that the Path must conform to a function <code>y = f(x)</code>.
*
* <p>The <code>Path</code> must not have gaps in the x direction and must not
* loop back on itself such that there can be two points sharing the same x coordinate.
* It is alright to have a disjoint line in the vertical direction:</p>
* <p><blockquote><pre>
* Path path = new Path();
* path.lineTo(0.25f, 0.25f);
* path.moveTo(0.25f, 0.5f);
* path.lineTo(1f, 1f);
* </pre></blockquote></p>
* 构造一个普通Path路径或者贝塞尔曲线的插值器
*/
public class PathInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
// This governs how accurate the approximation of the Path is.
private static final float PRECISION = 0.002f;
private float[] mX; // x coordinates in the line
private float[] mY; // y coordinates in the line
/**
* Create an interpolator for an arbitrary <code>Path</code>. The <code>Path</code>
* must begin at <code>(0, 0)</code> and end at <code>(1, 1)</code>.
*
* @param path The <code>Path</code> to use to make the line representing the interpolator.
*/
public PathInterpolator(Path path) {
initPath(path);
}
public PathInterpolator(float controlX, float controlY) {
initQuad(controlX, controlY);
}
/**
* Create an interpolator for a cubic Bezier curve. The end points
* <code>(0, 0)</code> and <code>(1, 1)</code> are assumed.
*
* @param controlX1 The x coordinate of the first control point of the cubic Bezier.
* @param controlY1 The y coordinate of the first control point of the cubic Bezier.
* @param controlX2 The x coordinate of the second control point of the cubic Bezier.
* @param controlY2 The y coordinate of the second control point of the cubic Bezier.
*/
public PathInterpolator(float controlX1, float controlY1, float controlX2, float controlY2) {
initCubic(controlX1, controlY1, controlX2, controlY2);
}
private void initQuad(float controlX, float controlY) {
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(0, 0);
path.quadTo(controlX, controlY, 1f, 1f);
initPath(path);
}
private void initCubic(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2) {
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(0, 0);
path.cubicTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, 1f, 1f);
initPath(path);
}
private void initPath(Path path) {
float[] pointComponents = path.approximate(PRECISION);
int numPoints = pointComponents.length / 3;
if (pointComponents[1] != 0 || pointComponents[2] != 0
|| pointComponents[pointComponents.length - 2] != 1
|| pointComponents[pointComponents.length - 1] != 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The Path must start at (0,0) and end at (1,1)");
}
mX = new float[numPoints];
mY = new float[numPoints];
float prevX = 0;
float prevFraction = 0;
int componentIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; i++) {
float fraction = pointComponents[componentIndex++];
float x = pointComponents[componentIndex++];
float y = pointComponents[componentIndex++];
if (fraction == prevFraction && x != prevX) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The Path cannot have discontinuity in the X axis.");
}
if (x < prevX) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The Path cannot loop back on itself.");
}
mX[i] = x;
mY[i] = y;
prevX = x;
prevFraction = fraction;
}
}
/**
* Using the line in the Path in this interpolator that can be described as
* <code>y = f(x)</code>, finds the y coordinate of the line given <code>t</code>
* as the x coordinate. Values less than 0 will always return 0 and values greater
* than 1 will always return 1.
*
* @param t Treated as the x coordinate along the line.
* @return The y coordinate of the Path along the line where x = <code>t</code>.
* @see Interpolator#getInterpolation(float)
*/
@Override
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
if (t <= 0) {
return 0;
} else if (t >= 1) {
return 1;
}
// Do a binary search for the correct x to interpolate between.
int startIndex = 0;
int endIndex = mX.length - 1;
while (endIndex - startIndex > 1) {
int midIndex = (startIndex + endIndex) / 2;
if (t < mX[midIndex]) {
endIndex = midIndex;
} else {
startIndex = midIndex;
}
}
float xRange = mX[endIndex] - mX[startIndex];
if (xRange == 0) {
return mY[startIndex];
}
float tInRange = t - mX[startIndex];
float fraction = tInRange / xRange;
float startY = mY[startIndex];
float endY = mY[endIndex];
return startY + (fraction * (endY - startY));
}
}
1.11 OvershootInterpolator
OvershootInterpolator 该插值器运动曲线 先加速超过临界值1.0f 再慢慢又回落到1.0f,有一个回弹的效果。
可使用OvershootInterpolator(float tension)构造函数设置mTension弹力值,mTension值越大,超出目标值的时间点越靠前,超出目标值的回弹距离越大,回弹越明显。
其运动曲线如下图所示:

/**
* An interpolator where the change flings forward and overshoots the last value
* then comes back.
* 先超过临界值 再慢慢回到临界值
*/
public class OvershootInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mTension;
public OvershootInterpolator() {
mTension = 2.0f;
}
/**
* @param tension Amount of overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f, there is
* no overshoot and the interpolator becomes a simple
* deceleration interpolator.
*/
public OvershootInterpolator(float tension) {
mTension = tension;
}
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
// _o(t) = t * t * ((tension + 1) * t + tension)
// o(t) = _o(t - 1) + 1
t -= 1.0f;
return t * t * ((mTension + 1) * t + mTension) + 1.0f;
}
}
注:
使用PathInterpolator插值器会消耗更多的内存,不同于其他简单插值器,一般的插值器都是在算法上来生成插值,而PathInterpolator是在初始化时依赖Path算法生成一系列插值点存储,源码显示是以0.02为step在0到1范围内取点,生成500个x样本和500个y样本共计1000个float数据,相比其他插值器消耗了相当1000倍的内存,虽然对目前手机性能来说微不足道,但在动画这种要求高性能的操作时建议谨慎使用,不要频繁初始化,尽量复用同参数的插值器,以提高性能。
二、Easing 插值器
Easing算法是业界著名的一组插值器算法,涵盖了各种速率的曲线算法。
其涵盖的曲线算法如下图所示:
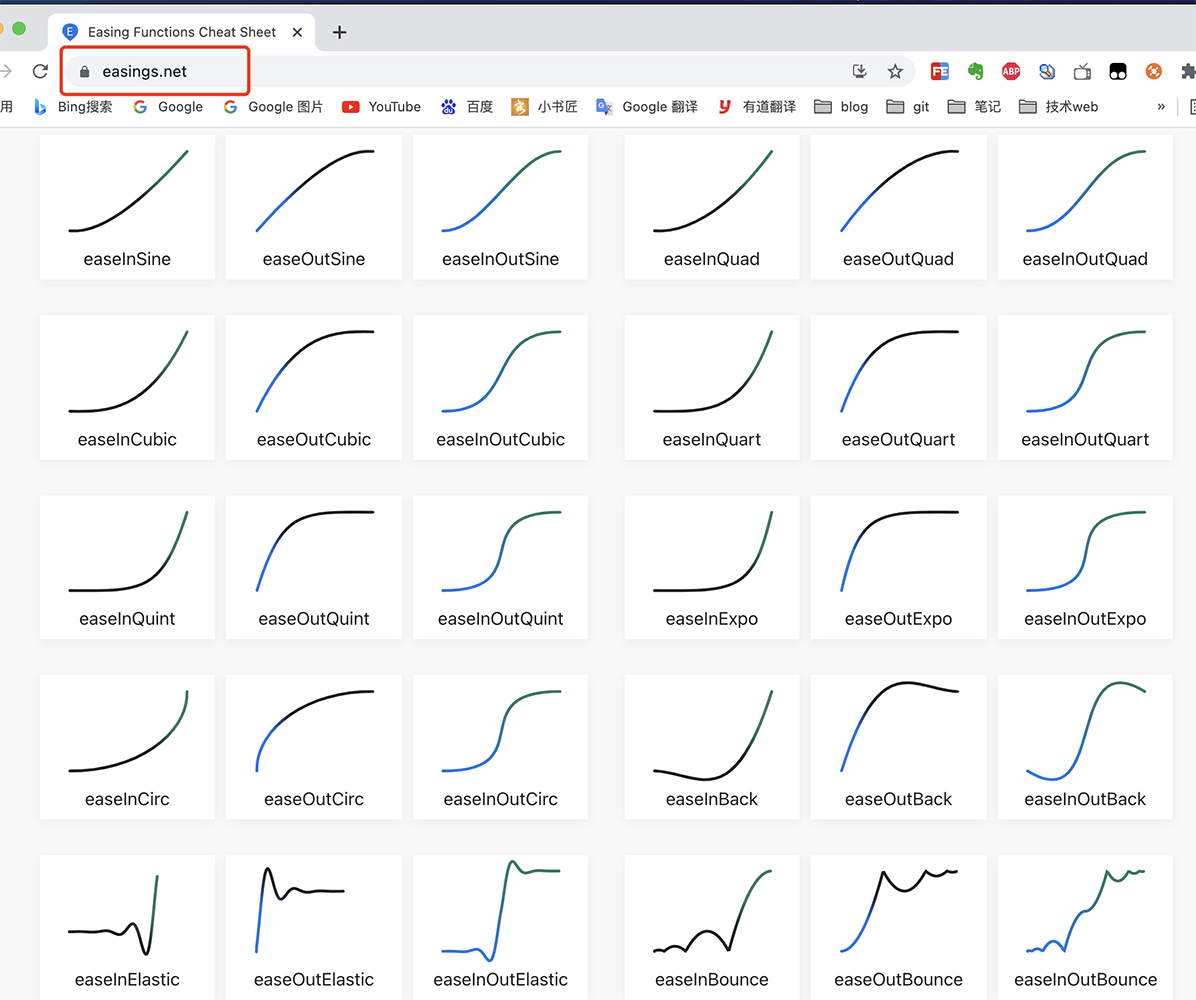
注:
easings 官方网址:
https://easings.net/
easeInOutBounce
举例一个动画插值器 easeInOutBounce。Easing官方对于每一个动画插值器,均给出了完整的算法实现和动画运动曲线,开发者可以根据自己的需要自行选择对应的插值器算法,构造自己的动画插值器。
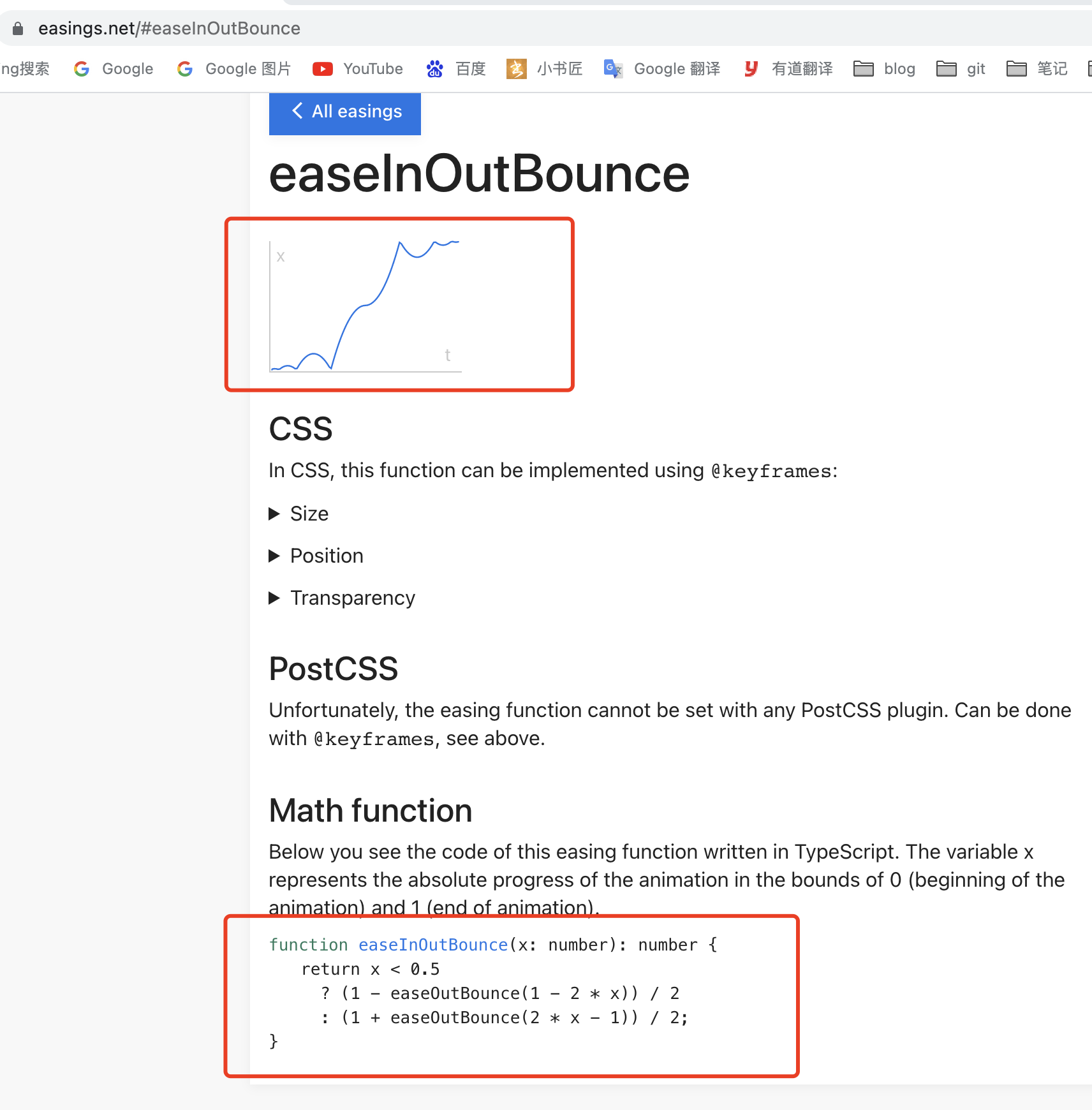
function easeInOutBounce(x: number): number {
return x < 0.5
? (1 - easeOutBounce(1 - 2 * x)) / 2
: (1 + easeOutBounce(2 * x - 1)) / 2;
}
三、调试插值器
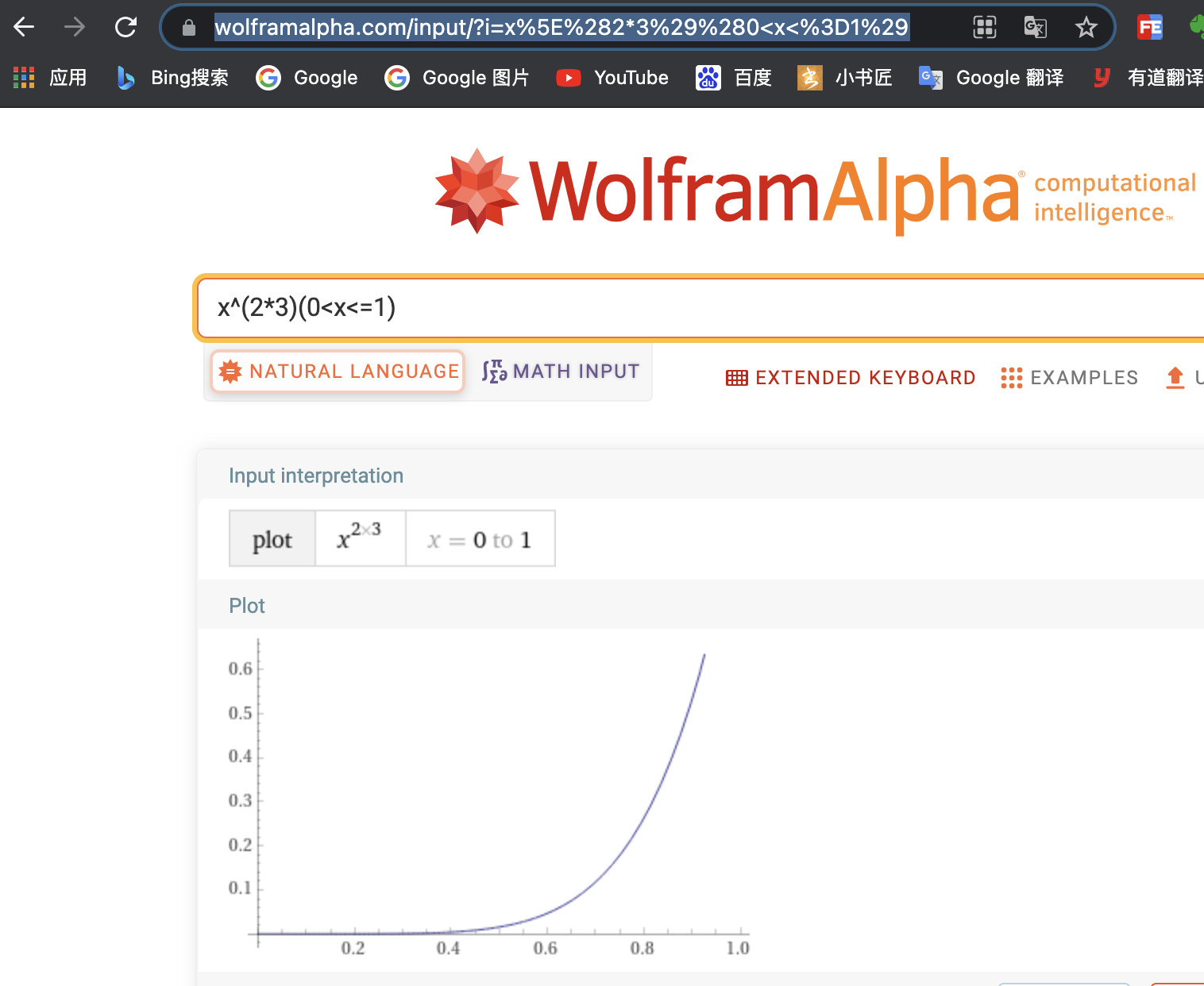
调试动画插值器,可以使用如下小工具:
wolframalpha 调试动画插值器:
https://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=x%5E%282*3%29%280%3Cx%3C%3D1%29
参考
wolframalpha调试工具:
https://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=x%5E%282*3%29%280%3Cx%3C%3D1%29
cubic-bezier辅助工具:
https://cubic-bezier.com/
easings 插值器:
https://easings.net/
3D勋章实现方案:
https://xiaxl.blog.csdn.net/article/details/77048507
= THE END =
