一、定义
在模板模式(Template Pattern)中,一个抽象类公开定义了执行它的方法的方式/模板。它的子类可以按需要重写方法实现,但调用将以抽象类中定义的方式进行。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。模板方法模式实际上是封装一个固定流程,该流程由几个步骤组成,具体步骤可以由子类进行不同实现,从而让固定的流程产生不同的结果,它非常简单,其实就是类的继承机制,但它却是一个应用非常广泛的模式,模板方法模式的本质是抽象封装流程,具体进行实现。
模版方法模式中有两个主要的角色
- 抽象的模版方法 AbstractTemplate
- 定义了一个或多个抽象操作,以便让子类实现。这些抽象操作叫做基本操作,它们是一个顶级逻辑的组成步骤。
- 定义并实现了一个模板方法。这个模板方法一般是一个具体方法,它给出了一个顶级逻辑的骨架,而逻辑的组成步骤在相应的抽象操作中,推迟到子类实现。顶级逻辑也有可能调用一些具体方法。
- 具体的模版方法 ConcreteTemplate
- 实现父类所定义的一个或多个抽象方法,它们是一个顶级逻辑的组成步骤。
- 每一个抽象模板角色都可以有任意多个具体模板角色与之对应,而每一个具体模板角色都可以给出这些抽象方法(也就是顶级逻辑的组成步骤)的不同实现,从而使得顶级逻辑的实现各不相同。
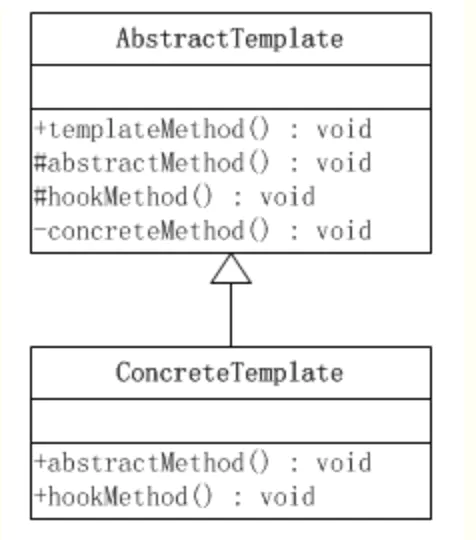
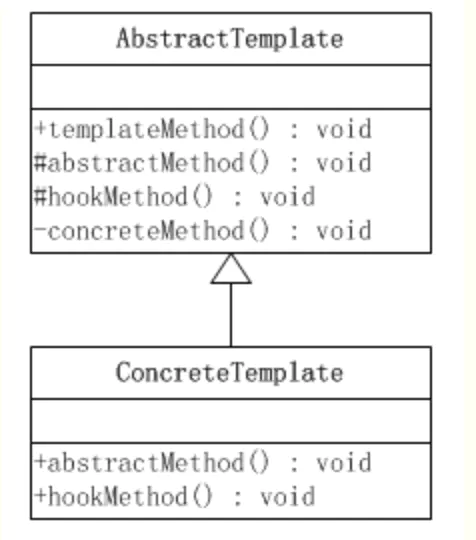
二、模板模式的案例
//抽象的模版类 public abstract class AbstractTemplate { /** * 模版方法:顶层的统一实现逻辑,子类不能更改或者替换 */ public void templateMethod() { System.out.println("顶层模版类的模版方法"); abstractMethod(); hoodMethod(); concreteMethod(); } /** * 抽象方法:子类必须实现和替换的方法 */ public abstract void abstractMethod(); /** * 钩子方法:子类可以选择性的实现或者不实现的方法 */ public void hoodMethod() { } /** * 基本方法:顶层模版类实现的方法,子类不能更改的方法 */ public void concreteMethod() { System.out.println("顶层模版类实现的具体方法"); } }
//具体的模版类 public class ConcreteTemplate extends AbstractTemplate{ @Override public void abstractMethod() { System.out.println("子类实现的抽象方法"); } @Override public void hoodMethod() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("子类更改的钩子方法"); } }
public class TemplatePatternMain { public static void main(String[] args) { AbstractTemplate template = new ConcreteTemplate(); template.templateMethod(); } }
三、模板模式在源码中的应用
下面代码是JDK 中的 AbstractList源码部分
package java.util; public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> { protected transient int modCount = 0; protected AbstractList() { } public boolean add(E var1) { this.add(this.size(), var1); return true; } public abstract E get(int var1);
从上面源码可以看到 get()是一个抽象方法,那么它的逻辑就是交给子类来实现,其实我们天天在用的ArrayList 就是 AbstractList 的子类。同理,有 AbstractList 就有 AbstractSet 和AbstractMap, 不信的朋友可以去看下对应的源码。现在上来都是封装的架构,现在的开发人员可能用的慢慢少了,以前很多程序员天天在用的HttpServlet,有三个方法 service()和 doGet()、doPost()方法,都是模板方法的抽象实现。看源码部分可以发现,其实在码源中这三个方法其实也没做啥子事,我们大都是覆盖了他原方法自己写处理逻辑。这个场景其实也可以叫成模板模式
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet { private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE"; private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD"; private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET"; private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS"; private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST"; private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT"; private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE"; private static final String HEADER_IFMODSINCE = "If-Modified-Since"; private static final String HEADER_LASTMOD = "Last-Modified"; private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings"; private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings"); public HttpServlet() { } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } } protected long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest req) { return -1L; } protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { NoBodyResponse response = new NoBodyResponse(resp); this.doGet(req, response); response.setContentLength(); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } } protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } }
今年来吃的没事干自己在学JDBC及MyBatis封装自己数据库架构插件,所以吃的没事又看了一下其中的源码,其实在MyBatis 框架也有一些好玩的东西,来看一下其中的 BaseExecutor 类,它是一个基础的SQL 执行类,实现了大部分的 SQL 执行逻辑,然后把几个方法交给子类定制化完成
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class); protected Transaction transaction; protected Executor wrapper; protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad> deferredLoads; protected PerpetualCache localCache; protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache; protected Configuration configuration; protected int queryStack = 0; private boolean closed; protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { this.transaction = transaction; this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache"); this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache"); this.closed = false; this.configuration = configuration; this.wrapper = this; } public Transaction getTransaction() { if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } else { return this.transaction; } } public void close(boolean forceRollback) { try { try { this.rollback(forceRollback); } finally { if (this.transaction != null) { this.transaction.close(); } } } catch (SQLException var11) { log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + var11); } finally { this.transaction = null; this.deferredLoads = null; this.localCache = null; this.localOutputParameterCache = null; this.closed = true; } } public boolean isClosed() { return this.closed; } public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId()); if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } else { this.clearLocalCache(); return this.doUpdate(ms, parameter); } } public List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException { return this.flushStatements(false); } public List<BatchResult> flushStatements(boolean isRollBack) throws SQLException { if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } else { return this.doFlushStatements(isRollBack); } } public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); CacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); return this.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } else { if (this.queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { this.clearLocalCache(); } List list; try { ++this.queryStack; list = resultHandler == null ? (List)this.localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { this.handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { list = this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { --this.queryStack; } if (this.queryStack == 0) { Iterator i$ = this.deferredLoads.iterator(); while(i$.hasNext()) { BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad = (BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad)i$.next(); deferredLoad.load(); } this.deferredLoads.clear(); if (this.configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { this.clearLocalCache(); } } return list; } } public <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); return this.doQueryCursor(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); } public void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType) { if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } else { BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad = new BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad(resultObject, property, key, this.localCache, this.configuration, targetType); if (deferredLoad.canLoad()) { deferredLoad.load(); } else { this.deferredLoads.add(new BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad(resultObject, property, key, this.localCache, this.configuration, targetType)); } } } public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) { if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } else { CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey(); cacheKey.update(ms.getId()); cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset()); cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit()); cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry(); Iterator i$ = parameterMappings.iterator(); while(i$.hasNext()) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)i$.next(); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); Object value; if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { MetaObject metaObject = this.configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } cacheKey.update(value); } } if (this.configuration.getEnvironment() != null) { cacheKey.update(this.configuration.getEnvironment().getId()); } return cacheKey; } } public boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key) { return this.localCache.getObject(key) != null; } public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException { if (this.closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed"); } else { this.clearLocalCache(); this.flushStatements(); if (required) { this.transaction.commit(); } } } public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException { if (!this.closed) { try { this.clearLocalCache(); this.flushStatements(true); } finally { if (required) { this.transaction.rollback(); } } } } public void clearLocalCache() { if (!this.closed) { this.localCache.clear(); this.localOutputParameterCache.clear(); } } protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement var1, Object var2) throws SQLException; protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean var1) throws SQLException; protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement var1, Object var2, RowBounds var3, ResultHandler var4, BoundSql var5) throws SQLException; protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement var1, Object var2, RowBounds var3, BoundSql var4) throws SQLException; protected void closeStatement(Statement statement) { if (statement != null) { try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException var3) { } } } protected void applyTransactionTimeout(Statement statement) throws SQLException { StatementUtil.applyTransactionTimeout(statement, statement.getQueryTimeout(), this.transaction.getTimeout()); } private void handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key, Object parameter, BoundSql boundSql) { if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { Object cachedParameter = this.localOutputParameterCache.getObject(key); if (cachedParameter != null && parameter != null) { MetaObject metaCachedParameter = this.configuration.newMetaObject(cachedParameter); MetaObject metaParameter = this.configuration.newMetaObject(parameter); Iterator i$ = boundSql.getParameterMappings().iterator(); while(i$.hasNext()) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)i$.next(); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.IN) { String parameterName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); Object cachedValue = metaCachedParameter.getValue(parameterName); metaParameter.setValue(parameterName, cachedValue); } } } } } private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { this.localCache.putObject(key, ExecutionPlaceholder.EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); List list; try { list = this.doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { this.localCache.removeObject(key); } this.localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { this.localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; } protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Connection connection = this.transaction.getConnection(); return statementLog.isDebugEnabled() ? ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, this.queryStack) : connection; } public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor wrapper) { this.wrapper = wrapper; } private static class DeferredLoad { private final MetaObject resultObject; private final String property; private final Class<?> targetType; private final CacheKey key; private final PerpetualCache localCache; private final ObjectFactory objectFactory; private final ResultExtractor resultExtractor; public DeferredLoad(MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, PerpetualCache localCache, Configuration configuration, Class<?> targetType) { this.resultObject = resultObject; this.property = property; this.key = key; this.localCache = localCache; this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); this.resultExtractor = new ResultExtractor(configuration, this.objectFactory); this.targetType = targetType; } public boolean canLoad() { return this.localCache.getObject(this.key) != null && this.localCache.getObject(this.key) != ExecutionPlaceholder.EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER; } public void load() { List<Object> list = (List)this.localCache.getObject(this.key); Object value = this.resultExtractor.extractObjectFromList(list, this.targetType); this.resultObject.setValue(this.property, value); } } }
上面的源码中如 doUpdate、doFlushStatements、doQuery、doQueryCursor 这几个方法就是交给了它的子类去实现了

从上面类图可以看到他有四个子类,随便找两个子类的实现对比下
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; int var6; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, (ResultHandler)null, (BoundSql)null); stmt = this.prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); var6 = handler.update(stmt); } finally { this.closeStatement(stmt); } return var6; }
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, (ResultHandler)null, (BoundSql)null); BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); String sql = boundSql.getSql(); Statement stmt; if (sql.equals(this.currentSql) && ms.equals(this.currentStatement)) { int last = this.statementList.size() - 1; stmt = (Statement)this.statementList.get(last); this.applyTransactionTimeout(stmt); handler.parameterize(stmt); BatchResult batchResult = (BatchResult)this.batchResultList.get(last); batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject); } else { Connection connection = this.getConnection(ms.getStatementLog()); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, this.transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); this.currentSql = sql; this.currentStatement = ms; this.statementList.add(stmt); this.batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject)); } handler.batch(stmt); return -2147482646; }
从上面可以看到SimpleExecutor是一种常规执行器,每次执行都会创建一个statement,用完后关闭,而BatchExecutor是批处理型执行器,doUpdate预处理存储过程或批处理操作
四、总结
优点:
1、利用模板方法将相同处理逻辑的代码放到抽象父类中,可以提高代码的复用性。
2、将不同的代码不同的子类中,通过对子类的扩展增加新的行为,提高代码的扩展性。
3、把不变的行为写在父类上,去除子类的重复代码,提供了一个很好的代码复用平台,符合开闭原则。
缺点:
1、类数目的增加,每一个抽象类都需要一个子类来实现,这样导致类的个数增加。
2、类数量的增加,间接地增加了系统实现的复杂度。
3、继承关系自身缺点,如果父类添加新的抽象方法,所有子类都要改一遍。
补充:这种玩意其实在算法场景中应用的比较多,或者是在共性多的场景也可以这么玩
git:源码:https://github.com/ljx958720/design_patterns.git