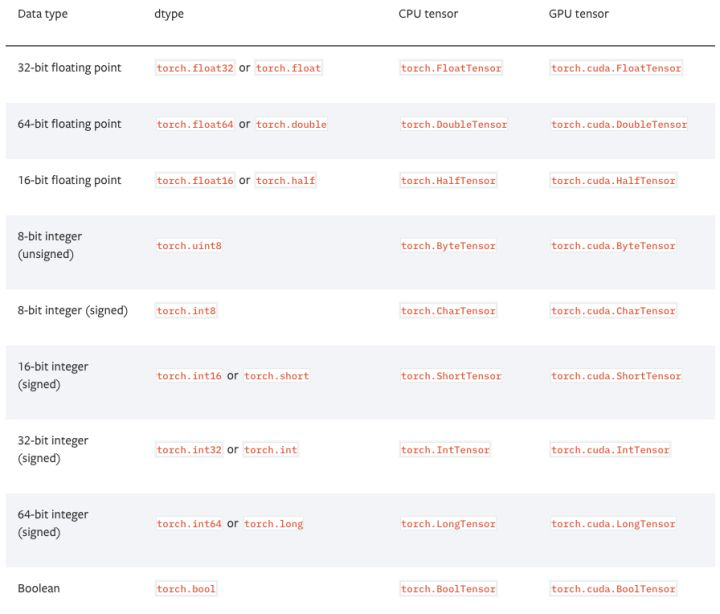
1、在pytorch中,有以下9种张量类型
2、查看张量的基本信息
tensor=torch.randn(3,4,5) print(tensor.size()) print(tensor.type()) print(tensor.dim())
torch.Size([3, 4, 5])
torch.FloatTensor
3
3、命名张量
张量命名是一个非常有用的方法,这样可以方便地使用维度的名字来做索引或其他操作,大大提高了可读性、易用性,防止出错。
# 在PyTorch 1.3之前,需要使用注释 # Tensor[N, C, H, W] images = torch.randn(32, 3, 56, 56) images.sum(dim=1) images.select(dim=1, index=0)
# PyTorch 1.3之后 NCHW = [‘N’, ‘C’, ‘H’, ‘W’] images = torch.randn(32, 3, 56, 56, names=NCHW) images.sum('C').size()#按通道相加
torch.Size([32, 32, 32])
不过需要注意:1.4版本中该特性正在处于测试阶段,因此就不要随便的使用了。
#选择第0个通道 images.select('C',index=0).size()
torch.Size([32, 32, 32])
# 也可以这么设置 tensor = torch.rand(3,4,1,2,names=('C', 'N', 'H', 'W')) # 使用align_to可以对维度方便地排序 tensor = tensor.align_to('N', 'C', 'H', 'W')
4、数据类型转换
# 设置默认类型,pytorch中的FloatTensor远远快于DoubleTensor torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.FloatTensor) # 类型转换 tensor = tensor.cuda() tensor = tensor.cpu() tensor = tensor.float() tensor = tensor.long()
5、tensor和numpy.ndarray转换
除了CharTensor,其他所有CPU上的张量都支持转换为numpy格式然后再转换回来。
ndarray = tensor.cpu().numpy() tensor = torch.from_numpy(ndarray).float() tensor = torch.from_numpy(ndarray.copy()).float() # If ndarray has negative stride.
6、tensor和PIL.Image转换
pytorch中的张量默认采用[N, C, H, W]的顺序,并且数据范围在[0,1],需要进行转置和规范化
PIL.Image转换为tensor
from PIL import Image import numpy as np image=r'/content/drive/My Drive/colab notebooks/image/test.jpg' tensor=torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(Image.open(image))).permute(2,0,1).float()/255.0 tensor.size()
torch.Size([3, 300, 200])
另一种方式:
import torchvision tensor=torchvision.transforms.functional.to_tensor(PIL.Image.open(path)) tensor.size()
torch.Size([3, 300, 200])
tensor转换为PIL.Image
img=Image.fromarray(torch.clamp(tensor*255,min=0,max=255).byte().permute(1,2,0).cpu().numpy()) print(type(img))
<class 'PIL.Image.Image'>
另一种方式:
image = torchvision.transforms.functional.to_pil_image(tensor)
7、np.ndarray和PIL.Image进行转换
np.ndarray转换为PIL.Image
image = PIL.Image.fromarray(ndarray.astype(np.uint8))
PIL.Image转换为np.ndarray
ndarray = np.asarray(PIL.Image.open(path))
8、从只包含一个元素的tensor中取出值
value = torch.rand(1) print(value) print(value.item())
tensor([0.2959])
0.2958560585975647
9、改变张量的形状
# 在将卷积层输入全连接层的情况下通常需要对张量做形变处理, # 相比torch.view,torch.reshape可以自动处理输入张量不连续的情况。 tensor = torch.rand(2,3,4) shape = (6, 4) tensor = torch.reshape(tensor, shape)
10、打乱顺序
tensor = tensor[torch.randperm(tensor.size(0))] # 打乱第一个维度
11、水平翻转
# pytorch不支持tensor[::-1]这样的负步长操作,水平翻转可以通过张量索引实现 # 假设张量的维度为[N, C, H, W]. tensor = tensor[:,:,:,torch.arange(tensor.size(3) - 1, -1, -1).long()]
12、复制张量
# Operation | New/Shared memory | Still in computation graph | tensor.clone() # | New | Yes | tensor.detach() # | Shared | No | tensor.detach.clone()() # | New | No |
13、张量拼接
''' 注意torch.cat和torch.stack的区别在于torch.cat沿着给定的维度拼接, 而torch.stack会新增一维。例如当参数是3个10x5的张量,torch.cat的结果是30x5的张量, 而torch.stack的结果是3x10x5的张量。 ''' tensor = torch.cat(list_of_tensors, dim=0) tensor = torch.stack(list_of_tensors, dim=0)
t1=torch.randn(10,5) t2=torch.randn(10,5) t3=torch.randn(10,5) s1=torch.cat([t1,t2,t3],dim=0) s2=torch.stack([t1,t2,t3],dim=0) print(s1.size()) print(s2.size())
torch.Size([30, 5])
torch.Size([3, 10, 5])
14、将整数标签转换为ont-hot码
tensor=torch.tensor([0,2,1,3]) N=tensor.size(0) num_classes=4 one_hot=torch.zeros(N,num_classes).long() one_hot.scatter_(dim=1, index=torch.unsqueeze(tensor, dim=1), src=torch.ones(N, num_classes).long())
tensor([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1]])
15、得到非零元素
torch.nonzero(tensor) # index of non-zero elements torch.nonzero(tensor==0) # index of zero elements torch.nonzero(tensor).size(0) # number of non-zero elements torch.nonzero(tensor == 0).size(0) # number of zero elements
16、判断两个张量相等
torch.allclose(tensor1, tensor2) # float tensor torch.equal(tensor1, tensor2) # int tensor
17、张量扩展
# Expand tensor of shape 64*512 to shape 64*512*7*7. tensor = torch.rand(64,512) torch.reshape(tensor, (64, 512, 1, 1)).expand(64, 512, 7, 7).size()
torch.Size([64, 512, 7, 7])
18、矩阵乘法
# Matrix multiplcation: (m*n) * (n*p) * -> (m*p). result = torch.mm(tensor1, tensor2) # Batch matrix multiplication: (b*m*n) * (b*n*p) -> (b*m*p) result = torch.bmm(tensor1, tensor2) # Element-wise multiplication. result = tensor1 * tensor2
19、计算两组数据之间的两两欧式距离
利用广播机制
dist = torch.sqrt(torch.sum((X1[:,None,:] - X2) ** 2, dim=2))