测试中断言的重要性
一、断言的作用:
1.断言也就是检查点,重在判断我们通过页面得出来的值与期望值是否相等,如果相等,则代表断言成功,程序会继续往下执行,如果不相等,则代表断言失败,程序就会在断言失败处中止。
示例:
二、断言的API:
1.Assert.assertEquals
2.Assert.assertFalse(condition)
3.Assert.assertNotEquals(actual1, actual2)
4.Assert.assertNotNull(object)
5.Assert.assertNotSame(actual, expected, message)
6.Assert.assertNull(object, message)
7.Assert.assertSame(actual, expected)
8.Assert.assertTrue(condition)
三、封装断言类
断言结果对程序的影响
1.场景:假如对一个表格里的数据做一个循环比较,如果一断言失败就退出,那我们就无法一下子找出全部不符合要求的数据了,那么我们可不可以在断言时,如果断言失败则不退出,等到把整个循环做完后,再整体判断是否有断言失败的地方?
示例:
脚本格式
具体代码
Assertion.java代码:
package com.selenium.utils; import org.testng.Assert; public class Assertion { public static boolean flag = true; public static void verifyEquals(Object actual, Object expected) { try { Assert.assertEquals(expected, actual); } catch (Error e) { flag = false; Log.logError("数据对比错误-> 期望值为:" + expected + "实际值为:" + actual); } } public static void verifyEquals(Object actual, Object expected, String message) { try { Assert.assertEquals(expected, actual, message); } catch (Error e) { flag = false; Log.logError("数据对比错误-> 期望值为:" + expected + "实际值为:" + actual); } } }
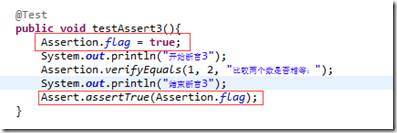
在代码中使用如下:
package com.selenium.test; import org.junit.Assert; import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import com.selenium.utils.Assertion; public class testAssertion { // @Test(dataProvider = "number") public void testAssertAndLog4j(String text) { String expected = "b"; String actual = text; Assertion.flag = true; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.println("断言开始:" + i); Assertion.verifyEquals(actual, expected, "---测试两个字符串是否相同"); System.out.println("断言结束:" + i); } Assert.assertTrue(Assertion.flag); } @DataProvider public Object[][] number() { return new Object[][] { { "a" }, { "b" }, { "c" } }; } }
最后打个广告,不要介意哦~
最近我在Dataguru学了《软件自动化测试Selenium2》网络课程,挺不错的,你可以来看看!要是想报名,可以用我的优惠码 G863,立减你50%的固定学费!
链接:http://www.dataguru.cn/invite.php?invitecode=G863