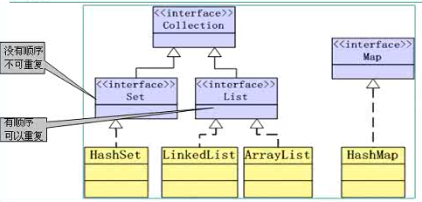
Guava:谷歌开发的集合库,通过build path->Add External JARs 把guava.jar包加进去。 版本控制工具:1.CVS 2.SVN 3.git 所以需要下载git客户端。 import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList; /** * 只读设置 */ public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("a"); list.add("b"); list.add("c"); //对原有的list进行包装,相等于原有List的一个视图,快照,不够安全 List<String> readList =Collections.unmodifiableList(list); readList.add("d");//对这个视图增操作,错误,抛出java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException(不被支持的异常)。 list.add("d"); //正确,改变原有List,视图也一起改变,没有达到真正的目的,所以不够安全。 // guava对只读设置 安全可靠,并且相对简单 List<String> immutableList =ImmutableList.of("a", "b", "c"); //初始化List immutableList.add("d");//java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException } } import com.google.common.base.Function; import com.google.common.base.Functions; import com.google.common.base.Predicate; import com.google.common.collect.Collections2; import com.google.common.collect.Lists; import com.google.common.collect.Sets; /** * 函数式编程 :解耦 * 1、Predicate * 2、Function * * 工具:Collections2.filter() 过滤器 * Collections2.transfer() 转换 * Functions.compose()组合式函数编程 */ public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //组合式函数编程 //确保容器中的字符串长度不超过5,超过进行截取,后全部大写 List<String> list =Lists.newArrayList("bjsxt","good","happiness");//静态创建List, //确保容器中的字符串长度不超过5,超过进行截取 Function<String,String> f1 =new Function<String,String>(){ @Override public String apply(String input) { return input.length()>5?input.substring(0,5):input; } }; //转成大写 Function<String,String> f2 =new Function<String,String>(){ @Override public String apply(String input) { return input.toUpperCase(); } }; //String =f2(f1(String)) Function<String,String> f =Functions.compose(f1, f2); Collection<String> resultCol =Collections2.transform(list, f); for(String temp:resultCol){ System.out.println(temp); } } /** * 转换 */ public static void test2(){ //类型转换 Set<Long> timeSet =Sets.newHashSet(); timeSet.add(10000000L); timeSet.add(99999999999999999L); timeSet.add(2000000000L); Collection<String> timeStrCol =Collections2.transform(timeSet, new Function<Long,String>(){ @Override public String apply(Long input) { return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").format(input); }}); for(String temp:timeStrCol){ System.out.println(temp); } } /** * 过滤器 */ public static void test1(){ //创建List 静态初始化 List<String> list =Lists.newArrayList("moom","son","dad","bjsxt","refer"); //找出回文 palindrome backwords mirror words //匿名内部类对象: 匿名内部类,同时创建类对象 Collection<String> palindromeList =Collections2.filter(list, new Predicate<String>(){ @Override public boolean apply(String input) {//如果这个类只使用一次,并且这个类的对象也只使用一次,就用匿名内部类对象。 //业务逻辑 return new StringBuilder(input).reverse().toString().equals(input);//字符串的反转等于自身。 } }); for(String temp:palindromeList){ System.out.println(temp); } } } import com.google.common.base.Preconditions; import com.google.common.collect.Constraint; import com.google.common.collect.Constraints; import com.google.common.collect.Sets; /** * 加入约束条件:非空、长度验证 * Constraint * Preconditions * Constraints */ public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<String> sets =Sets.newHashSet(); //创建约束 Constraint<String> constraint =new Constraint<String>(){ @Override public String checkElement(String element) { //非空验证 Preconditions.checkNotNull(element); //长度验证 5-20为字符串 Preconditions.checkArgument(element.length()>=5 && element.length()<=20); return element; } }; Set<String> cs =Constraints.constrainedSet(sets, constraint); //cs.add(null); //java.lang.NullPointerException //cs.add("good"); //java.lang.IllegalArgumentException cs.add("bjsxt"); for(String str:cs){ System.out.println(str); } } } import com.google.common.collect.Sets;//谷歌的jar包 import com.google.common.collect.Sets.SetView; /** * 集合的操作:交集、差集、并集 * Sets.intersection() * Sets.difference() * Sets.union(); */ public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Integer> sets =Sets.newHashSet(1,2,3,4,5,6); Set<Integer> sets2 =Sets.newHashSet(3,4,5,6,7,8,9); //交集 System.out.println("交集为:"); SetView<Integer> intersection =Sets.intersection(sets, sets2); for(Integer temp:intersection){ System.out.println(temp);//3456 } //差集 System.out.println("差集为:"); SetView<Integer> diff =Sets.difference(sets, sets2); for(Integer temp:diff){ System.out.println(temp);//12 } //并集 System.out.println("并集为:"); SetView<Integer> union =Sets.union(sets, sets2); for(Integer temp:union){ System.out.println(temp);//123456789 } } } import com.google.common.collect.HashMultiset; import com.google.common.collect.Multiset; /** * 统计单词出现的次数 * 1、HashMap 分拣存储+面向对象思维 -->判断 * 2、Multiset :无序+可重复 .count() 增强了可读性 +操作简单 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str ="this is a cat and that is a mice where is the food"; //分割字符串 String[] strArray =str.split(" "); //存储到Multiset中 Multiset<String> set =HashMultiset.create(); for(String strTemp:strArray){ set.add(strTemp); } //获取所有的单词 Set Set<String> letters =set.elementSet(); for(String temp:letters){ System.out.println(temp+"-->"+set.count(temp));//统计人员访问网站的 次数 } /*mice-->1 that-->1 cat-->1 is-->3 food-->1 a-->2 the-->1 where-->1 this-->1 and-->1*/ } } import com.google.common.collect.ArrayListMultimap; import com.google.common.collect.Multimap; /** * 分析查看 教师 教授的每门课程 * Multimap :key-value key可以重复 */ public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> cours =new HashMap<String,String>(); //加入测试数据 cours.put("改革开放", "邓爷爷"); cours.put("三个代表", "江主席"); cours.put("科学发展观", "胡主席"); cours.put("和谐社会", "胡主席"); cours.put("八荣八耻", "胡主席"); cours.put(".1..", "习主席"); cours.put("..2.", "习主席"); cours.put(".3..", "习主席"); //Multimap Multimap<String,String> teachers =ArrayListMultimap.create(); //迭代器 Iterator<Map.Entry<String,String>> it =cours.entrySet().iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<String,String> entry =it.next(); String key =entry.getKey(); //课程 String value =entry.getValue(); //教师 //教师 -->课程 teachers.put(value, key); } //查看Multimap Set<String> keyset =teachers.keySet(); for(String key:keyset){ Collection<String> col =teachers.get(key); System.out.println(key+"-->"+col); } /*邓爷爷-->[改革开放] 江主席-->[三个代表] 习主席-->[.3.., ..2., .1..] 胡主席-->[科学发展观, 八荣八耻, 和谐社会]*/ } } import com.google.common.collect.BiMap; import com.google.common.collect.HashBiMap; /** * HashMap 键唯一,值可以重复 * BiMap:双向Map(Bidirectional Map ) 键与值都不能重复(unique -valued map) */ public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { BiMap<String,String> bimap=HashBiMap.create(); bimap.put("bjsxt", "bjsxt@sina.com"); bimap.put("good","good@qq.com"); //通过邮箱找用户 String user =bimap.inverse().get("good@qq.com"); System.out.println(user);//good System.out.println(bimap.inverse().inverse()==bimap);//true } } import com.google.common.collect.HashBasedTable; import com.google.common.collect.Table; import com.google.common.collect.Table.Cell; import com.google.common.collect.Tables; /** * 双键的Map -->Table -->rowKey+columnKey+value//类似于一个表格,2个作为key,另外一个作为value. * 1、方法 * 所有的行数据:cellSet() * 所有的学生: rowKeySet()//查看其中一列 * 所有的课程:columnKeySet()//查看另一列 * 所有的成绩: values()//查看所有的value * 学生对应的课程: rowMap() +get(学生) * row(学生) * 课程对应的学生: columnMap +get(课程) * column(课程) */ public class Demo08 { public static void main(String[] args) { Table<String,String,Integer> tables=HashBasedTable.create(); //测试数据 tables.put("a", "javase", 80); tables.put("b", "javase", 90); tables.put("a", "oracle", 100); tables.put("c", "oracle", 95); //所有的行数据 Set<Cell<String,String,Integer>> cells =tables.cellSet(); for(Cell<String,String,Integer> temp:cells){ System.out.println(temp.getRowKey()+"-->"+temp.getColumnKey()+"-->"+temp.getValue()); } System.out.println("==========学生查看成绩=============="); System.out.print("学生 "); //所有的课程 Set<String> cours =tables.columnKeySet(); for(String t:cours){ System.out.print(t+" "); } System.out.println(); //所有的学生 Set<String> stus =tables.rowKeySet(); for(String stu:stus){ System.out.print(stu+" "); Map<String,Integer> scores =tables.row(stu); for(String c:cours){ System.out.print(scores.get(c)+" "); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("==========课程查看成绩=============="); System.out.print("课程 "); //所有的学生 Set<String> stuSet =tables.rowKeySet(); for(String t:stuSet){ System.out.print(t+" "); } System.out.println(); //所有的课程 Set<String> courSet =tables.columnKeySet(); for(String c:courSet){ System.out.print(c+" "); Map<String,Integer> scores =tables.column(c); for(String s:stuSet){ System.out.print(scores.get(s)+" "); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("===========转换==========="); Table<String,String,Integer> tables2 =Tables.transpose(tables); //所有的行数据 Set<Cell<String,String,Integer>> cells2 =tables2.cellSet(); for(Cell<String,String,Integer> temp:cells2){ System.out.println(temp.getRowKey()+"-->"+temp.getColumnKey()+"-->"+temp.getValue()); } } } import org.apache.commons.collections4.Predicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.PredicateUtils; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.EqualPredicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.NotNullPredicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.UniquePredicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.list.PredicatedList; /** 函数式编程 之 Predicate 断言 封装条件或判别式 if..else替代 1、 new EqualPredicate<类型>(值) EqualPredicate.equalPredicate(值); 2、NotNullPredicate.INSTANCE 3、UniquePredicate.uniquePredicate() 4、自定义 new Predicate() +evaluate PredicateUtils.allPredicate(可以传2个以上的断言器),andPredicate(只能传2个断言器),anyPredicate(多个断言器,只要其中一个 为true即可) PredicatedXxx.predicatedXxx(容器,判断) * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo01 { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("======自定义判断======"); //自定义的判别式 Predicate<String> selfPre =new Predicate<String>(){ @Override public boolean evaluate(String object) { return object.length()>=5 && object.length()<=20; }}; Predicate notNull=NotNullPredicate.notNullPredicate(); Predicate all =PredicateUtils.allPredicate(notNull,selfPre);//多个断言器 List<String> list =PredicatedList.predicatedList(new ArrayList<String>(),all);//用这个断言器来限制容器。 list.add("bjsxt"); list.add(null);//报异常 list.add("bj");//报异常 } /** * 判断唯一 */ public static void unique(){ System.out.println("====唯一性判断===="); Predicate<Long> uniquePre =UniquePredicate.uniquePredicate(); List<Long> list =PredicatedList.predicatedList(new ArrayList<Long>(), uniquePre); list.add(100L); list.add(200L); list.add(100L); //出现重复值,抛出异常 } /** * 判断非空 */ public static void notNull(){ System.out.println("====非空判断===="); Predicate notNull0 = NotNullPredicate.INSTANCE; Predicate notNull = NotNullPredicate.notNullPredicate(); //String str ="bjs"; String str = null; System.out.println(notNull.evaluate(str)); //如果非空为true ,否则为false //添加容器值的判断 List<Long> list =PredicatedList.predicatedList(new ArrayList<Long>(), notNull);//要求容器list不能添加null值。 list.add(1000L); list.add(null); //验证失败,出现异常 } /** * 比较相等判断 */ public static void equal(){ System.out.println("======相等判断======"); Predicate<String> pre0 =new EqualPredicate<String>("bjsxt");//实例化一个对象 Predicate<String> pre =EqualPredicate.equalPredicate("bjsxt");//创建对象 boolean flag =pre.evaluate("bj");//是否相等 System.out.println(flag); } } import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Predicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.SwitchTransformer; /** 解耦,业务处理与判断进行分类 函数式编程 Transformer 类型转化 1、new Transformer() +transform 2、SwitchTransformer CollectionUtils.collect(容器,转换器) */ public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("===自定义类型转换=="); //判别式 Predicate<Employee> isLow=new Predicate<Employee>(){//匿名内部类 @Override public boolean evaluate(Employee emp) { return emp.getSalary()<10000; } }; Predicate<Employee> isHigh=new Predicate<Employee>(){//匿名内部类 @Override public boolean evaluate(Employee emp) { return emp.getSalary()>=10000; } }; Predicate[] pres ={isLow,isHigh}; //转换,将Employee转成Level, Transformer<Employee,Level> lowTrans =new Transformer<Employee,Level>(){ @Override public Level transform(Employee input) { return new Level(input.getName(),"卖身中"); }}; Transformer<Employee,Level> highTrans =new Transformer<Employee,Level>(){ @Override public Level transform(Employee input) { return new Level(input.getName(),"养身中"); }}; Transformer[] trans ={lowTrans,highTrans}; //二者进行了关联 Transformer switchTrans =new SwitchTransformer(pres, trans, null); //容器 List<Employee> list =new ArrayList<Employee>(); list.add(new Employee("老马",1000000)); list.add(new Employee("老裴",999)); Collection<Level> levelList = CollectionUtils.collect(list,switchTrans);//参数为容器和转换规则 //遍历容器 Iterator<Level> levelIt =levelList.iterator(); while(levelIt.hasNext()){ System.out.println(levelIt.next()); /*(码农:老马,水平:养身中) (码农:老裴,水平:卖身中)*/ } } /** * 内置类型的转换 */ public static void inner(){ System.out.println("===内置类型转换 长整形时间日期,转成指定格式的字符串=="); //类型转换器,将long类型转成String, Transformer<Long,String> trans =new Transformer<Long,String>(){ @Override public String transform(Long input) { return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日").format(input); }}; //容器 List<Long> list =new ArrayList<Long>(); list.add(999999999999L); list.add(300000000L); //工具类 ,程序猿出钱---开发商---农民工出力 Collection<String> result=CollectionUtils.collect(list, trans);//将容器和类型转换器连接起来 //遍历查看结果 for(String time:result){ System.out.println(time); } } } /** * 员工类 * @author Administrator * */ public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; //alt +/ public Employee() { } //alt+shift+s o public Employee(String name, double salary) { super(); this.name = name; this.salary = salary; } //alt+shift+s +r tab 回车 shift+tab 回车 public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(double salary) { this.salary = salary; } @Override public String toString() { return "(码农:"+this.name+",敲砖钱:"+this.salary+")"; } } /** * 等级类 * @author Administrator * */ public class Level { private String name; private String level; public Level() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Level(String name, String level) { super(); this.name = name; this.level = level; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getLevel() { return level; } public void setLevel(String level) { this.level = level; } @Override public String toString() { return "(码农:"+this.name+",水平:"+this.level+")"; } } import org.apache.commons.collections4.Closure; import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Predicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedClosure; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.IfClosure; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.WhileClosure; /** 函数式编程 Closure 闭包 封装特定的业务功能 1、Closure 2、IfClosure IfClosure.ifClosure(断言,功能1,功能2) 3、WhileClosure WhileClosure.whileClosure(断言,功能,标识) 4、ChainedClosure.chainedClosure(功能列表); CollectionUtils.forAllDo(容器,功能类对象); */ public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { basic(); ifClosure(); whileClosure(); chainClosure(); } /** * 折上减 先打折商品,进行9折,满百再减20 */ public static void chainClosure(){ List<Goods> goodsList =new ArrayList<Goods>(); goodsList.add(new Goods("javase视频1",120,true)); goodsList.add(new Goods("javaee视频2",100,false)); goodsList.add(new Goods("高新技术视频",80,false)); //满百减20 Closure<Goods> subtract=new Closure<Goods>(){ public void execute(Goods goods) { if(goods.getPrice()>=100){ goods.setPrice(goods.getPrice()-20); } }}; //打折 Closure<Goods> discount=new Closure<Goods>(){ public void execute(Goods goods) { if(goods.isDiscount()){ goods.setPrice(goods.getPrice()*0.9); } }}; //链式操作 Closure<Goods> chainClo=ChainedClosure.chainedClosure(discount,subtract); //关联 CollectionUtils.forAllDo(goodsList,chainClo); //查看操作后的数据 for(Goods temp:goodsList){ System.out.println(temp); /*(商品:javase视频1,价格:88.0,是否打折:是) (商品:javaee视频2,价格:80.0,是否打折:否) (商品:高新技术视频,价格:80.0,是否打折:否)*/ } } /** * 确保所有的员工工资都大于10000,如果已经超过的不再上涨 */ public static void whileClosure(){ //数据 List<Employee> empList =new ArrayList<Employee>(); empList.add(new Employee("bjsxt",20000)); empList.add(new Employee("is",10000)); empList.add(new Employee("good",5000)); //业务功能 每次上涨0.2 Closure<Employee> cols=new Closure<Employee>(){ public void execute(Employee emp) { emp.setSalary(emp.getSalary()*1.2); }}; //判断 Predicate<Employee> empPre=new Predicate<Employee>(){ @Override public boolean evaluate(Employee emp) { return emp.getSalary()<10000; } }; //false 表示 while结构 先判断后执行 true do..while 先执行后判断 Closure<Employee> whileCols =WhileClosure.whileClosure(empPre, cols, false);//empPre为true则进入cols, //工具类 CollectionUtils.forAllDo(empList, whileCols) ; //操作后的数据 Iterator<Employee> empIt=empList.iterator(); while(empIt.hasNext()){ System.out.println(empIt.next()); /*(码农:bjsxt,敲砖钱:20000.0) (码农:is,敲砖钱:10000.0) (码农:good,敲砖钱:10368.0) 涨到超过一万为止。*/ } } /** * 二选一 如果是打折商品,进行9折,否则满百减20 */ public static void ifClosure(){ List<Goods> goodsList =new ArrayList<Goods>(); goodsList.add(new Goods("javase视频1",120,true)); goodsList.add(new Goods("javaee视频2",100,false)); goodsList.add(new Goods("高新技术视频",80,false)); //满百减20 Closure<Goods> subtract=new Closure<Goods>(){ public void execute(Goods goods) { if(goods.getPrice()>=100){ goods.setPrice(goods.getPrice()-20); } }}; //打折 Closure<Goods> discount=new Closure<Goods>(){ public void execute(Goods goods) { if(goods.isDiscount()){ goods.setPrice(goods.getPrice()*0.9); } }}; //判断 Predicate<Goods> pre=new Predicate<Goods>(){ public boolean evaluate(Goods goods) { return goods.isDiscount(); }}; //二选一 Closure<Goods> ifClo=IfClosure.ifClosure(pre,subtract,discount); //关联 CollectionUtils.forAllDo(goodsList,ifClo); //查看操作后的数据 for(Goods temp:goodsList){ System.out.println(temp); /*(商品:javase视频,价格:108.0,是否打折:是) (商品:javaee视频,价格:80.0,是否打折:否) (商品:高新技术视频,价格:80.0,是否打折:否)*/ } } /** * 基本操作 */ public static void basic(){ //数据 List<Employee> empList =new ArrayList<Employee>(); empList.add(new Employee("bjsxt",20000)); empList.add(new Employee("is",10000)); empList.add(new Employee("good",5000)); //业务功能 Closure<Employee> cols=new Closure<Employee>(){//匿名内部类对象 public void execute(Employee emp) { emp.setSalary(emp.getSalary()*1.2);//工资加倍 }}; //工具类 CollectionUtils.forAllDo(empList, cols) ; //操作后的数据 Iterator<Employee> empIt=empList.iterator(); while(empIt.hasNext()){ System.out.println(empIt.next()); /*(码农:bjsxt,敲砖钱:24000.0) (码农:is,敲砖钱:12000.0) (码农:good,敲砖钱:6000.0)*/ } } } public class Goods { private String name; private double price; //折扣 private boolean discount; public Goods() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Goods(String name, double price, boolean discount) { super(); this.name = name; this.price = price; this.discount = discount; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public boolean isDiscount() { return discount; } public void setDiscount(boolean discount) { this.discount = discount; } @Override public String toString() { return "(商品:"+this.name+",价格:"+this.price+",是否打折:"+(discount?"是":"否")+")"; } } import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils; /** * 集合操作 * 1、并集 * CollectionUtils.union(); * 2、交集 * CollectionUtils.intersection(); * CollectionUtils.retainAll(); * 3、差集 * CollectionUtils.subtract(); */ public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Integer> set1 =new HashSet<Integer>(); set1.add(1); set1.add(2); set1.add(3); Set<Integer> set2 =new HashSet<Integer>(); set2.add(2); set2.add(3); set2.add(4); //并集 System.out.println("=========并集============"); Collection<Integer> col =CollectionUtils.union(set1,set2); for(Integer temp:col){ System.out.println(temp); } //交集 System.out.println("=========交集============"); //col =CollectionUtils.intersection(set1, set2); col =CollectionUtils.retainAll(set1, set2); for(Integer temp:col){ System.out.println(temp); } //差集 System.out.println("=========差集============"); col =CollectionUtils.subtract(set1, set2); for(Integer temp:col){ System.out.println(temp); } } } 队列: import java.util.Queue; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Predicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.NotNullPredicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.queue.CircularFifoQueue; import org.apache.commons.collections4.queue.PredicatedQueue; import org.apache.commons.collections4.queue.UnmodifiableQueue; /** Queue队列(先进先出),栈(后进先出) 1、循环队列:CircularFifoQueue 2、只读队列:不可改变队列 UnmodifiableQueue 3、断言队列:PredicatedQueue.predicatedQueue() */ public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { circular(); readOnly(); predicate(); } /** * 断言队列 */ public static void predicate(){ //循环队列 CircularFifoQueue<String> que =new CircularFifoQueue<String>(2); que.add("a"); que.add("b"); que.add("c"); Predicate notNull=NotNullPredicate.INSTANCE; //包装成对应的队列 Queue<String> que2=PredicatedQueue.predicatedQueue(que, notNull); que2.add(null); } /** * 只读队列 */ public static void readOnly(){ //循环队列 CircularFifoQueue<String> que =new CircularFifoQueue<String>(2); que.add("a"); que.add("b"); que.add("c"); Queue<String> readOnlyQue =UnmodifiableQueue.unmodifiableQueue(que); readOnlyQue.add("d"); } /** * 循环队列 */ public static void circular(){ //循环队列 CircularFifoQueue<String> que =new CircularFifoQueue<String>(2); que.add("a"); que.add("b"); que.add("c"); //查看 for(int i=0;i<que.size();i++){ System.out.println(que.get(i)); } } } import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.collections4.BidiMap; import org.apache.commons.collections4.IterableMap; import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapIterator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Predicate; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bidimap.DualHashBidiMap; import org.apache.commons.collections4.iterators.ArrayListIterator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.iterators.FilterIterator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.iterators.LoopingIterator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.iterators.UniqueFilterIterator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.map.HashedMap; /** 迭代器的扩展 1、MapIterator 以后不再使用map.keySet.iterator访问 接口IterableMap,实现类 HashedMap 2、UniqueFilterIterator 去重迭代器 3、FilterIterator 自定义过滤 +Predicate 4、LoopingIterator 循环迭代器 5、ArrayListIterator 数组迭代器 */ public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { mapIt(); uniqueIt(); filterIt(); loopIt(); arrayIt(); } /** * 数组迭代器 */ public static void arrayIt(){ System.out.println("===== 数组迭代器 ===="); int[] arr ={1,2,3,4,5}; //数组迭代器 Iterator<Integer> it0 =new ArrayListIterator<Integer>(arr); //指定起始索引和结束索引 Iterator<Integer> it =new ArrayListIterator<Integer>(arr,1,3); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next());//2,3 } } /** * 循环迭代器 */ public static void loopIt(){ System.out.println("===== 循环迭代器 ===="); List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("refer"); list.add("dad"); list.add("bjsxt"); list.add("moom"); Iterator<String> it =new LoopingIterator(list); for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ System.out.println(it.next()); /*refer dad bjsxt moom refer dad bjsxt moom*/ } } /** * 自定义迭代器 */ public static void filterIt(){ System.out.println("=====自定义迭代器 ===="); List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("refer"); list.add("dad"); list.add("bjsxt"); list.add("moom"); //自定义条件判断 Predicate<String> pre =new Predicate<String>(){ public boolean evaluate(String value) { //回文判断 return new StringBuilder(value).reverse().toString().equals(value); }}; //去除重复的过滤器 Iterator<String> it =new FilterIterator(list.iterator(),pre); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); /*refer dad moom*/ } } /** * 去重迭代器 */ public static void uniqueIt(){ System.out.println("=====去重迭代器 ===="); List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("a"); list.add("b"); list.add("a"); //去除重复的过滤器 Iterator<String> it =new UniqueFilterIterator(list.iterator()); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); /*a b*/ } } /** * map迭代器 */ public static void mapIt(){ System.out.println("=====map迭代器===="); IterableMap<String,String> map =new HashedMap<String,String>(); map.put("a","bjsxt"); map.put("b", "sxt"); map.put("c", "good"); //使用 MapIterator MapIterator<String,String> it =map.mapIterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String key =it.next(); String value =it.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"-->"+value); /*a-->bjsxt c-->good b-->sxt*/ } } } import org.apache.commons.collections4.BidiMap; import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapIterator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bidimap.DualHashBidiMap; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bidimap.DualTreeBidiMap; /** 双向Map 要求键与值都不能重复 接口BidiMap inverseBidiMap() 实现类1、DualTreeBidiMap :有序 实现类2、DualHashBidiMap :无序 */ public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { hashMap(); treeMap(); } /** * 有序的双向Map(key会自动排列) */ public static void treeMap(){ System.out.println("=====有序的双向Map===="); BidiMap<String,String> map =new DualTreeBidiMap<String,String>(); map.put("zbj", "bj@test.com"); map.put("sxt", "sxt@qq.com");//{sxt=sxt@qq.com, zbj=bj@test.com} //遍历查看 MapIterator<String,String> it =map.inverseBidiMap().mapIterator();//{bj@test.com=zbj, sxt@qq.com=sxt} while(it.hasNext()){ String key =it.next(); String value =it.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"-->"+value); //bj@test.com-->zbj //sxt@qq.com-->sxt } } /** * 无序的双向Map */ public static void hashMap(){ System.out.println("=====无序的双向Map===="); BidiMap<String,String> map =new DualHashBidiMap<String,String>(); map.put("bj", "bj@test.com"); map.put("sxt", "sxt@qq.com");//{sxt=sxt@qq.com, bj=bj@test.com} //反转 System.out.println(map.inverseBidiMap().get("sxt@qq.com"));//先要反转,然后通过value找到key,sxt //遍历查看 MapIterator<String,String> it =map.inverseBidiMap().mapIterator();//{sxt@qq.com=sxt, bj@test.com=bj} while(it.hasNext()){ String key =it.next(); String value =it.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"-->"+value); /*sxt@qq.com-->sxt bj@test.com-->bj*/ } } } import org.apache.commons.collections4.Bag; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.HashBag; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.TreeBag; /** 接口Bag 包 允许重复 实现类1、HashBag 无序 实现类2、TreeBag 有序 统计单词的出现次数 */ public class Demo08 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { hashBag(); treeBag(); String str ="this is a cat and that is a mice where is the food"; //分割字符串 String[] strArray =str.split(" "); Bag<String> bag =new TreeBag<String>(); for(String temp:strArray){ bag.add(temp);//[2:a,1:and,1:cat,1:food,3:is,1:mice,1:that,1:the,1:this,1:where] } System.out.println("====统计次数==="); Set<String> keys =bag.uniqueSet();//[a, and, cat, food, is, mice, that, the, this, where] for(String letter:keys){ System.out.println(letter+"-->"+bag.getCount(letter)); /*a-->2 and-->1 cat-->1 food-->1 is-->3 mice-->1 that-->1 the-->1 this-->1 where-->1*/ } } /** * 有序 */ public static void treeBag(){ System.out.println("=====有序的包===="); Bag<String> bag =new TreeBag<String>(); bag.add("a"); bag.add("a",5); bag.remove("a", 2); bag.add("b"); bag.add("c");//[4:a,1:b,1:c],有序 Iterator<String> it =bag.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next());//aaaabc } } /** * 无序 */ public static void hashBag(){ System.out.println("=====无序的包===="); Bag<String> bag =new HashBag<String>(); bag.add("a"); bag.add("a",5);//加5次a,[6:a] bag.remove("a", 2);//移除2个a,[4:a] bag.add("b"); bag.add("c");//[1:b,1:c,4:a],一个b,一个c,4个a, Iterator<String> it =bag.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next());//bcaaaa } } } 总结: set没有顺序,顺序指的是索引的顺序不是指内容。 1.迭代器:Iterator, 2.比较器:实体类可以排序(实现Comparable重写compareTo),还可以用排序比较器(实现Comparator重写compare),TreeSet、TreeMap. 3.泛型:反泛型类,泛型方法,泛型接口,泛型擦出,通配符? 4.6个接口:Collection,set,List,Map,Iterator,Comparable 5.9个常用类: 1) 查看多余修改时推荐使用ArrayList(add,remove,set(修改),get,foreach,)。 2) 修改多余查看推荐使用LinkList,多了链头与链尾的方法。 3)HashSet:元素不能重复,所以要求元素要重写hashCode和equals方法. 4)Treeset:要求元素可以排序或者提供排序的业务类。 5)HashMap:键不能重复必须重写hashCode和equals方法,值可以重复,put(),remove(),get(). 6)Properties:资源配置文件, 7)Hashtable:键与值都不能为null, 8)Stack:栈 9)Collections:工具类