开篇:上一篇我们了解了一个ASP.Net页面请求的核心处理入口,它经历了三个重要的入口,分别是:ISAPIRuntime.ProcessRequest()、HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest()以及HttpApplication.Init()。其中,在HttpApplication的Init()方法中触发了请求处理管道事件的执行,本篇我们就来看看所谓的请求处理管道。
(1)Part 1:前奏
(2)Part 2:核心
(3)Part 3:管道
(4)Part 4:WebForm页面生命周期
(5)Part 5:MVC页面声命周期
一、所谓“请求处理管道”
HttpApplication对象是ASP.NET中处理请求的重要对象,但是,这种类型的对象实例不是由程序员来创建的,而是由ASP.NET帮助我们创建的。为了便于扩展处理工作,HttpApplication采用处理管道的方法进行处理,将处理的过程分为多个步骤,每个步骤通过事件的形式暴露给程序员,这些事件按照固定的处理顺序依次触发,程序员通过编写事件处理方法就可以自定义每一个请求的扩展处理过程。
①传说中的19个事件
对于HttpApplication来说,到ASP.NET 4.0版本,提供了19个重要的标准事件,如下图所示:
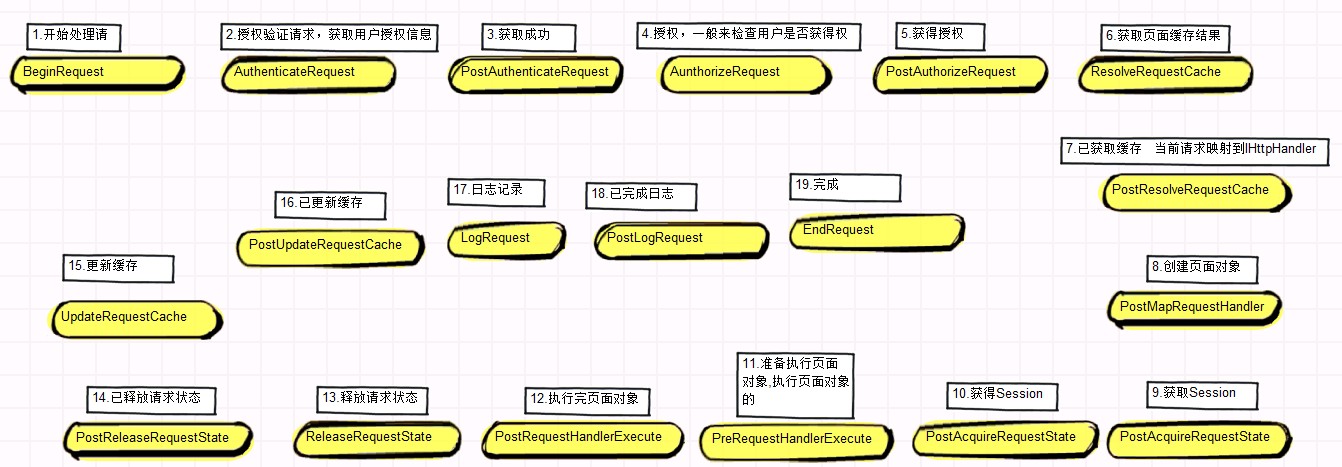
在整个请求处理管道中,HttpContext上下文被依次传输到各个处理事件中,由不同的处理单元(HttpModule、HttpHandler、Page等)进行处理。从这里可以看出,ASP.NET请求处理管道就像是一个大型的AOP框架。
②HttpModule与HttpHandler
在进一步深入了解之前,让我们先来了解一下什么是HttpModule和HttpHandlers。他们帮助我们在ASP.NET页面处理过程的前后注入自定义的逻辑处理。他们之间主要的差别在于:
- 如果你想要注入的逻辑是基于像'.aspx','.html'这样的扩展文件,那么你可以使用HttpHandler。换句话说,HttpHandler是一个基于处理器的扩展。
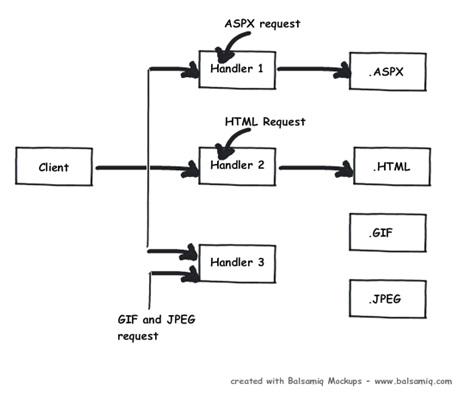
- HttpHandler总结:在ASP.NET WebForm中,无论是一般处理程序还是WebPage都实现了IHttpHandler接口,而ASP.NET MVC中也有MvcHandler实现了IHttpHandler接口;
- 如果你想要在ASP.NET管道事件中注入逻辑,那么你可以使用HttpModule。也可以说,HttpModule是一个基于处理器的事件。
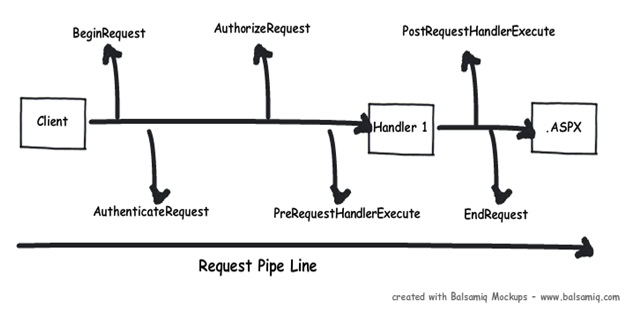
- HttpModule总结:刚刚我们说到ASP.NET请求处理管道就像是一个大型的AOP框架,因此我们可以借助HttpModule自定义地注册或移除一些事件逻辑,以完成我们想要的效果。ASP.NET默认实现了针对WebForm和MVC的HttpModule,像ASP.NET MVC中默认使用的是UrlRoutingModule。具体实现方式是:通过改写Global文件或自定义一个实现IHttpModule接口的类并在Web.config中进行注册。
-
<?xml version="1.0"?> <configuration> <system.web> <httpModules> <add name="myHttpModule" type="FirstModule"/> </httpModules> </system.web> </configuration>public class FirstModule : IHttpModule { public void Dispose() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void Init(HttpApplication context) { context.BeginRequest += new EventHandler(context_BeginRequest); } void context_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication application = sender as HttpApplication; application.Context.Response.Write("第三方过滤器:哇哈哈!"); } }
③19个事件中我们可以做些什么?
一个十分有价值的问题就是在什么事件中我们又可以做些什么?下表就展示了这个问题的答案:
| Section | Event | Description |
| HttpModule | BeginRequest | 此事件标志着一个新的请求,它保证在每个请求中都会被触发。 |
| HttpModule | AuthenticateRequest | 此事件标志ASP.NET运行时准备验证用户。任何身份验证代码都可以在此注入。 |
| HttpModule | AuthorizeRequest | 此事件标志ASP.NET运行时准备授权用户。任何授权代码都可以在此注入。 |
| HttpModule | ResolveRequest | 在ASP.NET中我们通常使用OutputCache指令做缓存。在这个事件中,ASP.NET运行时确定是否能够从缓存中加载页面,而不是从头开始生成。任何缓存的具体活动可以被注入这里。 |
| HttpModule | AcquireRequestState | 此事件标志着ASP.NET运行时准备获得Session会话变量。可以对Session变量做任何你想要做的处理。 |
| HttpModule | PreRequestHandlerExecute | 恰好在ASP.NET 开始执行事件处理程序前发生。可以预处理你想做的事。 |
| HttpHandler | ProcessRequest | HttpHandler逻辑被执行。在这个部分我们将为每个页面扩展写需要的逻辑。 |
| Page | Init | 此事件发生在ASP.NET页面且可以用来: 1、动态地创建控件,如果你一定要在运行时创建控件; 2、任何初始化设置 3、母版页及其设置 在这部分中我们没有获得viewstate、postedvalues及已经初始化的控件。 |
| Page | Load | 在这部分ASP.NET控件完全被加载且在这里你可以写UI操作逻辑或任何其他逻辑。NOTE:这个事件也是我们最常见且最常用的一个事件。 |
| Page | Validate | 如果在页面上你有验证器,你同样想在这里做一下检查。 |
| Page | Render | 是时候将输出发送到浏览器。如果你想对最终的HTML做些修改,你可以在这里输入你的HTML逻辑。 |
| Page | Unload | 页面对象从内存中卸载。 |
| HttpModule | PostRequestHandlerExecute | 可以注入任何你想要的逻辑,在处理程序执行之后。 |
| HttpModule | ReleaseRequestState | 如果你想要保存对某些状态变量的更改,例如:Session变量的值。 |
| HttpModule | UpdateRequestCache | 在结束之前,你是否想要更新你的缓存。 |
| HttpModule | EndRequest | 这是将输出发送到客户端浏览器之前的最后一个阶段。 |
④自定义处理逻辑
我们可以通过一个示例程序代码来展示以上介绍的那些事件是怎样被最终触发的。在这个示例中,我们已经创建了一个HttpModule和HttpHandler,并且也在所有的事件中通过添加自定义逻辑代码展示了一个简单的响应。
下面是HttpModule类,它跟踪了所有的事件并将其添加到了一个全局的集合中。

public class clsHttpModule : IHttpModule
{
......
void OnUpdateRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnUpdateRequestCache");
}
void OnReleaseRequestState(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnReleaseRequestState");
}
void OnPostRequestHandlerExecute(object sender, EventArgs a)
{ objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnPostRequestHandlerExecute");
}
void OnPreRequestHandlerExecute(object sender, EventArgs a)
{ objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnPreRequestHandlerExecute");
}
void OnAcquireRequestState(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnAcquireRequestState");
}
void OnResolveRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnResolveRequestCache");
}
void OnAuthorization(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:OnAuthorization");
}
void OnAuthentication(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:AuthenticateRequest");
}
void OnBeginrequest(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:BeginRequest");
}
void OnEndRequest(object sender, EventArgs a)
{
objArrayList.Add("httpModule:EndRequest");
objArrayList.Add("<hr>");
foreach (string str in objArrayList)
{
httpApp.Context.Response.Write(str + "<br>") ;
}
}
}
下面是HttpHandler类的一个代码片段,它跟踪了ProcessRequest事件。

public class clsHttpHandler : IHttpHandler
{
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{ clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("HttpHandler:ProcessRequest");
context.Response.Redirect("Default.aspx");
}
}
同上,我们也可以跟踪来自ASP.NET Page页面的所有事件。

public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_init(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("Page:Init");
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("Page:Load");
}
public override void Validate()
{
clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("Page:Validate");
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("Page:Event");
}
protected override void Render(HtmlTextWriter output)
{
clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("Page:Render");
base.Render(output);
}
protected void Page_Unload(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
clsHttpModule.objArrayList.Add("Page:UnLoad");
}
}
下图则显示了上面我们所讨论的所有事件的执行顺序:

二、WebForm经历的管道事件概览
在ASP.NET WebForm应用中,其在请求处理管道中主要经历了三个重要阶段:
①在第八个事件中创建Page类对象并转换为IHttpHandler接口
从上面的介绍中可以看到,第八个事件是:PostMapRequestHandler。在这个事件中,对于访问不同的资源类型,ASP.NET具有不同的HttpHandler对其进程处理。对于每个请求,ASP.NET会通过扩展名选择匹配相应的HttpHandler类型,成功匹配后,该实现被触发。因此,如果请求的扩展名是.aspx,便会生成Page类对象,而Page类对象是实现了IHttpHandler接口的。

②在第九个到第十事件之间根据SessionId获取Session

从上面的介绍中可以看到,第九到第十个事件是:AcquireRequestState,PostAcquireRequestState。这期间首先会接收到浏览器发过来的SessionId,然后先会将IHttpHandler接口尝试转换为IRequiresSessionState接口,如果转换成功,ASP.NET会根据这个SessionId到服务器的Session池中去查找所对应的Session对象,并将这个Session对象赋值到HttpContext对象的Session属性。如果尝试转换为IRequiresSessionState接口不成功,则不加载Session。

③在第十一个事件与第十二个事件之间执行页面生命周期
从上面的介绍中可以看到,第十一和第十二个事件是:PreRequestHandlerExecute,PostRequestHandlerExecute。在这两个事件之间,ASP.NET最终通过请求资源类型相对应的HttpHandler实现对请求的处理,其实现方式是调用在第八个事件创建的页面对象的ProcessRequest方法。
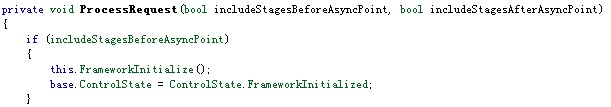 在FrameworkInitialize()这个方法内部就开始打造WebForm的页面控件树,在其中调用了ProcessRequestMain方法,在这个方法里面就执行了整个ASP.NET WebFom页面生命周期。至于WebForm页面生命周期的细节,我们在本系列后续的Part 4再来细细研究。
在FrameworkInitialize()这个方法内部就开始打造WebForm的页面控件树,在其中调用了ProcessRequestMain方法,在这个方法里面就执行了整个ASP.NET WebFom页面生命周期。至于WebForm页面生命周期的细节,我们在本系列后续的Part 4再来细细研究。
当我们直接使用*.ashx页面的时候,它的ProcessRequest()方法就直接调用了一个FrameworkInitialize(),并最终生成响应报文,发送回客户端。
当我们在使用*.aspx页面的时候,它继承自Page类,而Page类实现了IHttpHandler接口,然后了调用Page类的ProcessRequest()方法,其中会构建页面控件树,然后一个一个地去呈现。
三、ASP.NET MVC经历的管道事件概览
在ASP.NET MVC中,最核心的当属“路由系统”,而路由系统的核心则源于一个强大的System.Web.Routing.dll组件。

在这个System.Web.Routing.dll中,有一个最重要的类叫做UrlRoutingModule,它是一个实现了IHttpModule接口的类,在请求处理管道中专门针对ASP.NET MVC请求进行处理。首先,我们要了解一下UrlRoutingModule是如何起作用的。
(1)IIS网站的配置可以分为两个块:全局 Web.config 和本站 Web.config。Asp.Net Routing属于全局性的,所以它配置在全局Web.Config 中,我们可以在如下路径中找到:“$WindowsMicrosoft.NETFramework版本号ConfigWeb.config“
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- the root web configuration file -->
<configuration>
<system.web>
<httpModules>
<add name="UrlRoutingModule-4.0" type="System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule" />
</httpModules>
</system.web>
</configuration>
(2)通过在全局Web.Config中注册 System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule,IIS请求处理管道接到请求后,就会加载 UrlRoutingModule类型的Init()方法。其源码入下:

public class UrlRoutingModule : IHttpModule
{
// Fields
private static readonly object _contextKey = new object();
private static readonly object _requestDataKey = new object();
private RouteCollection _routeCollection;
// Methods
protected virtual void Dispose()
{
}
protected virtual void Init(HttpApplication application)
{
if (application.Context.Items[_contextKey] == null)
{
application.Context.Items[_contextKey] = _contextKey;
// 这里为UrlRoutingModule 注册了一个PostResolveRequestCache 事件处理方法:OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache().
application.PostResolveRequestCache += new EventHandler(this.OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache);
}
}
private void OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContextBase context = new HttpContextWrapper(((HttpApplication) sender).Context);
this.PostResolveRequestCache(context);
}
[Obsolete("This method is obsolete. Override the Init method to use the PostMapRequestHandler event.")]
public virtual void PostMapRequestHandler(HttpContextBase context)
{
}
public virtual void PostResolveRequestCache(HttpContextBase context)
{
RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context);
if (routeData != null)
{
IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler;
if (routeHandler == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoRouteHandler"), new object[0]));
}
if (!(routeHandler is StopRoutingHandler))
{
RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(context, routeData);
context.Request.RequestContext = requestContext;
IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext);
if (httpHandler == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoHttpHandler"), new object[] { routeHandler.GetType() }));
}
if (httpHandler is UrlAuthFailureHandler)
{
if (!FormsAuthenticationModule.FormsAuthRequired)
{
throw new HttpException(0x191, SR.GetString("Assess_Denied_Description3"));
}
UrlAuthorizationModule.ReportUrlAuthorizationFailure(HttpContext.Current, this);
}
else
{
context.RemapHandler(httpHandler);
}
}
}
}
void IHttpModule.Dispose()
{
this.Dispose();
}
void IHttpModule.Init(HttpApplication application)
{
this.Init(application);
}
// Properties
public RouteCollection RouteCollection
{
get
{
if (this._routeCollection == null)
{
this._routeCollection = RouteTable.Routes;
}
return this._routeCollection;
}
set
{
this._routeCollection = value;
}
}
}
从源码中可以看出,在UrlRoutingModule中为请求处理管道中的第七个事件PostResolveRequestCache注册了一个事件处理方法:OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache。从这里可以看出:ASP.NET MVC的入口在UrlRoutingModule,即订阅了HttpApplication的第7个管道事件PostResolveRequestCahce。换句话说,是在HtttpApplication的第7个管道事件处对请求进行了拦截。

现在我们将ASP.NET MVC的请求处理分为两个重要阶段来看看:
①在第七个事件中创建实现了IHttpHandler接口的MvcHandler
当请求到达UrlRoutingModule的时候,UrlRoutingModule取出请求中的Controller、Action等RouteData信息,与路由表中的所有规则进行匹配,若匹配,把请求交给IRouteHandler,即MVCRouteHandler。我们可以看下UrlRoutingModule的源码来看看,以下是几句核心的代码:
public virtual void PostResolveRequestCache(HttpContextBase context)
{
// 通过RouteCollection的静态方法GetRouteData获取到封装路由信息的RouteData实例
RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context);
if (routeData != null)
{
// 再从RouteData中获取MVCRouteHandler
IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler;
......
if (!(routeHandler is StopRoutingHandler))
{
......
// 调用 IRouteHandler.GetHttpHandler(),获取的IHttpHandler 类型实例,它是由 IRouteHandler.GetHttpHandler获取的,这个得去MVC的源码里看
IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext);
......
// 合适条件下,把之前将获取的IHttpHandler 类型实例 映射到IIS HTTP处理管道中
context.RemapHandler(httpHandler);
}
}
}
MVCRouteHandler的作用是用来生成实现IHttpHandler接口的MvcHandler:
namespace System.Web.Routing
{
public interface IRouteHandler
{
IHttpHandler GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext);
}
}
那么,MvcRouteHandler从何而来呢?众所周知,ASP.NET MVC项目启动是从Global中的Application_Start()方法开始的,那就去看看它:
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
......
//这里要注册路由了
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
}
}
public class RouteConfig
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
// 玄机就在这了,这个MapRoute位于System.Web.Mvc.RouteCollectionExtensions
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
于是,我们再去看看Route类的这个MapRoute()方法的源码:
public static Route MapRoute(this RouteCollection routes, string name, string url, object defaults, object constraints, string[] namespaces)
{
......
// 终于等到你,还好我没放弃。
Route route = new Route(url, new MvcRouteHandler()) {
Defaults = new RouteValueDictionary(defaults),
Constraints = new RouteValueDictionary(constraints),
DataTokens = new RouteValueDictionary()
};
......
return route;
}
从上面的源码可以得知为什么可以从RouteData中拿到MvcRouteHadnler?因为当我们在HttpApplication的第一个管道事件,使用MapRoute()方法注册路由的时候,已经通过Route类的构造函数把MvcRouteHandler注入到路由中了。
刚刚我们知道MvcRouteHandler是用来生成实现IHttpHandler接口的MvcHandler,那么我们继续从UrlRoutingModule的源码可以看到,通过HttpHandler的GetHttpHandler()方法获取到了实现了IHttpHandler接口的MvcHandler:
// 调用 IRouteHandler.GetHttpHandler(),获取的IHttpHandler 类型实例,它是由 IRouteHandler.GetHttpHandler获取的,这个得去MVC的源码里看
IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext);
......
// 合适条件下,把之前将获取的IHttpHandler 类型实例 映射到IIS HTTP处理管道中
context.RemapHandler(httpHandler);
于是,我们进入ASP.NET MVC的源码看看MvcHandlerd的实现,这里我看的是MVC 4.0的源码:
protected virtual IHttpHandler GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext)
{
requestContext.HttpContext.SetSessionStateBehavior(GetSessionStateBehavior(requestContext));
return new MvcHandler(requestContext);
}
可以看出,在这里创建了MvcHandler实例。换句话说,MvcRouteHandler把请求交给了MvcHandler去做请求处理管道中后续事件的处理操作了。

②在第十一个事件与第十二个事件之间调用MvcHandler的ProcessRequest()方法
(1)在WebForm中,此阶段会调用Page类对象的ProcessRequest()方法。在ASP.NET MVC中,会调用MvcHandler的ProcessRequest()方法,此方法会激活具体请求的Controller类对象,触发Action方法,返回ActionResult实例。
(2)如果ActionResult是非ViewResult,比如JsonResult, ContentResult,这些内容将直接被输送到Response响应流中,显示给客户端;如果是ViewResult,就会进入下一个渲染视图环节。
(3)在渲染视图环节,ViewEngine找到需要被渲染的视图,View被加载成WebViewPage<TModel>类型,并渲染生成Html,最终返回Html。
TIP:有关此ProcessRequest()处理环节的详细内容,请等待本系列Part 5中的介绍。
参考资料
致谢:本文参阅了大量园友的文章,也直接使用了大量园友制作的图,在此对以下各位园友表示感谢。
(1)Darren Ji,《ASP.NET MVC请求处理管道声明周期的19个关键环节》:http://www.cnblogs.com/darrenji/p/3795661.html
(2)木宛城主,《ASP.NET那点不为人知的事儿》:http://www.cnblogs.com/OceanEyes/archive/2012/08/13/aspnetEssential-1.html
(3)Tony He,《ASP.NET请求处理机制》:http://www.cnblogs.com/cilence/archive/2012/05/28/2520712.html
(4)两会的博客,《IIS是怎样处理ASP.NET请求的》:http://www.cnblogs.com/hkncd/archive/2012/03/23/2413917.html
(5)wjn2000,《ASP.NET请求处理过程(IIS6)》:http://www.cnblogs.com/wjn2010/archive/2011/04/21/2024341.html
(6)农村出来的大学生,《ASP.NET网页请求处理全过程(反编译)》:http://www.cnblogs.com/poorpan/archive/2011/09/25/2190308.html
(7)碧血轩,《ASP.NET页面生命周期》,http://www.cnblogs.com/xhwy/archive/2012/05/20/2510178.html
(8)吴秦,《ASP.NET 应用程序与页面生命周期(意译)》,http://www.cnblogs.com/skynet/archive/2010/04/29/1724020.html
(9)我自己,《【翻译】ASP.NET应用程序和页面声明周期》:http://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/3958305.html
(10)Shivprasad koirala,《ASP.NET Application and Page Life Cycle》:http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/73728/ASP-NET-Application-and-Page-Life-Cycle
(11)学而不思则罔,《ASP.NET Routing与MVC之一:请求如何到达MVC》:http://www.cnblogs.com/acejason/p/3869731.html
(12)初心不可忘,《综述:ASP.NET MVC请求处理管道》:http://www.cnblogs.com/luguobin/archive/2013/03/15/2962458.html
作者:周旭龙
