Title:
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.

The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped. Thanks Marcos for contributing this image!
菜鸟果然不会,看了别人的思路。
两个比较好的思路,一个是找出最高峰,然后分别从两边靠拢。在靠拢中记录当前的最高的,具体见http://www.cnblogs.com/lichen782/p/Leetcode_Trapping_Rain_Water.html
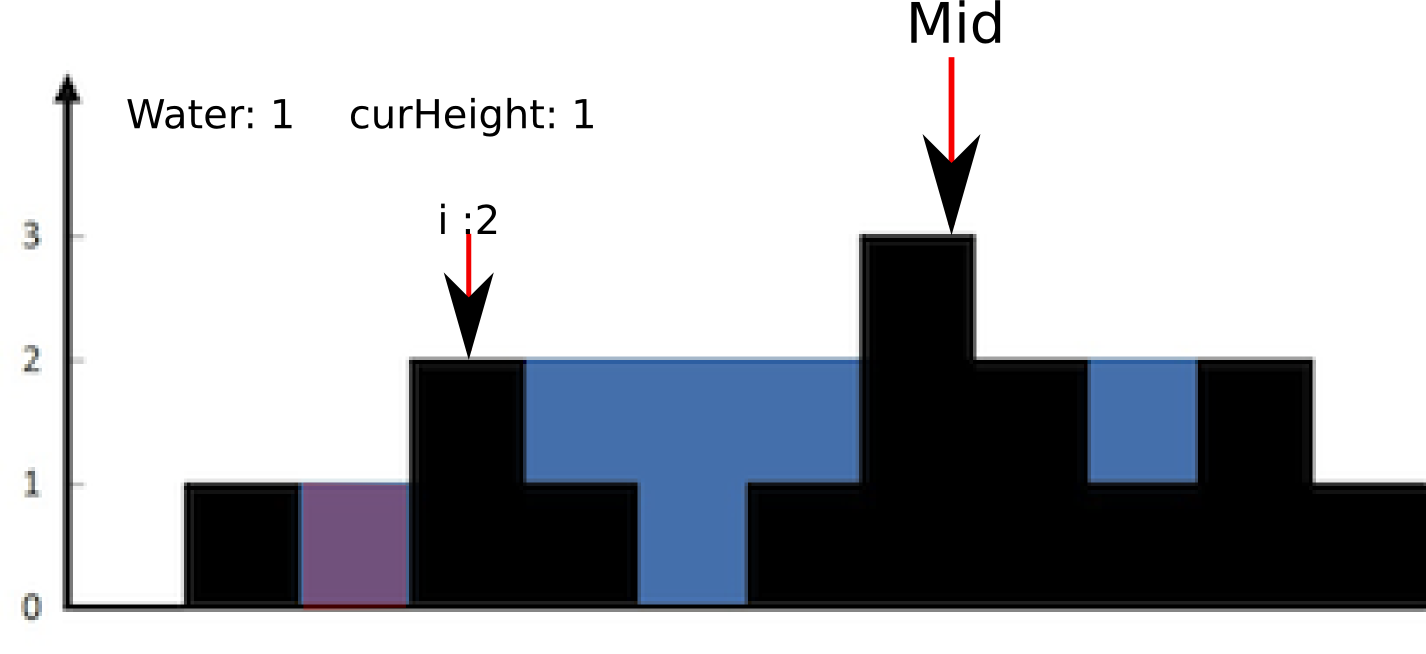
首先,找到最高的一个柱子,例如例子中的3。

然后遍历左半边。从i=0开始靠近mid,遍历过程中维护一个curHeight,表示这当前遇到的最大的height值;如果当前的bar的height小于最大值,那么当前的bar能贡献的water就是height - curMaxHeight。否则的话,更新curMaxHeight。
为了更好理解这个算法,我们来track下这个过程:





class Solution{ public: int trap(vector<int> & height){ if (height.size() <=1 ) return 0; int n = height.size(); int hi_index = 0; for (int i = 0 ; i < height.size(); i++){ if (height[i]> height[hi_index]){ hi_index= i; } } int cur_h = 0; int water = 0; for (int i = 0 ; i < hi_index; i++){ if (height[i] > cur_h) cur_h = height[i]; else{ water += (cur_h - height[i]); } } cur_h = 0; for (int i = height.size()-1; i > hi_index; i--){ if (height[i] > cur_h) cur_h = height[i]; else water += (cur_h - height[i]); } return water; } };
第二种思路是使用单调栈。这里是单调递减栈。
int trap(vector<int> & height) { stack<int> stk; // descending int result = 0; int i = 0; int n = height.size(); while (i < n) { if (stk.size() == 0 || height[stk.top()] > height[i]) { stk.push(i); // the index i++; } else { // A[i] >= stk.top(); int j = stk.top(); stk.pop(); if (stk.size() != 0) { result += (i - stk.top() - 1) * (min(height[stk.top()], height[i]) - height[j]); } } } return result; }