本周开始暑假就正式结束了,这周因为学校安排的认识实习的缘故并没有什么进度,只学习了部分Python线程相关的东西
首先是单线程的测试,下图是运行效果图
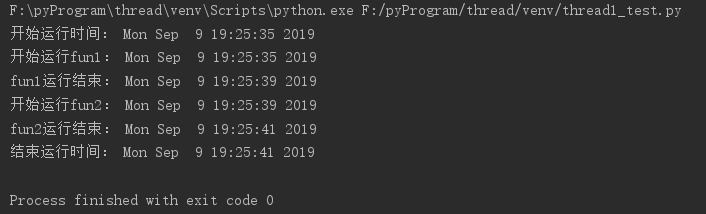
代码如下:
1 from time import sleep,ctime 2 def fun1(): 3 print('开始运行fun1:',ctime()) 4 #休眠4s 5 sleep(4) 6 print('fun1运行结束:',ctime()) 7 def fun2(): 8 print('开始运行fun2:',ctime()) 9 # 休眠2s 10 sleep(2) 11 print('fun2运行结束:', ctime()) 12 def main(): 13 print("开始运行时间:",ctime()) 14 #在单线程中调用fun1函数和fun2函数 15 fun1() 16 fun2() 17 print("结束运行时间:",ctime()) 18 if __name__=='__main__': 19 main()
接下来是多线程程序测试,效果图如下:
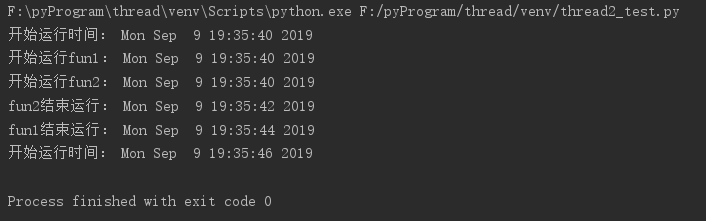
代码如下:
1 import _thread as thread 2 from time import sleep,ctime 3 def fun1(): 4 print('开始运行fun1:',ctime()) 5 #休眠4s 6 sleep(4) 7 print('fun1运行结束:',ctime()) 8 def fun2(): 9 print('开始运行fun2:',ctime()) 10 #休眠2s 11 sleep(2) 12 print('fun2运行结束:',ctime()) 13 def main(): 14 print('开始运行时间:',ctime()) 15 #启动一个线程运行fun1函数 16 thread.start_new_thread(fun1(),()) 17 #启动一个线程运行fun2函数 18 thread.start_new_thread(fun2(),()) 19 #休眠6s 20 sleep(6) 21 print('结束运行时间:',ctime()) 22 if __name__=='__main__': 23 main()
然后是为线程函数传递参数的测试,效果图如下:
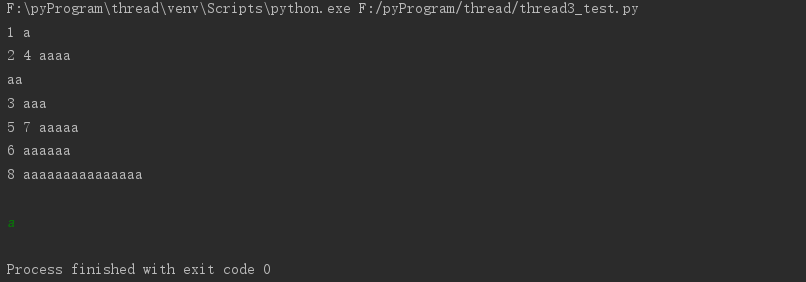
代码如下:
1 import random 2 from time import sleep,ctime 3 import _thread as thread 4 #线程函数,其中a和b是通过start_new_thread函数传入的参数 5 def fun(a,b): 6 print(a,b) 7 # 随机休眠一段时间(1~4秒) 8 sleep(random.randint(1,4)) 9 #启动8个线程 10 for i in range(8): 11 # 为每一个线程函数传入两个参数值 12 thread.start_new_thread(fun,(i+1,'a'*(i+1))) 13 # 通过从终端输入一个字符串的方式让程序暂停 14 input()
接下来是线程和锁的测试,效果图如下:
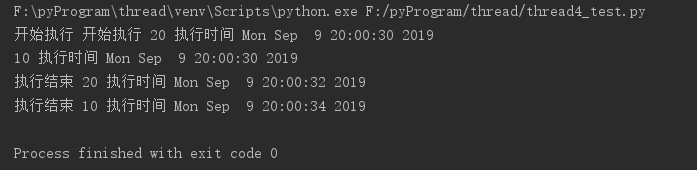
代码如下:
1 import _thread as thread 2 from time import sleep,ctime 3 # 线程函数,index是一个整数类型的索引,sec是休眠时间(单位:秒),lock是锁对象 4 def fun(index,sec,lock): 5 print('开始执行',index,'执行时间',ctime()) 6 #休眠 7 sleep(sec) 8 print('执行结束',index,'执行时间',ctime()) 9 # 释放锁对象 10 lock.release() 11 def main(): 12 # 创建第一个锁对象 13 lock1=thread.allocate_lock() 14 # 获取锁,相当于把锁锁上 15 lock1.acquire() 16 # 启动第一个线程,并传入第一个锁对象,10是索引,4是休眠时间,lock1是锁对象 17 thread.start_new_thread(fun,(10,4,lock1)) 18 # 创建第二个锁对象 19 lock2 = thread.allocate_lock() 20 # 获取锁,相当于把锁锁上 21 lock2.acquire() 22 # 启动第二个线程,并传入第一个锁对象,10是索引,4是休眠时间,lock1是锁对象 23 thread.start_new_thread(fun, (20, 2, lock2)) 24 # 使用while循环和locked方法判断lock1和lock2是否被释放 25 while lock1.locked() or lock2.locked(): 26 pass 27 if __name__=='__main__': 28 main()
以上就是本周所有内容了,下周将继续U-NET神经网络的学习和实践,加油!!!