1356. Something Easier
Time limit: 1.0 second
Memory limit: 64 MB
Memory limit: 64 MB
“How do physicists define prime numbers? Very easily: prime numbers are the number 2 and all the odd numbers greater than 2. They may show that this definition corresponds to the mathematical one: 3 is prime, 5 is prime, 7 is prime… 9? 9 is certainly not prime. Then: 11 is prime, 13 is prime. So 9 is the experiment mistake.”
From mathematical analysis course
Once physicist and mathematician argued how many prime numbers one needed for the purpose that their sum was equal to N. One said that it wasn’t known and the other that 3 was always enough. The question is how many.
Input
The first line contains T, an amount of tests. Then T lines with integer N follow (0 ≤ T ≤ 20; 2 ≤ N ≤ 109).
Output
For each test in a separate line you should output prime numbers so that their sum equals to N. An amount of such prime numbers is to be minimal possible.
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
7 2 27 85 192 14983 3 7 |
2 23 2 2 2 83 11 181 14983 3 7 |
题意
一位物理学家和一位数学家正在争论最少几个质数的和为N。 其中一个说这无从知晓,另一个说3个就够了。
input
第一行包含一个整数T,表示测试点数量。 接下来T行,每行一个整数N。 (0<=T<=20,2<=N<=10^9)
output
输出一些质数,使它们的和为N,质数的个数要尽量少。
思路:根据哥德巴赫猜想,
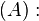 任一大于2的偶数都可写成两个质数之和。
任一大于2的偶数都可写成两个质数之和。
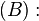 任一大于7的奇数都可写成三个素数之和。
任一大于7的奇数都可写成三个素数之和。
详细内容可参照维基百科http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%93%A5%E5%BE%B7%E5%B7%B4%E8%B5%AB%E7%8C%9C%E6%83%B3。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <sstream> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <queue> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <vector> 7 #include <list> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <algorithm> 10 #include <numeric> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <cstdio> 13 #include <cstdlib> 14 #include <cstring> 15 #include <ctime> 16 #include <set> 17 #include <deque> 18 #include <bitset> 19 #include <functional> 20 #include <utility> 21 #include <iomanip> 22 #include <cctype> 23 using namespace std; 24 25 #define FOR(i,a,b) for(i = (a); i < (b); ++i) 26 #define FORE(i,a,b) for(i = (a); i <= (b); ++i) 27 #define FORD(i,a,b) for(i = (a); i > (b); --i) 28 #define FORDE(i,a,b) for(i = (a); i >= (b); --i) 29 #define max(a,b) ((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b) 30 #define min(a,b) ((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b) 31 #define CLR(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a)) 32 #define PB(x) push_back(x) 33 34 typedef long long LL; 35 typedef vector<int> VI; 36 37 const int MAXN = 31623; 38 const int hash_size = 25000002; 39 const int INF = 0x7f7f7f7f; 40 41 bool p[MAXN]={0}, flag; 42 int prime[MAXN]={0}, q[4], n, d; 43 void init() 44 { 45 int i; 46 for(i = 2; i <= 31622; i++) 47 if(!p[i]) 48 { 49 prime[0]+=1; 50 prime[prime[0]]=i; 51 for(int j=i+i;j<=31622;j+=i) 52 p[j]=true; 53 } 54 } 55 56 bool isprime(int n){//判断n是否是一个质数 57 if (n == 2) 58 return true; 59 else { 60 int sq, i; 61 sq = int(sqrt(n*1.0)); 62 for (i = 2; i <= sq+1; ++i) 63 if (n%i == 0) 64 return false; 65 return true; 66 } 67 } 68 69 void dfs(int k,int x,int y) 70 {//将奇数进行分解 71 int i; 72 if (flag) return; 73 if (k == 1) 74 { 75 if (isprime(x)) 76 { 77 FORD(i, d, 1) 78 printf("%d ", prime[q[i]]);//进行输出 79 printf("%d ", x); 80 flag = true;//找到了一个分解 81 } 82 return; 83 } 84 for (i = y; i<=prime[0]; ++i) 85 { 86 if (prime[i]*k > x) return; 87 q[k] = i; 88 dfs(k-1, x-prime[i], i); 89 } 90 } 91 92 int main() 93 { 94 init(); 95 int t, i; 96 scanf("%d", &t); 97 while (t--) { 98 scanf("%d", &n); 99 if (isprime(n)) 100 printf("%d ", n); 101 else if (n&1) { 102 d = 1; 103 flag = false; 104 while (!flag) 105 dfs(++d, n, 1);//先分2分,再分3个 106 } 107 else { 108 int tmp; 109 FORE(i, 1, prime[0]) { 110 tmp = n - prime[i]; 111 if (isprime(tmp)) { 112 printf("%d %d ", prime[i], tmp); 113 break; 114 } 115 } 116 } 117 } 118 return 0; 119 }
