You have written on a piece of paper an array of n positive integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] and m good pairs of integers (i1, j1), (i2, j2), ..., (im, jm). Each good pair (ik, jk) meets the following conditions: ik + jk is an odd number and 1 ≤ ik < jk ≤ n.
In one operation you can perform a sequence of actions:
- take one of the good pairs (ik, jk) and some integer v (v > 1), which divides both numbers a[ik] and a[jk];
- divide both numbers by v, i. e. perform the assignments:
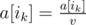 and
and 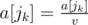 .
.
Determine the maximum number of operations you can sequentially perform on the given array. Note that one pair may be used several times in the described operations.
The first line contains two space-separated integers n, m (2 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100).
The second line contains n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — the description of the array.
The following m lines contain the description of good pairs. The k-th line contains two space-separated integers ik, jk (1 ≤ ik < jk ≤ n, ik + jk is an odd number).
It is guaranteed that all the good pairs are distinct.
Output the answer for the problem.
3 2
8 3 8
1 2
2 3
0
3 2
8 12 8
1 2
2 3
2
恶补网络流中
把数字奇偶分开,显然询问是1奇1偶的,那么相当于在二分图上搞了
枚举每一个质因数,建图,网络流。没了。拆点都不要
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#define LL long long
#define inf 0x3ffffff
#define S 0
#define T 99999
#define N 200010
using namespace std;
inline LL read()
{
LL x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct edge{int to,next,v;}e[10*N];
int head[N];
int a[N],h[N],q[N],u[N],v[N];
int n,m,cnt=1,ans;
inline void ins(int u,int v,int w)
{
e[++cnt].v=w;
e[cnt].to=v;
e[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
}
inline void insert(int u,int v,int w)
{
ins(u,v,w);
ins(v,u,0);
}
inline bool bfs()
{
int t=0,w=1;
memset(h,-1,sizeof(h));
q[1]=S;h[S]=0;
while (t<w)
{
int now=q[++t];
for (int i=head[now];i;i=e[i].next)
if (e[i].v&&h[e[i].to]==-1)
{
h[e[i].to]=h[now]+1;
q[++w]=e[i].to;
}
}
if (h[T]==-1)return 0;
return 1;
}
inline int dfs(int x,int f)
{
if (x==T||!f)return f;
int w,used=0;
for (int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next)
if (e[i].v&&h[e[i].to]==h[x]+1)
{
w=dfs(e[i].to,min(e[i].v,f-used));
e[i].v-=w;
e[i^1].v+=w;
used+=w;
if (f==used)return f;
}
if (!used)h[x]=-1;
return used;
}
inline void dinic(){while (bfs())ans+=dfs(S,inf);}
inline void solve(int x)
{
cnt=1;
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int t=0;
while (a[i]%x==0)t++,a[i]/=x;
if(i&1)insert(S,i,t);
else insert(i+n,T,t);
}
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)insert(u[i],v[i]+n,inf);
dinic();
}
int main()
{
n=read();m=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)a[i]=read();
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
u[i]=read();
v[i]=read();
if (u[i]%2==0)swap(u[i],v[i]);
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int t=sqrt(a[i]);
for (int j=2;j<=t;j++)if (a[i]%j==0)solve(j);
if (a[i]!=1)solve(a[i]);
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}