




程序代码
# coding: utf-8
'''
东南大学《数字图像处理》课程 作业8 - 图像分割
09017227 卓旭 written with Python 3
本程序内灰度图像作为二维数组,存储顺序为[行][列],像素点坐标表示为img[x][y],坐标系为
O--------> [y axis]
|
|
V [x axis]
'''
import imageio
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
IMAGE_PATH='./segImg.bmp'
'''
读入灰度图像,转为二维numpy数组
'''
def readImage(imagePath):
return imageio.imread(imagePath)
'''
图像分割
'''
def Seg(img):
# STEP 1 - 大尺度中值滤波去噪
res = cv2.medianBlur(img, 9)
# cv2.imshow('Step 1 - Median Blur', res)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# STEP 2 - 同态滤波消除光照影响
def Homo(I):
I = I + 1. # 避免log(0)
I_log = np.log(I)
# 7 X 7 均值窗口滤出低频
light_log = cv2.blur(I_log, (7, 7))
object_log = I_log - light_log
# 低频减益,高频不变
light_log = light_log * 0.1
object_log = object_log * 1.0
res = np.abs(np.exp(light_log)) * np.abs(np.exp(object_log))
res = res - 1.
minR, maxR = np.min(res), np.max(res)
rangeR = maxR - minR
for i in range(res.shape[0]):
for j in range(res.shape[1]):
res[i, j] = (res[i, j] - minR) / rangeR * 255.
return np.asarray(res, np.uint8)
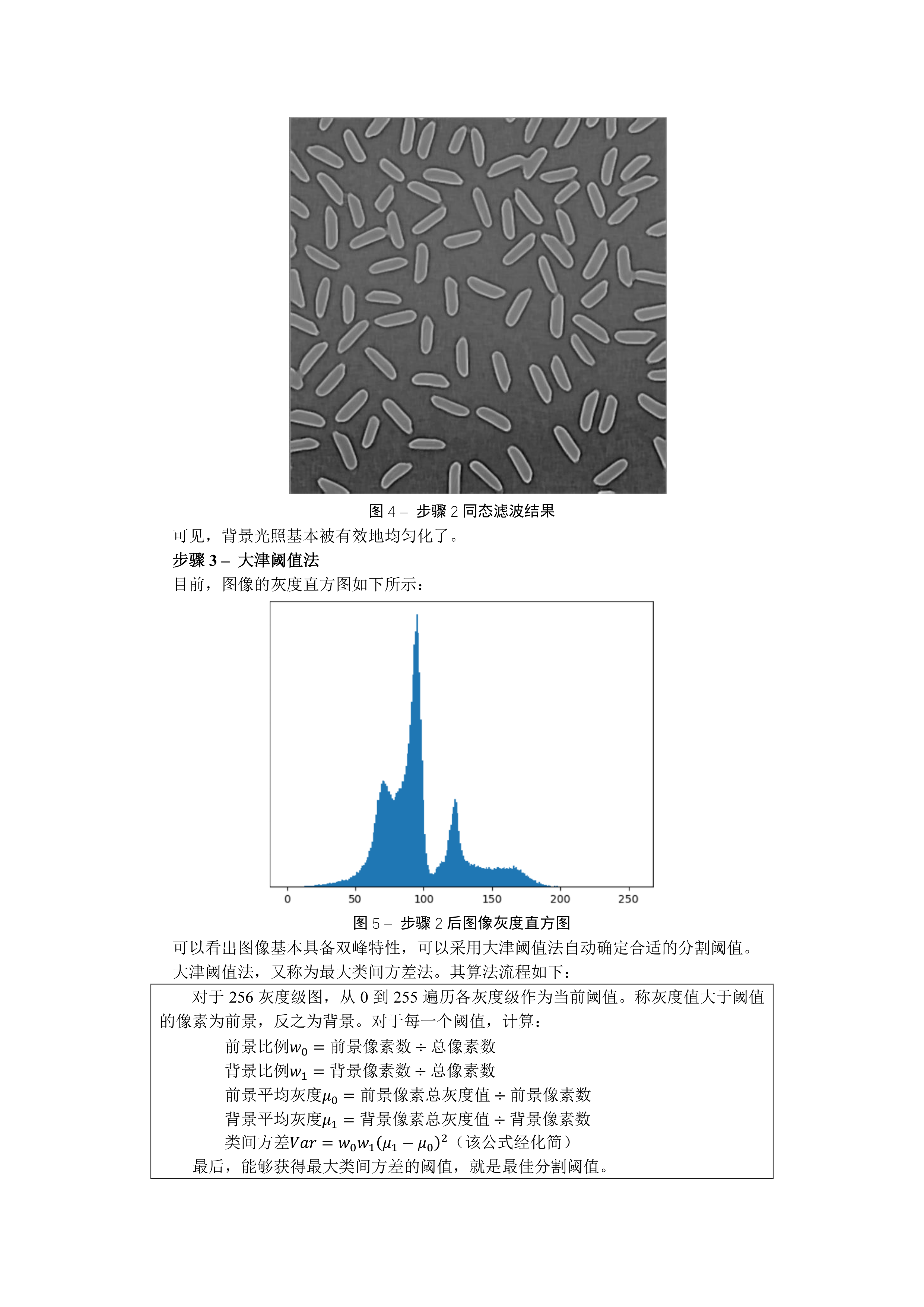
res = Homo(res)
# cv2.imshow('Step 2 - Homo Filter', res)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# 绘制灰度直方图
# plt.hist(res.ravel(), 256)
# plt.show()
# STEP 3 - 大津算法确定最佳阈值
def Otsu(I):
var_max = 0; best_th = 0
for th in range(0, 256):
mask_fore = I > th; mask_back = I <= th # 按当前测试阈值分割
len_fore = np.sum(mask_fore); len_back = np.sum(mask_back) # 前后景像素数
if len_fore == 0: # 已经分不出前景了,没有必要继续提高阈值了
break
if len_back == 0: # 背景过多,说明阈值不够,继续提高
continue
# 算法相关参数
total_pixel = I.shape[0] * I.shape[1] # 图像尺寸
w0 = float(len_fore) / total_pixel; w1 = float(len_back) / total_pixel # 两类的占比
u0 = float(np.sum(I * mask_fore)) / len_fore; u1 = float(np.sum(I * mask_back)) / len_back # 两类的平均灰度
var = w0 * w1 * ((u0 - u1) ** 2) # 类间方差
if var > var_max:
var_max = var; best_th = th
return best_th
OtsuThreshold = Otsu(res)
# 按该阈值进行二值化
for i in range(res.shape[0]):
for j in range(res.shape[1]):
res[i, j] = 255 if res[i, j] > OtsuThreshold else 0
# cv2.imshow('Step 3 - Otsu Threshold', res)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# STEP 4 - 利用形态学方法填充空洞
def Fill(I):
SEED_POINT = (233, 233)
cpy = I.copy()
flood_fill_mask = np.zeros((cpy.shape[0] + 2, cpy.shape[1] + 2), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.floodFill(cpy, flood_fill_mask, SEED_POINT, 255) # 漫水填充
# 取补
for i in range(cpy.shape[0]):
for j in range(cpy.shape[1]):
cpy[i, j] = 255 if cpy[i, j] == 0 else 0
# 做并运算
for i in range(I.shape[0]):
for j in range(I.shape[1]):
res[i, j] = 255 if (cpy[i, j] == 255 or res[i, j] == 255) else 0
return res
res = Fill(res)
return np.asarray(res, np.uint8)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("开始计算...")
res = Seg(readImage(IMAGE_PATH))
imageio.imwrite('SegOut.bmp', res)
cv2.imshow('Seg Result', res)
cv2.waitKey(0)





