乘风破浪:LeetCode真题_040_Combination Sum II
一、前言
这次和上次的区别是元素不能重复使用了,这也简单,每一次去掉使用过的元素即可。
二、Combination Sum II
2.1 问题
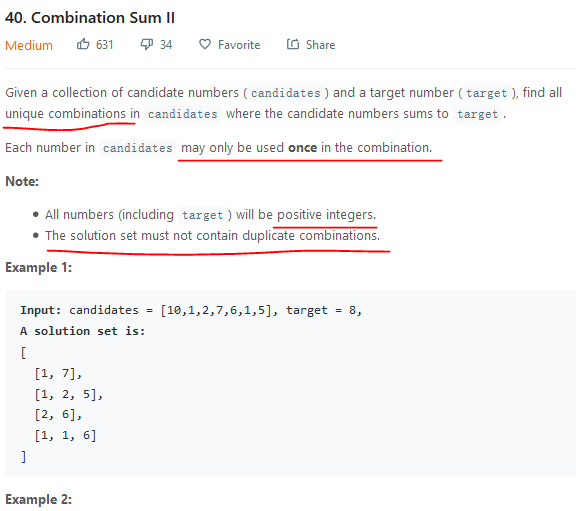
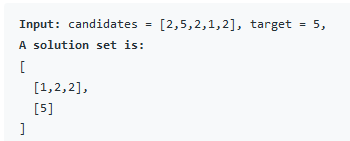
2.2 分析与解决
通过分析我们可以知道使用递归就可以解决问题,并且这次我们从头遍历一次就不会出现多次使用某一个元素了。
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
ans = new ArrayList<>();
track(candidates, 0, target, new ArrayList<>());
return ans;
}
private void track(int[] candidates, int index, int target, List<Integer> list) {
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(list);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target < candidates[i] || (i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]))//重要
continue;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(list);
temp.add(candidates[i]);
track(candidates, i + 1, target - candidates[i], temp);
}
}
}
如果这里没有(i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1])判断的话,就会造成重复的结果,究其原因是如果两个相同,之前的添加之后会进入到下一个递归里面运行了,而我们这个时候如果不过滤再次运行就会重复。
三、总结
递归在我们的程序中用的非常多,一定要熟练深刻掌握。