序列化模块
一 序列化模块 pickle
1.1 基本认识
- 序列化:把不能够直接存储的数据变成可存储的过程就是序列化
- 反序列化:把储存的数据拿出来恢复成原来的数据类型就是反序列化
例如,一个文件不可以写的数据
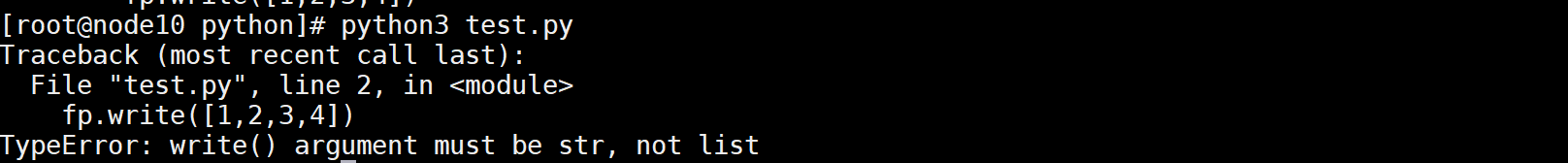
[root@node10 python]# cat test.py with open('0209.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: fp.write(123)
执行
使用列表
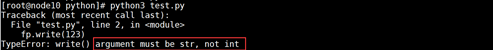
with open('0209.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: fp.write([1,2,3,4])
执行报错
换成字典
with open('0209.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: fp.write({"a":1,"b":2})
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 2, in <module> fp.write({"a":1,"b":2}) TypeError: write() argument must be str, not dict
只能写的只能是字符串或者字节流
对于不能写入文件的数据,只有序列化才能写入php的序列化使用(serialize)反序列化(unserialize)
1.2 使用pickle模块
dumps 把任意对象序列化成一个bytes
import pickle #引入模块 引入pickle模块 #dumps 把任意对象序列化成一个bytes dic = {"a":1,"b":2} res = pickle.dumps(dic) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py b'x80x03}qx00(Xx01x00x00x00aqx01Kx01Xx01x00x00x00bqx02Kx02u.'
loads 把任意bytes反序列化成原来数据
import pickle #dumps 把任意对象序列化成一个bytes dic = {"a":1,"b":2} res = pickle.dumps(dic) print(res) res = pickle.loads(res) print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py b'x80x03}qx00(Xx01x00x00x00aqx01Kx01Xx01x00x00x00bqx02Kx02u.' {'a': 1, 'b': 2} <class 'dict'>
函数序列化
import pickle def func(): print("我是一个函数") res = pickle.dumps(func) print(res) print("<==>") res = pickle.loads(res) res()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py b'x80x03c__main__ func qx00.' <==> 我是一个函数
迭代器序列化
import pickle from collections import Iterator,Iterable it = iter(range(10)) print(isinstance(it,Iterator)) res = pickle.dumps(it) print(res) res = pickle.loads(res) print(res) for i in range(3): print(next(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py True b'x80x03cbuiltins iter qx00cbuiltins range qx01Kx00K Kx01x87qx02Rqx03x85qx04Rqx05Kx00b.' <range_iterator object at 0x7f6618065cc0> 0 1 2
所有的数据类型都可以通过pickle进行序列化
dump 把对象序列化后写入到file-like Object(即文件对象)
import pickle dic = {"a":1,"b":2} with open("0209_1.txt",mode="wb") as fp: # pickle.dump(数据类型,文件对象) 先把数据变成二进制字节流 在存储在文件当中 pickle.dump(dic,fp) #load 把file-like Object(即文件对象)中的内容拿出来,反序列化成原来数据 with open("0209_1.txt",mode="rb") as fp: res = pickle.load(fp) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py {'a': 1, 'b': 2} [root@node10 python]# cat 0209_1.txt ▒}q(XaqKXbqKu.
二 json模块
2.1 基本认识
json 的功能也是序列化,不过他序列化的最终结果是一个字符串
不同的语言之间,进行数据交流都使用json数据格式
所有语言都能够识别的数据格式叫做json ,json数据格式
python 中能够使用json格式的数据类型 只有如下:int float bool str list tuple dict None [不包含complex set]
语言和语言之间的交流用json(字符串)
数据之间的传输和存储用pickle(二进制字节流)
2.2 序列话字符串
第一对 dumps 和 loads 把数据序列化或者反序列化成字符串
import json dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1} res = json.dumps(dic) print(res,type(res))
执行
{
"name": "u5218u94c1u86cb",
"age": 18,
"sex": "u5973u6027",
"family": ["father", "u5988u5988"],
"agz": 1
}
<class 'str'>
识别中文编码
- ensure_ascii=True (默认值) 如果想要显示中文 如下:ensure_ascii = False
- sort_keys=False 对字典的键进行排序 (会按照ascii 字符的从小到大进行排序)
import json dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1} res = json.dumps(dic,ensure_ascii=False,sort_keys=True) print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py {
"age": 18,
"agz": 1,
"family": ["father", "妈妈"],
"name": "刘铁蛋",
"sex": "女性"
}
<class 'str'>
2.3 数据存储转化
第二对 dump 和 load 应用在数据的存储的转化上
import json
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1} with open("0209_2.txt",mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: json.dump(dic,fp,ensure_ascii=False) with open("0209_2.txt",mode="r",encoding="utf-8") as fp: res = json.load(fp) print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} <class 'dict'> [root@node10 python]# cat 0209_2.txt {"name": "刘铁蛋", "age": 18, "sex": "女性", "family": ["father", "妈妈"], "agz": 1}
2.4 pickle 和 json 之间的用法区别
- json 可以连续dump , 但是不能连续load , load是一次性拿出所有数据而不能识别.
- 可以使用loads ,一行一行的读取,一行一行的通过loads来转化成原有数据类型
json
import json dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1} with open("0209_3.txt" , mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: json.dump(dic,fp) fp.write(' ') json.dump(dic,fp) fp.write(' ') print("<===>") with open("0209_3.txt" ,mode="r",encoding="utf-8") as fp: # load 是一次性把所有的数据拿出来,进行识别 # load 不能识别多个数据混在一起的情况 # 用loads 来解决load 不能识别多个数据的情况 # res = json.load(fp) for i in fp: print(i,type(i)) res = json.loads(i) print(res,type(res)) # print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py <===> {"name": "u5218u94c1u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "u5973u6027", "family": ["father", "u5988u5988"], "agz": 1} <class 'str'> {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} <class 'dict'> {"name": "u5218u94c1u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "u5973u6027", "family": ["father", "u5988u5988"], "agz": 1} <class 'str'> {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} <class 'dict'> [root@node10 python]# cat 0209_3.txt {"name": "u5218u94c1u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "u5973u6027", "family": ["father", "u5988u5988"], "agz": 1} {"name": "u5218u94c1u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "u5973u6027", "family": ["father", "u5988u5988"], "agz": 1}
pickle
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
import pickle
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="wb") as fp:
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="rb") as fp:
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} [root@node10 python]# cat 0209_4.txt ▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
使用try
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
import pickle
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="wb") as fp:
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="rb") as fp:
try:
while True:
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
except:
pass
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} {'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} [root@node10 python]# cat 0209_4.txt ▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
2.5 try的异常处理
try: ... except: 把有问题的代码赛到try 代码块当中 如果发生异常报错,直接执行except其中的代码块 优点:不会因为报错终止程序运行
示例:
listvar = [1,15,2] print(listvar[15])
执行

使用try函数
try : listvar = [1,15,2] print(listvar[15]) except: pass
再次执行不会报错
json 和 pickle 两个模块的区别:
- json序列化之后的数据类型是str,所有编程语言都识别,但是仅限于(int float bool)(str list tuple dict None),json不能连续load,只能一次性拿出所有数据
- pickle序列化之后的数据类型是bytes,所有数据类型都可转化,但仅限于python之间的存储传输.pickle可以连续load,多套数据放到同一个文件中
三 math数学模块
ceil() 向上取整操作 (对比内置round)
import math res = math.ceil(4.01) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 5
floor() 向下取整操作 (对比内置round)
import math
res = math.floor(3.99) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 3
pow() 计算一个数值的N次方(结果为浮点数) (对比内置pow)
import math res = math.pow(2,3) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 8.0
math模块中的pow没有第三个参数
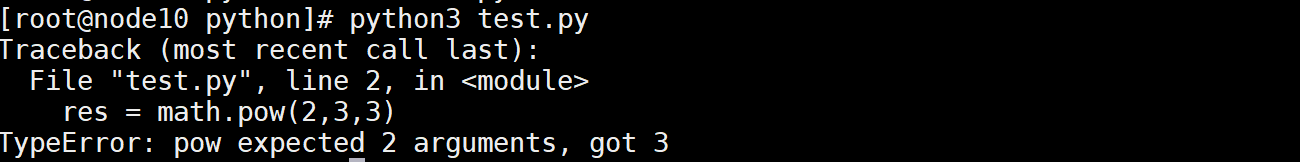
import math res = math.pow(2,3,3) print(res)
执行报错
sqrt() 开平方运算(结果浮点数)
import math res = math.sqrt(10) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 3.1622776601683795
fabs() 计算一个数值的绝对值 (结果浮点数) (对比内置abs)
import math res = math.fabs(-56) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 56.0
modf() 将一个数值拆分为整数和小数两部分组成元组
import math res = math.modf(14.677) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py (0.6769999999999996, 14.0)
copysign() 将参数第二个数值的正负号拷贝给第一个
import math res = math.copysign(-1,-5) print(res) # 得到浮点数结果 , 它的正负号取决于第二个值
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py -1.0
fsum() 将一个容器数据中的数据进行求和运算 (结果浮点数)(对比内置sum)
import math listvar = [1,2,3,4,5,99,6] res = math.fsum(listvar) print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 120.0
圆周率常数 pi
import math print(math.pi)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 3.141592653589793